1 引言
本文深入分析了并网逆变器的3种控制目标,为实现对逆变型分布式电源并网的有效控制,建立了统一的参考电流矢量表达式,结合正负序双电流独立内环控制与线性无功功率控制,在不平衡情况下,能有效抑制并网电流谐波,控制并网点电压,改善系统不平衡度。
2 不平衡电网下并网逆变器的数学模型
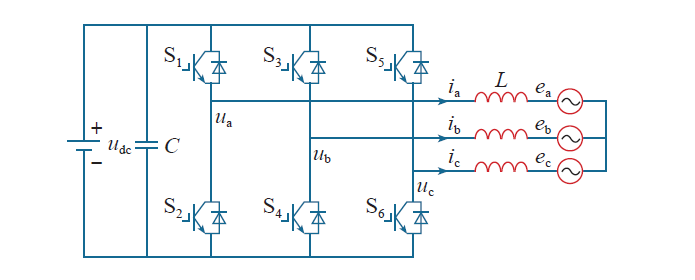
三相并网逆变器拓扑结构如图1所示。
图1
图1
并网逆变器主电路拓扑结构
Fig.1
Main circuit topology structure of grid-connected inverter
图1中,ea、eb、ec为电网电压;ua、ub、uc为逆变器输出电压;ia、ib、ic为逆变器输出电流;udc为直流侧电压;C为直流侧电容。
在电网不平衡情况下,不考虑零序电压分量,电网电压可分解为正序分量和负序分量
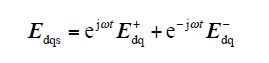
式中,Edq+ = ed+ + jeq+,Edq- = ed-+jeq-;ω为电网电压角频率。
根据图1,可得并网逆变器在静止坐标下的数学模型为
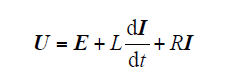
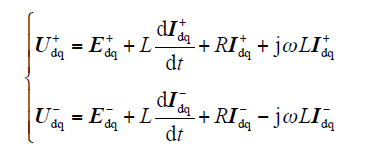
当电网电压不平衡时,并网逆变器输出复功率为
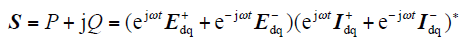
同时,瞬时有功功率和无功功率为
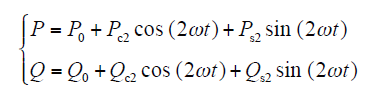
式中,P0与Q0为瞬时有功功率和无功功率平均值;Ps2、Pc2为有功功率正弦、余弦峰值;Qs2、Qc2为无功功率正弦、余弦峰值,在dq坐标系中,这些值为
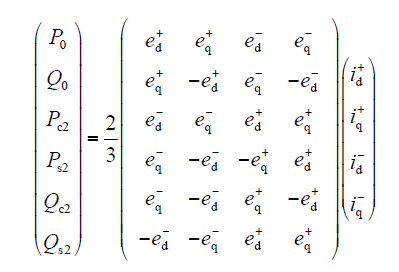
由式(5)可知,当电网电压不平衡时,逆变型分布式电源输出的瞬时有功功率和无功功率都含有2次谐波分量,从而导致并网电流不对称和直流侧电压的2倍频脉动。因此,需采用不平衡控制策略,对并网电流和直流侧电压进行较好的控制,提高逆变型分布式电源并网的可靠性。式(6)中,有6个功率项,采用4个电流项,只能对功率的4个项进行控制,因此,采用一种控制策略无法同时实现所有的控制目标。
