1 引言
器件、电路拓扑和控制是电力电子技术的三大组成部分。目前电力电子技术在这三个核心支柱方面都取得了长足的发展,并趋于成熟[1]。随着人们对电力电子技术的不断研究和应用,各个领域对电力电子产品的性能要求不断提高,这就无形中增加了设计难度,使设计周期越来越长。如果电力电子产品的开发长期停滞在客户定制的状态,将导致其开发成本居高不下,同时也将影响其可靠性的进一步提高。解决这个问题最为有效的途径之一就是电力电子系统集成。
电力电子系统集成分为三个层次[2],第一层次是元器件级集成,分为有源器件集成(包括功率器件和驱动、保护、通信等电路集成)和无源元件集成(包括变压器、电感、电容等电磁集成);第二层次是模块级集成,即利用集成好的有源器件和无源元件,组合成不同的电能变换模块;第三层次是系统级集成,利用各种电能变换模块组合成特定的电能变换系统。
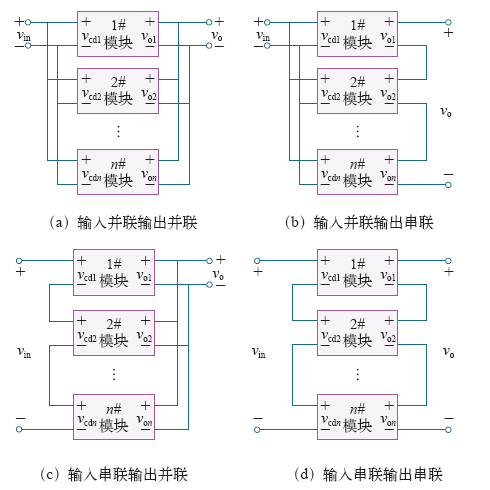
第三层次的系统级集成有很多种类,其中一种就是标准化模块的串并联。按照能量转换方式的不同,标准化模块可以分为DC-DC变换器、DC-AC逆变器、AC-DC整流器和AC-AC变频器四类。按照输入输出端联接方式的不同,串并联组合系统可分为图1所示的输入并联输出并联(Input Parallel Output Parallel,IPOP)、输入并联输出串联(Input Parallel Output Series,IPOS)、输入串联输出并联(Input Series Output Parallel,ISOP)和输入串联输出并联(Input Series Output Series,ISOS)四种[3-4]。其中,IPOP系统适用于输入电压较低、输出电流较大的场合,IPOS系统适用于输入电压较低和输出电压较高的场合,ISOP系统适用于输入电压较高、输出电流较大的场合,而ISOS系统则适用于输入电压和输出电压均较高的场合。
图1
采用标准化模块组成的串并联系统有很多优点:①每个模块承担功率为整个系统的1/n(n为系统中模块的数量),故可降低系统的开发难度及成本;②可实现系统的冗余运行,以提高系统的可靠性;③当采用交错控制技术时,系统的效率和功率密度可以得到提高;④方便对系统进行重构以适应不同的输入和输出性能要求。
对于标准化模块构成的串并联组合系统而言,其关键问题包括两个方面,其一是要保证系统中各模块间的功率均衡,其二则是要实现系统的分布式控制及冗余运行。本文以串并联逆变器组合系统为研究对象,围绕以上两方面关键问题综合阐述四种串并联组合系统所采用控制策略的研究现状及发展趋势。由于该组合系统中基本模块是逆变器,其输出端是交流电,实现其功率均衡即意味着模块间输出的有功功率和无功功率必须相等,所以相比DC-DC串并联组合系统来说其控制策略更为复杂。
2 IPOP逆变器系统
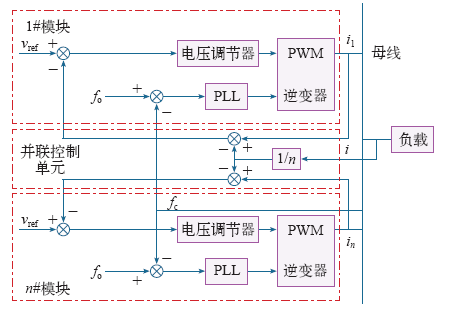
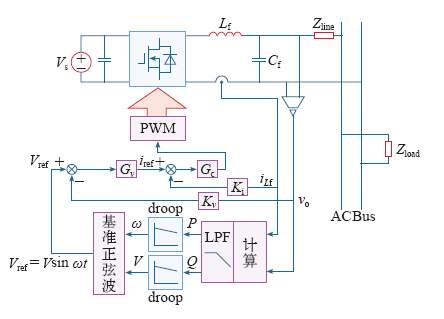
IPOP逆变器系统即通常所说的逆变器并联系统,其适用于输入电压低、输出电流大的场合,如UPS和航空静止变流器等系统中。IPOP逆变器系统的输入端、输出端并联,这就使得系统中各模块的输入、输出电压分别强制保证相等,故只需控制各模块输出电流相等即可实现系统的稳定工作及功率均衡。现有的控制方法均是研究其输出端均流(即输出端环流抑制)的问题,根据主控单元的分散程度可将其控制方法分成三类:集中式、主从式和分布式;而根据各模块之间有无互联线连接又可以分为有互联线方式和无互联线控制方式,无互联线的控制方式即所谓外特性下垂法,它实质上也是一种分布式的控制方式。
2.1 集中式控制方式
图2
