1 引言
智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活。尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] 。然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] 。这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] 。例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响。2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州。因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行。
在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制。为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究。结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法。此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略。进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法。基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究。此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题。
本文提出了基于神经网络观测器的攻击检测方法,主要贡献如下所述。
(1) 考虑虚假数据攻击可以欺骗传统基于Kalman的卡方检测方法,本文通过设计神经网络观测器,可以获得虚假数据攻击下内部状态的实际变化,进而给出基于状态残差的检测逻辑。
(2) 考虑先验阈值对攻击检测性能的影响,本文设计了自适应阈值来替代传统的先验阈值,可以提高虚假数据攻击的检测性能。最后,通过在IEEE三电机六总线上仿真验证所提攻击检测方法的优越性。
本文的逻辑结构如下:第2节给出了电网线性模型和虚假数据攻击特性;第3节中提出了基于内部状态残差变化的神经网络观测器检测方法,以及自适应阈值设计;第4节中仿真验证了本文所提攻击检测方法的优越性;最后,第5节给出本文结论和工作展望。
2 电网模型和问题描述
2.1 智能电网模型
考虑到智能电网的复杂性,在系统中所有部分均可能受到恶意攻击,为简化研究程度,本文研究对象为智能电网的电机侧。考虑电网系统内部状态变化,建立第$i(i=1,2,\cdots,n)$ [17 ]
(1) $\left\{ \begin{align} & {{{\dot{\delta }}}_{i}}={{\omega }_{i}} \\ & {{{\dot{\omega }}}_{i}}=-\frac{{{D}_{i}}}{{{J}_{i}}}{{\omega }_{i}}+\frac{1}{{{J}_{i}}}({{P}_{{{M}_{i}}}}-{{P}_{{{E}_{i}}}}) \\\end{align} \right.$
式中,${{\delta }_{i}}$ ${{\omega }_{i}}$ ${{J}_{i}}$ ${{D}_{i}}$ ${{P}_{{{M}_{i}}}}$ ${{P}_{{{E}_{i}}}}$