3 不平衡时并网逆变器的控制策略
3.1 电流内环控制策略
(1)控制目标1。有效抑制直流侧电压2倍频脉动,保持并网有功功率恒定,消除有功功率2倍频脉动,即Pc2 = Ps2 = 0,代入式(6)可得
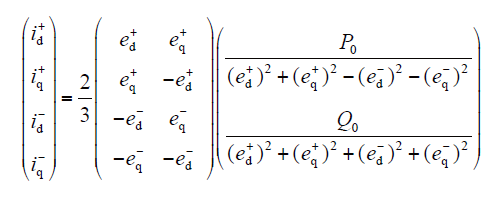
(2)控制目标2。保持并网无功功率恒定,消除无功功率2倍频脉动,即Qc2 = Qs2 = 0,代入式(6)可得
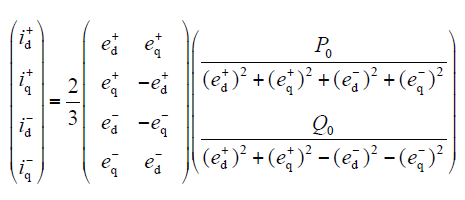
(3)控制目标3。控制负序电流为零,保持逆变型分布式电源并网电流对称,即id- = iq- = 0,代入式(6)可得
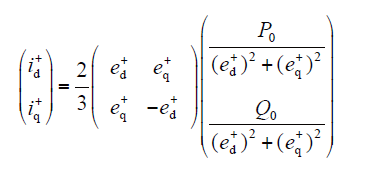
结合式(7)~式(9),可得正、负序参考电流矢量的统一表达式为
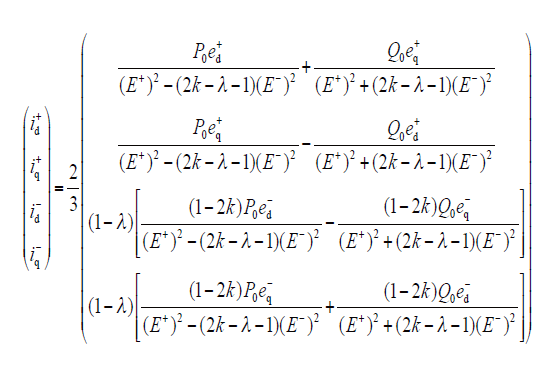
式中,(E+)2 = (ed+)2 + (eq+)2,(E-)2 = (ed-)2 + (eq-)2,0≤k≤1, 0≤λ≤1。
分析式(10)可得,选取不同参数,可实现三种不同控制目标。当k = 1、λ = 0,实现控制目标1;当k = 0、λ = 0,实现控制目标2;当k = 1、λ = 1,实现控制目标3。参数λ主要控制负序电流,当λ = 1时,参考电流矢量不含负序分量,但并网有功功率和无功功率都存在2倍频脉动。而λ = 0时,通过调节k值可有效控制并网有功功率和无功功率的2倍频脉动。但这3种控制目标都是极端情况,而且互相冲突,一种控制目标性能的改善会导致另一种性能的恶化[15]。在实际运用中,参数k、λ可以在0~1之间变化,兼顾多个控制指标。
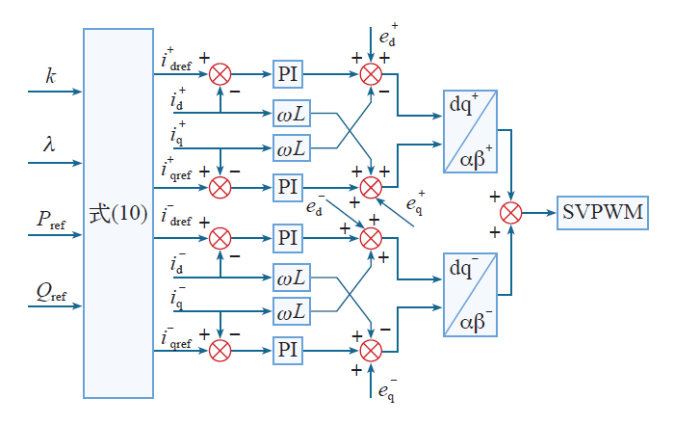
图2
图2
正负序双电流内环独立控制图
Fig.2
Positive and negative sequence current loop independent control
图3
3.2 功率外环控制策略