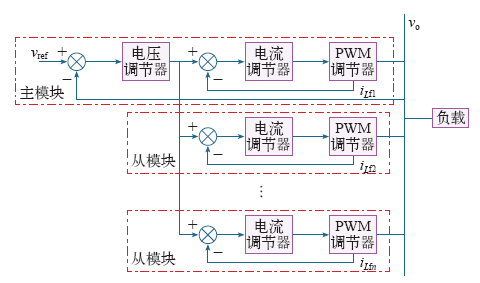
2.2 主从控制方式
图3
2.3 分布式控制方式
2.3.1 平均电流法
图4
图4
基于平均电流控制的分布式控制方案
Fig.4
A distributed control strategy based on average current control
文献[17]针对基于平均电流控制的分布式并联控制方案中的电感电流反馈导致输出外特性较差这一缺陷,引入了负载电流前馈(前馈点在电流给定平均点之前(如图中虚线所示))以改善单模块及系统的输出外特性,保留了原方案的均流效果及限流功能不变。
2.3.2 无互联线的外特性下垂法
图5
图5
无互联线控制方式(输出阻抗呈感性)
Fig.5
Steady-state invariant frequency and amplitude droop control( the output impedance is inductive)
针对上述动态特性方面的缺陷,文献[28]在外特性下垂回路的控制器中引入微分分量,加快了系统的动态响应,减少了暂态下的电压、电流冲击。
综上可见,针对IPOP逆变器系统输出端均流控制方法的研究经历了从集中式到主从式、再到分布式,从有互联线的控制方法到无互联线的外特性下垂法的发展历程。目前,对于该系统的研究已趋于成熟,所提方案在确保实现功率均衡的同时也逐步实现了系统的模块化和冗余控制。
3 IPOS逆变器系统
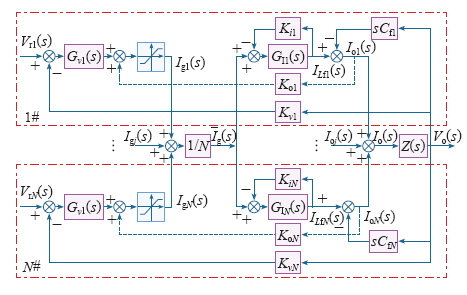
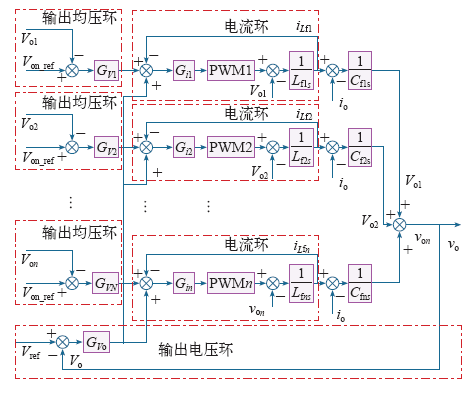
图6
图6中,vref是系统输出电压环的电压基准,GVo为输出电压环的PI调节器,Gi1~Gin为电流环的PI调节器,Lf1~Lfn为滤波电感感值,Cf1~Cfn为滤波电容值,Kc1~Kcn是电流内环的等效增益,GV1~GVN是输出均压环的PI调节器,输出均压环电压给定参考值Vo_ref的值等于vo/n。共用的输出电压环保证整个系统的正弦输出,其PI调节器GVo的输出作为各模块电流内环的初始给定信号,由于实际中每个模块反馈的电感电流并不完全一致,故引入输出均压环来调节电流环给定值以实现各模块输出均压。采用该控制策略系统的动态响应好,输出电压谐波失真度小,不管模块间的参数是否一致电压均分的精度都很高。但实质上这还是一种集中式的控制策略,为了进一步提高系统的可靠性还需进一步研究其分布式、冗余控制的实现方法。
4 ISOP逆变器系统
ISOP逆变器系统适用于输入电压较高、输出电流大的场合,如高输入电压的电力机车及城市轨道交通供电系统等。对于该系统,若假设各模块传输效率均为100%,那么各模块的输入功率等于其输出有功功率,即
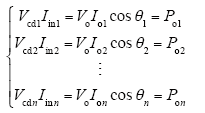
式中,Vcd1、Vcd2、…、Vcdn分别为各模块的输入分压电容电压;Iin1、Iin2、…、Iinn分别为各模块的输入电流;Po1、Po2、…、Pon分别为各模块的输出有功功率;Vo为各模块的输出电压有效值;Io1、Io2、…、Ion为各模块的输出电流有效值;θ1、θ2、…、θn分别为各模块的输出功率因数角。
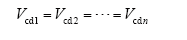
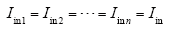
结合式(1)可得
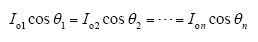
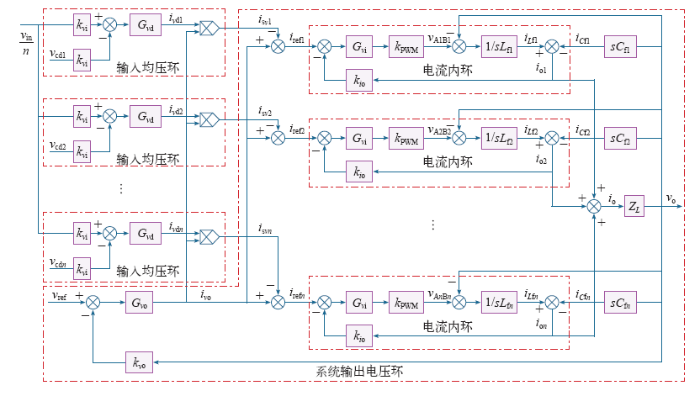