(2) $\begin{array}{c}x(\dot{t})=\boldsymbol{A} x(t)+\boldsymbol{B} u(t)+\omega(t) \\x(t)=\left(\begin{array}{c}\delta(t) \\\omega(t)\end{array}\right) \quad u(t)=\left(P_{M}-P_{E}\right) \\\boldsymbol{A}=\left(\begin{array}{cc}0 & I \\0 & -\frac{D}{J}\end{array}\right) \quad \delta(t)=\left[\delta_{1}(t), \cdots, \delta_{n}(t)\right]^{\mathrm{T}} \\\boldsymbol{B}=\left[\begin{array}{c}0 \\\frac{1}{J}\end{array}\right) \quad \omega(t)=\left[\omega_{1}(t), \cdots, \omega_{n}(t)\right]^{\mathrm{T}} \\D=\operatorname{diag}\left[D_{1}, \cdots, D_{n}\right] \quad J=\operatorname{diag}\left[J_{1}, \cdots, J_{n}\right] \\P_{M}=\left[P_{M_{1}}, \cdots, P_{M_{n}}\right] \quad P_{E}=\left[P_{E_{1}}, \cdots, P_{E_{n}}\right]\end{array}$
2.2 攻击特性描述
电网中的安全机制是通过输出残差与先验阈值的比较来判断系统是否遭受到外部攻击,其检测表达式如下[18 -19 ]
(3) $\left\{ \begin{align} & \begin{matrix} \left\| r \right\|=\left\| z-H(\widehat{x}) \right\|<\tau & \\\end{matrix} \\ & \begin{matrix} \left\| r \right\|=\left\| z-H(\widehat{x}) \right\|\ge \tau & \\\end{matrix} \\\end{align} \right.$
式中,r 是测量残差;z 是测量输出;H τ 是先验阈值。
为了欺骗基于卡方的攻击检测机制,攻击者设计了虚假数据$a={{\left[ {{a}_{1}},{{a}_{2}},\cdots,{{a}_{m}} \right]}^{\mathrm{T}}}$ $a=Hc$
(4) $\begin{matrix} \left\| r \right\|=\left\| {{z}_{bad}}-H{{x}_{bad}} \right\|=\left\| z+a-H(\widehat{x}+c) \right\|= \\ \left\| z-H\widehat{x}+a-Hc \right\|<\tau \\\end{matrix}$
综上可知,虚假数据攻击对现有基于Kalman的输出估计检测方法具有欺骗特性,即攻击者可以通过注入一组虚假数据实现测量残差的无变化,进而掩盖对系统内部状态的改变。因此,虚假数据攻击的检测给智能电网的安全机制带来了巨大挑战。
2.3 问题描述
考虑电网系统存在虚假数据攻击f (t ),电网的系统模型表达式为
(5) $\left\{ \begin{align} & x(\dot{t})=Ax(t)+Bu(t)+w(t)+Ff(t) \\ & y(t)=Cx(t) \\\end{align} \right.$
式中,F f (t )是虚假数据攻击向量;$w(t)$
本文通过设计神经网络观测器来对智能电网系统中的内部状态进行观测,进而实现对虚假数据注入攻击的残差检测。
3 虚假数据攻击检测方法
3.1 观测器设计
引理3.1[20 ] :给定任意$\varepsilon >0$ L 2 型函数$f:{{\left[ 0,1 \right]}^{n}}\to {{R}^{m}}$ ε 平方误差精度内逼近函数f 。
基于引理3.1,本文采用如下RBF神经网络在线逼近虚假数据攻击,其形式如下
(6) $f(t)={{W}^{*\mathrm{T}}}\delta (x,u)+\varepsilon $