逆变器功率参考值根据外部条件设定,有功功率一般根据分布式电源(Distributed Generator,DG)的容量,无功功率一般为0。若DG接在低压系统,在IEEE Std.1547中DG接入的允许电压为额定电压的88%~110%,法国标准是90%~106%。DG接入会使公共连接点(Point of Common Coupling,PCC)电压升高,可能超过允许电压,对此PCC吸收无功功率降低电压。不对称故障会使电压降低,可能低于允许电压,对此PCC注入无功功率提高电压。电网不平衡情况下,通过调节无功功率降低负序电压分量,从而降低负序电压不平衡程度。
文献[16]提出线性无功功率控制,无功功率与电压关系如式(11)与式(12)所示,式中电压使用标幺值,功率使用有名值。
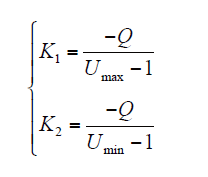
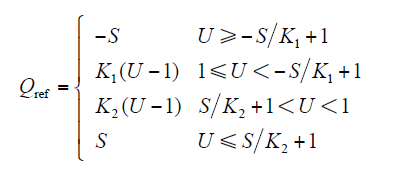
(12)中,Qref为无功功率参考值;U为当前的电压值;S为DG总容量,有功功率参考值为

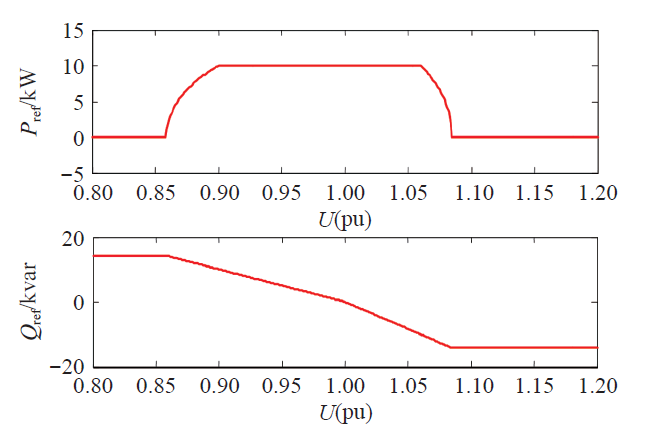
若有功功率Pn为10kW,无功功率Q为10kvar,S为14.14kV·A,电压允许范围采用法国标准,式(12)与式(13)对应的图如图4所示。
图4
线性无功功率控制可以根据电网电压变化改变无功的输出,通过对电网注入或吸收无功调整PCC电压。根据有功功率、无功功率的给定值,经式(10)可计算出正负序参考电流矢量。
4 仿真验证
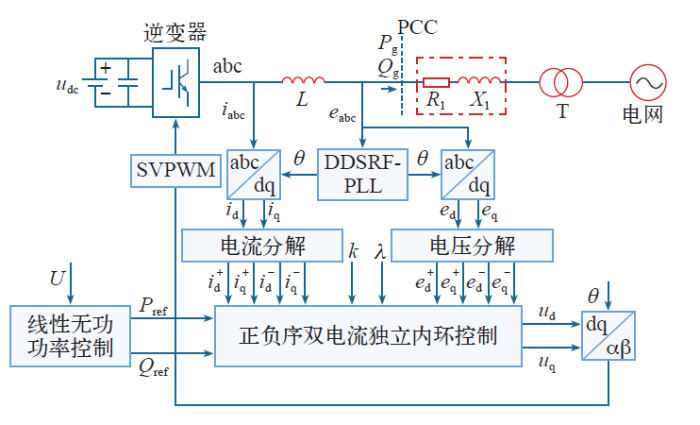
图5
图5
并网逆变器总控制框图
Fig.5
Overall control block diagram ofthe grid-connected inverter
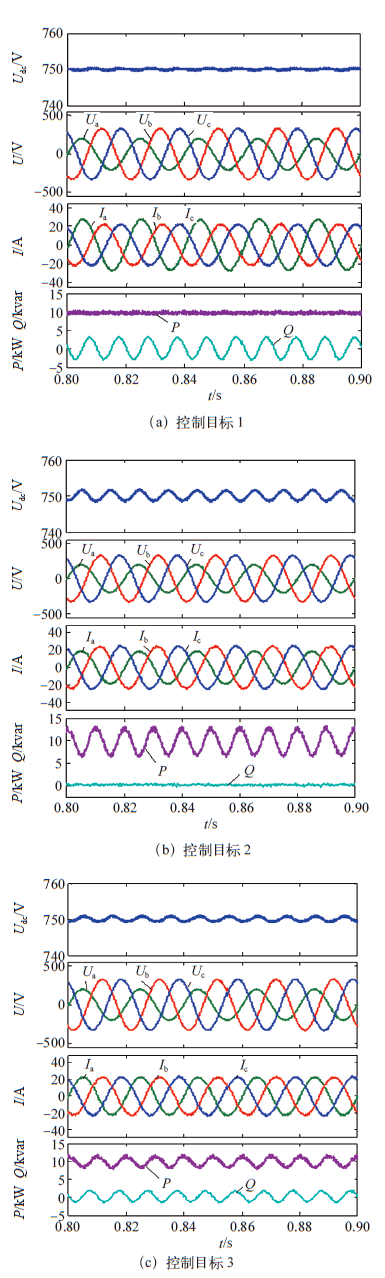
图6
图6
三种不平衡控制目标的仿真结果波形
Fig.6
Simulation waveforms of three kinds of unbalanced control objectives
表1 仿真参数
Tab.1
| 参 数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| 网侧电压/V | 380 |
| 直流侧电压/V | 750 |
| 直流侧电容/mF | 1 |
| 滤波电感/mH | 3 |