上述控制策略的控制环路由系统输出电压环、各模块输入均压环及电流内环组成。系统输出电压环用来保证ISOP逆变器系统输出电压稳定,其输出信号ivo作为各逆变器模块共用的电流内环给定信号。输入均压环用来实现各逆变器模块的输入均压,均压控制信号ivdj与系统输出电压环的输出信号ivo相乘得到与之同相位的正弦误差信号isvj,再将isvj叠加在原电流基准信号ivo上以微调各逆变器模块电流基准信号的幅值,从而得到最终的各逆变器模块电流基准信号irefj。在这里引入乘法器,是由于被控对象是逆变器,其电流基准信号不仅包含幅值信息,还包含相位信息,乘法器可以保证输入均压环产生的用于微调电流基准的信号isvj与共用的电流基准ivo保持相位相同,即保证了各逆变器模块的电流内环基准信号的相位相同,进而保证了各逆变器模块的输出电流相位相同。根据前述分析,在输入均压环和各逆变器模块的输出电流相位相同共同作用下,该控制策略可同时实现ISOP逆变器系统的输入均压和输出均流。
上述控制策略虽然实现了ISOP逆变器系统的功率均分,但该控制方式尚属于集中式控制,并未实现系统的分布式及冗余控制,限制了系统可靠性的提升。另一方面,由于该控制策略通过调节输出有功功率来实现功率均分,若系统处于空载或短路状态,即输出侧没有有功功率,则该控制策略失效,如何使系统在此类特殊负载情况下正常工作的控制方法仍有待研究。
图7
图7
ISOP逆变器系统集中式控制策略
Fig.7
A centralized control strategy for ISOP inverter system
5 ISOS逆变器系统
输入串联输出串联系统适用于输入电压和输出电压较高的场合,比如船舶电源、高速电气铁路等。若假设各逆变器模块的变换效率均为100%,则各模块的输入功率等于其输出有功功率,即
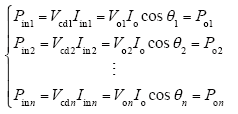
式中,Vcd1、Vcd2、…、Vcdn分别为各模块的输入分压电容电压;Iin1、Iin2、…、Iinn分别为各模块的输入电流;Iin为系统的输入电流;Pin1、Pin2、…、Pinn分别为各模块的输入功率;Po1、Po2、…、Pon分别为各模块的输出有功功率;Vo1、Vo2、…、Von分别为各模块的输出电压有效值;Io为系统的输出电流有效值;θ1、θ2、…、θn分别为各模块的输出功率因数角。
文献[17]指出输出均压控制策略的不稳定性,而如果采用输入端的控制策略则有
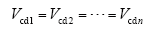
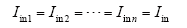
结合式(5)可得
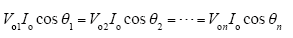
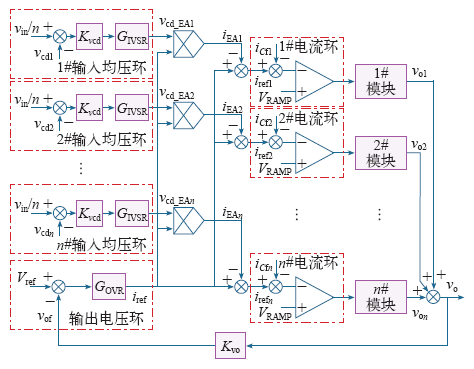
上述控制策略实质上仍是一种三环控制策略,与上述ISOP三环控制策略类似,它包括各模块公用的输出电压环、输入均压环及各模块自己的电流内环。公用的输出电压闭环控制总的输出电压稳定,其输出信号作为各模块公用的电流基准。由于被控对象是逆变器,其电流基准包含了幅值和相位信息,所以这里引入了乘法器以保证输入均压环用于微调电流基准的信号量与原来的电流基准保持相位同步。输入均压环中,各逆变器应分配到的输入电压Vin/n和其实际的输入电压之差(即输入电压误差信号)经Kvcd倍衰减后送入PI调节器GIVSR,其输出的直流误差信号vcd_EAj与电压环的输出信号iref相乘得到与之同相位的正弦误差信号iEAj,该信号叠加在原电流基准iref上以微调各模块电流基准的幅值。由于电流内环采样的是各模块的电容电流,所以输入均压环仅微调各模块电容电流基准的幅值,而它们的相位始终保持相同,从而各模块电容电流跟踪基准也保持相位一致。进一步地,由于各模块电容电流的方向与输出电压的方向相差π/2,所以上述控制也就保证了各模块输出电压的相位一致。可见该方法是通过控制输出电压同相位实现输出均压的。