式中,$\left[ x,u \right]$ ${{W}^{*}}={{\left[ W_{1}^{*},W_{2}^{*},\cdots,W_{n}^{*} \right]}^{\mathrm{T}}}$ ${{W}^{*}}=\arg \underset{W\in {{\Omega }_{w}}}{\mathop{\min }}\,\left[ \underset{X\in {{A}_{d}}}{\mathop{\sup }}\,\left| f(x,u,W)-\left. f(x,u,t) \right| \right. \right]$ W
(7) $\left\{ \begin{align} & \dot{\hat{x}}(t)=A\hat{x}(t)+Bu(t)+F\hat{f}(t)+K(y(t)-\hat{y}(t))+s(t) \\ & \hat{y}(t)=C\hat{x}(t) \\\end{align} \right.$
式中,K v 为对扰动和不确定性的补偿项;$\hat{x}(t)$ $\hat{y}(t)$ $s(t)=\frac{\alpha \hat{y}(t)}{\left| \hat{y}(t) \right|}$ $\hat{W}$ $\hat{f}(t)$
(8) $\hat{f}(t)={{\hat{W}}^{\mathrm{T}}}\delta (\hat{x},u)$
(9) $\left\{ \begin{align} & {{e}_{x}}(t)=x(t)-\hat{x}(t) \\ & {{e}_{y}}(t)=y(t)-\hat{y}(t) \\ & {{e}_{f}}(t)=f(t)-\hat{f}(t) \\\end{align} \right.$
(10) $\left\{ \begin{align} & {{{\dot{e}}}_{x}}(t)=(A-KC){{e}_{x}}+w(t)+F{{e}_{f}}(u,t)-s(t) \\ & {{e}_{y}}(t)=C{{e}_{x}}(t) \\ & {{e}_{f}}(t)=({{W}^{\ *\mathrm{T}}})\widetilde{\delta }+\varepsilon -{{\widetilde{W}}^{T}}\delta (\widehat{x},u) \\\end{align} \right.$
为确保设计式(10)中神经网络观测器误差稳定,给出如下定理。
定理3.1[20 ] :在假设3.1条件下,存在正定矩阵$P>0$ T K
(11) $\left( \begin{matrix} \Omega +{{C}^{\mathrm{T}}}C & P & PF \\ * & -{{\gamma }^{2}}{{I}_{\text{w}}} & 0 \\ * & 0 & -{{\gamma }^{2}}{{I}_{\text{t}}} \\\end{matrix} \right)<0$
(12) $\Omega ={{(A-KC)}^{\mathrm{T}}}P+P(A-KC)$
(13) $TC={{F}^{\mathrm{T}}}P$
(14) $\overset{\centerdot }{\mathop{\widehat{W}}}\,=\Lambda \delta \left( \widehat{x},u \right)e_{y}^{\mathrm{T}}{{T}^{\mathrm{T}}}$
3.2 自适应阈值设计
考虑外部扰动对检测阈值的影响,本节提出自适应阈值的设计来替代现有电网安全机制中的先验阈值,进而提高虚假数据攻击的检测性能。
(15) $\rho (x,\hat{x})=\frac{\left\| {{x}^{w}}+{{x}^{e}} \right\|}{\left\| x \right\|\centerdot \left\| {\hat{x}} \right\|}$
式中,${{x}^{w}}$ ${{x}^{e}}$
(16) $\rho (x,\hat{x})\le \frac{\left\| {{x}^{w}} \right\|+\left\| {{x}^{e}} \right\|}{\left\| x \right\|\centerdot \left\| {\hat{x}} \right\|}=\frac{J_{th}^{w}+J_{th}^{e}}{\left\| x \right\|\centerdot \left\| {\hat{x}} \right\|}$