| 额定容量/kW | 10 |
表2 三种不平衡控制目标的仿真结果数据
Tab.2
| 控制 目标 | 控制 参数 | 并网电流 THD(%) | 并网电流 不平衡度 (%) | 直流侧电 压2倍频 脉动(%) | 有功功率 2倍频脉 动(%) | 无功功率 2倍频脉 动(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | k=1 | 1.71 | 14.32 | ±0.04 | ±2.0 | ±32.5 |
| λ=0 | ||||||
| 2 | k=0 | 3.28 | 16.25 | ±0.24 | ±31.5 | ±1.8 |
| λ=0 | ||||||
| 3 | k=1 | 2.27 | 0.27 | ±0.15 | ±17.6 | ±18.4 |
| λ=1 |
三种控制策略都有效抑制了并网电流谐波,目标1消除了逆变型分布式电源向电网输送有功功率的2倍频脉动,PCC点输出电流虽不平衡但正弦度较好,THD为1.71%,并网电流不平衡度为14.32%,同时直流侧电压脉动基本消除,但向电网输送的无功功率脉动上升为±32.5%;控制目标2消除了逆变型分布式电源向电网输送无功功率的2倍频脉动,PCC点输出电流虽不平衡但正弦度较好,THD = 3.28%,并网电流不平衡度为16.25%,但直流侧电压脉动为±0.24%,同时向电网输送的有功功率脉动上升为±31.5%;控制目标3使PCC点输出正弦对称电流,THD = 2.27%,但逆变型分布式电源向电网输送的有功功率和无功功率脉动较大,分别为±17.6%和±18.4%,同时直流侧电压脉动为±0.15%。
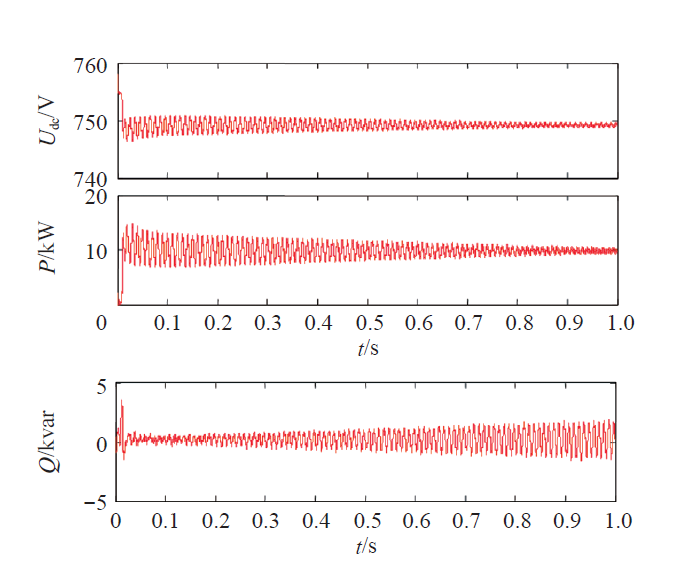
图7为参考电流矢量表达式中k和λ分别从0变化到1时的仿真结果。当λ = 0,使k从0到1变化,有功功率脉动不断减少,直流侧电压脉动也不断减少。由式(5)可知,系数Pc2、Ps2、Qc2和Qs2由电压不平衡引起,而有功功率被输送到直流侧并决定直流侧电压等级。因此,如果Pc2、Ps2不为零,直流侧电压会产生2倍频脉动,为保持直流侧电压恒定,系数Pc2、Ps2必须为零。由仿真结果可以得到直流侧电压脉动幅度正比于有功功率脉动。而当k = 0,使λ从0到1变化,并网逆变器输出无功功率明显增大。图7较好地验证了前面的理论分析,参考电流矢量表达式中的参数k和λ对并网质量有很大影响,可根据实际应用情况来优化这两个参数,从而实现三种控制目标之间的协调优化,使并网逆变器并网系统整体性能达到最优。