上述控制策略虽然实现了ISOS逆变器系统的功率均分,但由于模块间仍共用输出电压环,控制方式仍停留在集中式,如何实现系统的真正模块化和冗余控制仍有待研究。此外,与ISOP逆变器系统类似,ISOS逆变器系统处于空载或短路等特殊负载状态亦亟待研究。
图8
图8
ISOS逆变器系统采用的集中式控制策略
Fig.8
A centralized control strategy for ISOS in-verter system
6 结论与展望
本文综合阐述了四种串并联逆变器系统所采用控制策略的研究现状。对于输入并联逆变器系统来说,由于各模块间输入电压相等,所以只要控制输出端均流或均压即可实现模块间的功率均衡。而对于输入串联逆变器系统来说,由于输入端串联,为了实现功率均衡,必须采用输入端与输出端控制相结合的方式,所以控制相对复杂。目前,仅有IPOP系统实现了分布式和冗余控制,其他三种未来研究的主要目标就是要实现系统的分布式及冗余控制,以切实提高系统的可靠性。
参考文献
Power electronics technology at the dawn of the new millennium-status and future
[C].
倒装芯片集成电力电子模块
[J].
Integrated power electronics module using flip chip technology
[J].
Active in-put-voltage and load-current sharing in in-put-series and output-parallel connected modular dc-dc converters using dynamic input-voltage reference scheme
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2004.836671 URL [本文引用: 1]
Modularization structure for series-parallel connected converters
[C].
Uninterruptible power supplies: classification operation dynamics and control
[C].
A master and slave control strategy for parallel operation of three-phase UPS systems with different ratings
[J].
Current limitation control technique for parallel operation of UPS inverters
[J].
Combination voltage-controlled and current-controlled PWM inverter for UPS parallel operation
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.63 URL [本文引用: 1]
Analysis and implementation of a master-slave control based on a passivity approach for parallel inverters operation
[C].
一种实现瞬时均流的UPS冗余并联新方法
[J].