图7
图8
图9
表3 不同控制下的负序电压不平衡度
Tab.3
| 控制策略 | 电压正序分量 方均根值 | 电压负序分量 方均根值 | 负序电压 不平衡度εU2(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 242.7 | 84.5 | 34.82 |
| 2 | 250.15 | 82.14 | 32.84 |
| 3 | 257.3 | 80.28 | 31.20 |
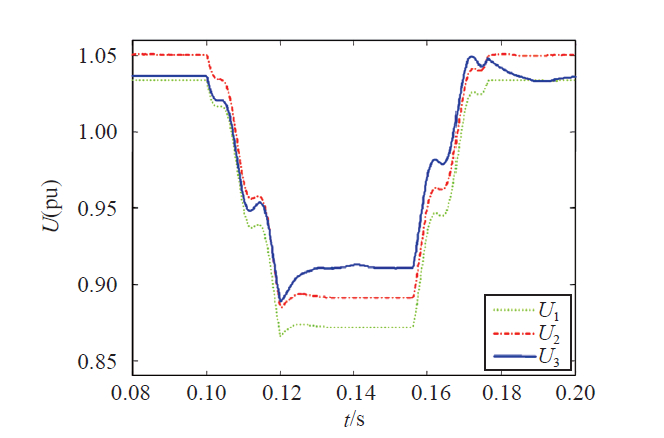
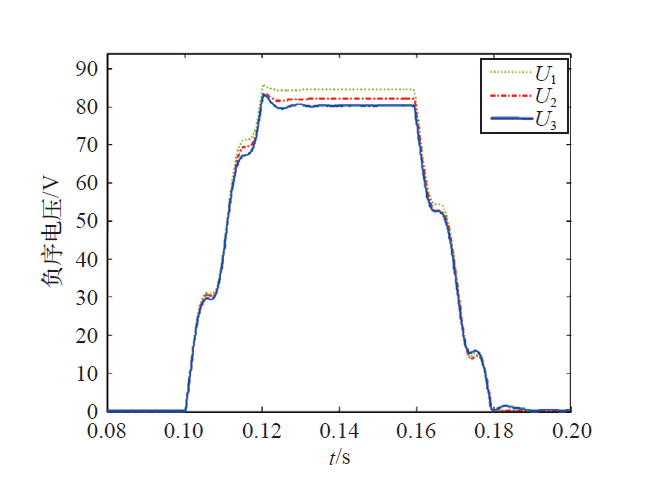
图中U1为没有接入分布式电源时PCC的电压;U2为电流内环正负序控制和功率外环逆变器固定发出10kW时PCC的电压;U3为电流内环正负序控制和功率外环线性无功功率控制时逆变器PCC的电压(电流普通控制策略不能满足并网电流谐波要求,故不考虑)。仿真结果表明,当发生不平衡电压凹陷时,对比U2与U1可知,分布式电源并网会引起PCC电压的升高,U3与U2相比更接近于额定电压。因此所提出的控制策略不仅能降低因DG并网引起的电压升高,而且能提高因不平衡电压凹陷引起的电压跌落,有效控制并网电压接近额定值的同时,也能降低并网点负序电压,降低系统不平衡度。因此该控制策略能更有效地调整分布式电源并网能力。
5 结论
本文通过对电网不平衡条件下并网逆变器的数学模型进行分析,可知并网逆变器控制无法同时实现消除有功功率脉动、消除负序电流和消除无功功率脉动三种控制目标的问题,从而建立了统一参考电流矢量表达式,结合线性无功功率控制与基于统一表达式的正负序双电流内环独立控制,在电网不平衡情况下,分析了三种控制目标对逆变型分布式电源并网的影响,并有效调整了PCC并网电压,降低了电压不平衡度。仿真结果表明,在电网不平衡情况下,文中的控制方法比普通控制提高了逆变型分布式电源并网能力,验证了该方法的有效性与正确性。
参考文献
分布式风光互补发电系统及其多目标优化控制策略研究
[J].
Muti-index optimization control strategy based on distributed PV and wind energy complemental generation system
[J].
基于内模控制的三相电压型PWM整流器不平衡控制策略研究
[J].
Study of internal model control based three-phase PWM rectifier under unbalanced input voltage condition
[J].
电网不平衡条件下光伏并网控制策略研究
[J].
Study on control strategy of grid connected PV inverter under unbalance grid conditions
[J].
Closed-form analysis of adjustable-speed drive performance under input-voltage unbalance and sag conditions
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIA.2006.872953 URL [本文引用: 1]
电网电压不平衡情况下PWM整流器恒频直接功率控制
[J].恒频直接功率控制(constant switching frequency direct power control,CSF-DPC)具有开关频率固定、动态性能好、系统采样频率较低等优点。电网电压不平衡会在脉宽调制(pulse width modulation,PWM)型整流器交流侧产生大量谐波电流,使系统有功功率大幅波动,恶化系统性能。针对上述情况,提出一种新型恒频直接功率控制策略。该策略首先分离出电网电压和电流正、负序分量;然后在正、负序双旋转坐标系下计算瞬时功率与参考值之间的误差,根据误差生成整流器正、负序参考电压;合成后采用空间矢量调制(space vector modulation,SVM)算法产生整流器电压,对功率进行补偿。该策略可有效抑制交流侧电流谐波,减小系统无功功率直流分量,稳定系统输出的有功功率,改善系统稳态性能。仿真与实验结果证明了该策略的正确性和有效性。
Direct power control in constant switching frequency for pwm rectifier under unbalanced grid voltage conditions
[J].恒频直接功率控制(constant switching frequency direct power control,CSF-DPC)具有开关频率固定、动态性能好、系统采样频率较低等优点。电网电压不平衡会在脉宽调制(pulse width modulation,PWM)型整流器交流侧产生大量谐波电流,使系统有功功率大幅波动,恶化系统性能。针对上述情况,提出一种新型恒频直接功率控制策略。该策略首先分离出电网电压和电流正、负序分量;然后在正、负序双旋转坐标系下计算瞬时功率与参考值之间的误差,根据误差生成整流器正、负序参考电压;合成后采用空间矢量调制(space vector modulation,SVM)算法产生整流器电压,对功率进行补偿。该策略可有效抑制交流侧电流谐波,减小系统无功功率直流分量,稳定系统输出的有功功率,改善系统稳态性能。仿真与实验结果证明了该策略的正确性和有效性。
Regulation of a PWM rectifier in the unbalanced network state using a generalized model
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.63 URL [本文引用: 1]
An Output-power-control strategy for a three-phase PWM rectifier under unbalanced supply conditions
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2008.918643 URL [本文引用: 1]
Flexible voltage support control for three-phase distributed generation inverters under grid fault
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TIE.2012.2185016
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Ancillary services for distributed generation (DG) systems become a challenging issue to smartly integrate renewable-energy sources into the grid. Voltage control is one of these ancillary services which can ride through and support the voltage under grid faults. Grid codes from the transmission system operators describe the behavior of the energy source, regulating voltage limits and reactive power injection to remain connected and support the grid under fault. On the basis that different kinds of voltage sags require different voltage support strategies, a flexible control scheme for three-phase grid-connected inverters is proposed. In three-phase balanced voltage sags, the inverter should inject reactive power in order to raise the voltage in all phases. In one-or two-phase faults, the main concern of the DG inverter is to equalize voltages by reducing the negative symmetric sequence and clear the phase jump. Due to system limitations, a balance between these two extreme policies is mandatory. Thus, over-and undervoltage can be avoided, and the proposed control scheme prevents disconnection while achieving the desired voltage support service. The main contribution of this work is the introduction of a control algorithm for reference current generation that provides flexible voltage support under grid faults. Two different voltage sags have been experimentally tested to illustrate the behavior of the proposed voltage support control scheme.