DOI:10.1111/1750-3841.14838
URL
PMID:31750946
[本文引用: 1]

Brown adipose tissue (BAT) prevents obesity and related diseases by uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation with adenosine triphosphate. Previous studies have demonstrated that polyphenols can promote the thermogenesis of BAT in mice. Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is a common phenolic acid found in fruits and vegetables, as well as traditional Chinese medicine, which is responsible for a variety of physiological activities. However, it is still unclear whether CGA has positive effects on the thermogenesis of BAT. In this study, CGA enhances the thermogenesis and proton leak of brown adipocytes, however, no changes are evident regarding the differentiation of C3 H10 T1/2 into brown adipocytes. Surprisingly, CGA promotes the uptake of glucose by upregulating the glucose transporter 2 and phosphofructokinase. Moreover, CGA increases the number and the function of mitochondrial. Taken together, CGA stimulates thermogenesis of brown adipocytes by promoting the uptake of glucose and the function of mitochondria. PRACTICAL APPLICATION: Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is widely found in fruits, vegetables, and traditional Chinese medicines, which has been considered to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory function. However, whether it has the function of resisting obesity and promoting thermogenesis is still unclear. In this study, brown adipocyte was used to explore the function and mechanism of CGA on thermogenesis. It provides new ideas for the utilization of foods rich in CGA and traditional Chinese medicine.
Control scheme for redundant parallel UPS within stantaneous current sharing
[J].
DOI:10.1111/1750-3841.14838
URL
PMID:31750946
[本文引用: 1]

Brown adipose tissue (BAT) prevents obesity and related diseases by uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation with adenosine triphosphate. Previous studies have demonstrated that polyphenols can promote the thermogenesis of BAT in mice. Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is a common phenolic acid found in fruits and vegetables, as well as traditional Chinese medicine, which is responsible for a variety of physiological activities. However, it is still unclear whether CGA has positive effects on the thermogenesis of BAT. In this study, CGA enhances the thermogenesis and proton leak of brown adipocytes, however, no changes are evident regarding the differentiation of C3 H10 T1/2 into brown adipocytes. Surprisingly, CGA promotes the uptake of glucose by upregulating the glucose transporter 2 and phosphofructokinase. Moreover, CGA increases the number and the function of mitochondrial. Taken together, CGA stimulates thermogenesis of brown adipocytes by promoting the uptake of glucose and the function of mitochondria. PRACTICAL APPLICATION: Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is widely found in fruits, vegetables, and traditional Chinese medicines, which has been considered to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory function. However, whether it has the function of resisting obesity and promoting thermogenesis is still unclear. In this study, brown adipocyte was used to explore the function and mechanism of CGA on thermogenesis. It provides new ideas for the utilization of foods rich in CGA and traditional Chinese medicine.
Modeling, analysis, and implementation of parallel multi-inverter systems with instantaneous average-current-sharing scheme
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.63 URL [本文引用: 1]
Novel control for redundant parallel UPSs with instantaneous current sharing
[C].
A decoupling control method for inverters in parallel operation
[J].
Redundant parallel control for current regulated inverters with in-stantaneous current sharing
[C].
Low cost compound current sharing control for inverters in parallel operation
[J].
Advanced control techniques for parallel inverter operation without control interconnections
[D].
DuanS, etal. The droop characteristic decoupling control of parallel connected UPS with no control interconnection
[C].
A voltage and frequency droop control method for parallel inverters
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.63 URL
An improved multiple-loop controller for parallel operation of single-phase inverters with no control interconnections
[C].
Communicationless parallel inverters based on inductor current feedback control
[C].
A wireless load sharing controller to improve the performance of parallel-connected inverters
[C].
Droop control method for the parallel operation of online uninterruptible power systems using resistive output impedance
[C].
Parallel control of the UPS inverters with frequency-dependent droop scheme
[C].
Output impedance design of parallel-connected UPS inverters with wireless load-sharing control
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2005.851634 URL
Drop control method with virtual output impedance for parallel operation of uninterruptible power supply systems in a microgrid
[J].
A wireless load sharing controller to improve dynamic performance of parallel-connected ups inverters
[C].
A novel control strategy for in-put-parallel-output-series inverter system
[C].
Control strategy for input-series-output-parallel high-frequency AC link inverters
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TIE.2011.2174538
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper presents a control strategy for input-series-output-parallel (ISOP) modular inverters. Each module is a high-frequency (HF) ac link (HFACL) inverter composed of an HF inverter, an HF transformer, and a cycloconverter. A PWM sequence generation based on DSP control is given, with which the circulating currents among all the constituent modules can be avoided automatically. To achieve input voltage sharing (IVS) and output current sharing (OCS) among the constituent inverter modules, a stable OCS scheme, which consists of one common output voltage regulation (OVR) loop and individual inner currents loops, is proposed. The OVR loop provides a common reference for all individual inner current loops, in which the current feedback for an individual module is the sum of all the other output currents instead of its own. The compensator designs of the OVR loop and individual inner current loops are also presented. With this control strategy, excellent IVS and OCS can be obtained. The effectiveness of the proposed control strategy is verified using the simulation and experimental results of a 1100-VA ISOP two-HFACL inverter system.