Dual current control scheme for PWM converter under unbalanced input voltage conditions
[J].DOI:10.1109/41.793344 URL [本文引用: 2]
不对称电网电压条件下三相并网型逆变器的控制
[J].介绍了一种用于三相并网型逆变器的新型电流控制器, 即比例谐振电流调节器(PR)。不平衡电网电压条件下, 该电流调节器可直接在两相静止坐标中对输出电流进行调节, 无需进行正、负序分解便可直接对输出电流的正、负序分量控制。在一台容量为1.5kVA的并网逆变器实验样机上, 分别对传统单个PI调节器、双dq、PI调节器和PR调节器进行了对比验证, 实验结果证明了所提PR电流控制方案可改善三相并网逆变器系统的动态性能, 提高系统的不对称故障穿越能力。
Investigation on control of three-phase grid-connected inverters under unbalanced grid voltage conditions
[J].介绍了一种用于三相并网型逆变器的新型电流控制器, 即比例谐振电流调节器(PR)。不平衡电网电压条件下, 该电流调节器可直接在两相静止坐标中对输出电流进行调节, 无需进行正、负序分解便可直接对输出电流的正、负序分量控制。在一台容量为1.5kVA的并网逆变器实验样机上, 分别对传统单个PI调节器、双dq、PI调节器和PR调节器进行了对比验证, 实验结果证明了所提PR电流控制方案可改善三相并网逆变器系统的动态性能, 提高系统的不对称故障穿越能力。
Improved grid synchronization control of doubly fed induction generator under unbalanced grid voltage
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TEC.2011.2158580
URL
[本文引用: 1]

An improved grid synchronization control scheme of the wind energy conversion system based on the doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) under unbalanced grid voltage is proposed in this paper. In both the positive and negative sequence models, respectively, the degrees of relevancy among rotor voltages, rotor currents, and stator voltages are calculated using the relative gain array (RGA) methodology. According to the analysis results of RGA, the main controller is designed to control positive sequence stator voltages directly with positive sequence rotor voltages, and the auxiliary controller is designed to control negative sequence stator voltages directly with negative sequence rotor voltages. Hence, the rotor current control loops are eliminated, which simplifies the structure of the controller. Simulation and hardware experimental results validate that the improved control scheme effectively controls stator voltages of the DFIG to accurately follow unbalanced grid voltage and, hence, avoids current, torque, and power impacts to both the DFIG and the grid at the time of connecting.
基于比例积分-降阶谐振调节器的并网逆变器不平衡控制
[J].不平衡电网电压条件下并网逆变器的有效控制,对提高其并网运行能力具有重要意义。提出一种新型调节器,即比例积分-降阶谐振(proportion integral plus reduced order resonant,PI-ROR)调节器,可以对交流信号进行无差控制,且易于数字化实现。不平衡电网电压条件下,该电流调节器可直接在正向同步旋转坐标中对输出电流进行无差控制,无需进行电流的正、负序分解。通过仿真和实验验证采用该调节器对不平衡电流控制的可行性,并对比该调节器与PI调节器的不平衡控制性能。仿真和实验结果表明,基于提出的PI-ROR调节器的不平衡控制方案可改善并网逆变器的动态性能,提高系统在电网电压不平衡条件下的运行能力。
Unbalanced control of grid-connected inverters based on proportion integral and reduced order resonant controllers
[J].不平衡电网电压条件下并网逆变器的有效控制,对提高其并网运行能力具有重要意义。提出一种新型调节器,即比例积分-降阶谐振(proportion integral plus reduced order resonant,PI-ROR)调节器,可以对交流信号进行无差控制,且易于数字化实现。不平衡电网电压条件下,该电流调节器可直接在正向同步旋转坐标中对输出电流进行无差控制,无需进行电流的正、负序分解。通过仿真和实验验证采用该调节器对不平衡电流控制的可行性,并对比该调节器与PI调节器的不平衡控制性能。仿真和实验结果表明,基于提出的PI-ROR调节器的不平衡控制方案可改善并网逆变器的动态性能,提高系统在电网电压不平衡条件下的运行能力。
电网不平衡情况下并网逆变器多目标协调控制策略研究
[J].
Research on multi-objective coordinated control strategies of grid-connected inverter under unbalanced voltage conditions
[J].
电网电压不平衡下光伏发电系统的改进功率控制
[J].
Improved power control of photovoltaic generation system under unbalanced grid voltage conditions
[J].
A voltage regulation system for distributed generation
[C].