式中,$J_{th}^{e}=\left\| Hx-H\hat{x} \right\|=\left\| HR \right\|$
(17) $\Psi =\underset{{{x}^{w}},{{x}^{e}}}{\mathop{\sup }}\,\left\| \rho (x,\hat{x}) \right\|$
(18) $R=\hat{x}(t)-x(t)$
基于式(17)和式(18),给出攻击检测逻辑决策为
(19) $\left\{ \begin{align} & \begin{matrix} \left| R \right|<\Psi & \\\end{matrix} \\ & \begin{matrix} \left| R \right|\ge \Psi & \\\end{matrix} \\\end{align} \right.$
基于以上逻辑检测决策,给出对应攻击检测算法如表1 所示。
3.3 检测性能分析指标
为了评价攻击检测性能,本文引入攻击检测率PD 和误报率PF 两个变量,表达式如下[21 ]
(20) $\left\{ \begin{align} & {{P}_{D}}\left( l/h,p \right)=1-\theta \left( \frac{l-p}{h} \right)+\theta \left( \frac{-l-p}{h} \right) \\ & {{P}_{D}}\left( l/h,p \right)=1-\chi {{P}_{F}}\left( l \right) \\\end{align} \right.$
式中,$h,p\in R$ χ 为虚报和漏报的比例系数;l 为检测阈值。
4 仿真结果分析
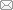
在如图1 所示的IEEE三电机六总线上验证所提攻击检测方法的性能,其中部分相关系统参数可参考文献[10 ]。首先通过与传统卡方检测方法的对比,验证所提检测方法的有效性。然后,通过与欧式检测方法对比可知,所提检测方法可以快速检测入侵的虚假数据攻击,提高了攻击的检测率。
图1
4.1 攻击检测方法有效性分析
假设电网系统正常运行,攻击者在t =8 s时注入虚假数据攻击,其中的虚假数据攻击模型为
(21) ${{z}_{bad}}_{{}}=H{{x}_{bad}}_{{}}+\Gamma {{y}_{k}}{{^{{}}}^{{}}}{{^{{}}}^{{}}}{{^{{}}}^{{}}}k\in T$
式中,$\Gamma =diag\left( {{\gamma }_{1}},\cdots,{{\gamma }_{n}} \right)$ ${{y}_{k}}$ ${{x}_{bad}}$ ${{z}_{bad}}$
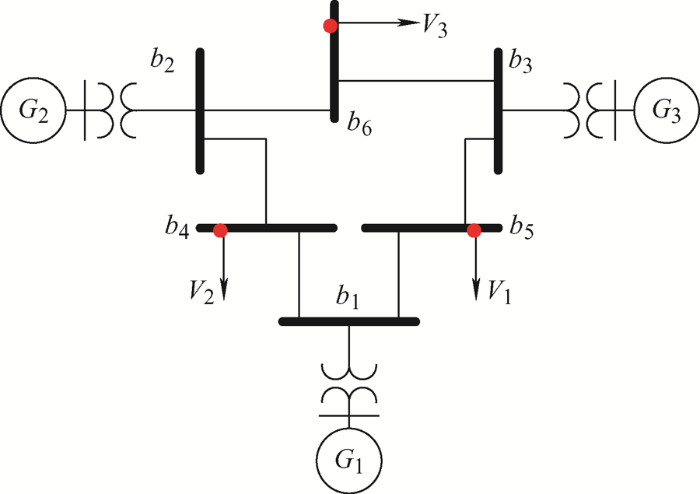
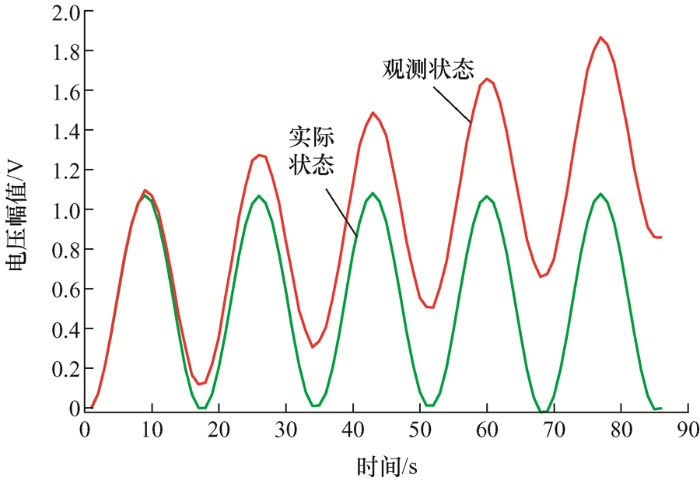
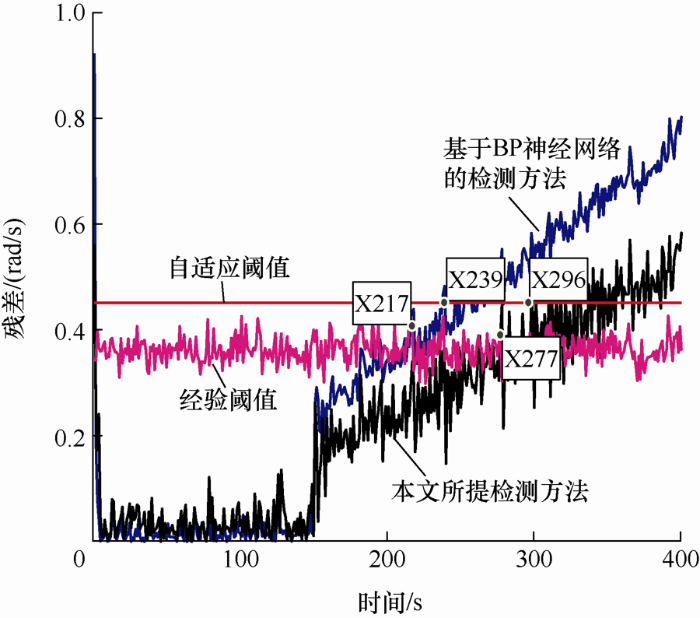
基于检测算法1,得到注入攻击后卡方检测系统状态变化(图2 )和检测结果(图3 ),可以发现攻击者成功改变了系统状态变化而未触发系统报警。基于本文所提的攻击检测方法,可以得到攻击检测结果如图3 所示。由于$\left| R \right|\ge \Psi $
图2
图3
4.2 攻击检测性能对比分析
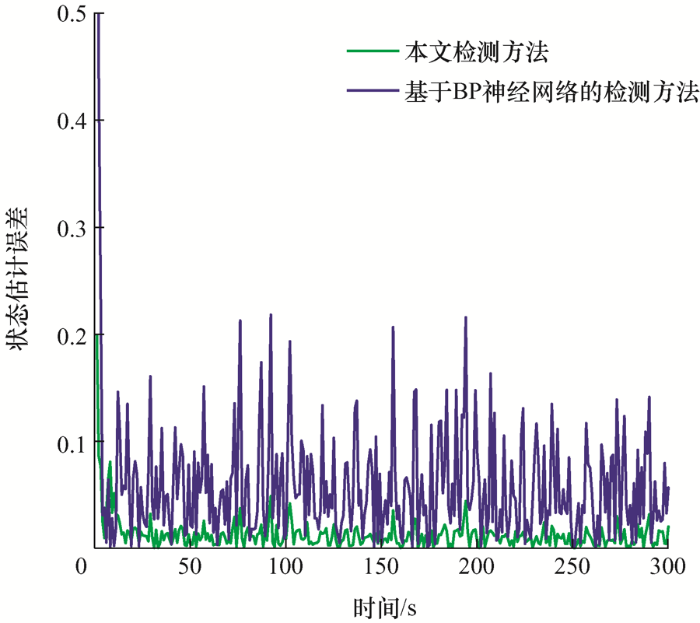
在t =200 s攻击入侵情况下,分别采用基于BP神经网络和本文算法1检测虚假数据攻击,如图4 和图5 所示。基于图4 的对比结果可以发现,本文所提的检测方法比基于BP神经网络方法得到的状态估计误差更小,进而获得更准确的估计状态。此外,在同一检测阈值的情况下,本文所提检测方法可以更快地检测到注入的虚假数据。图5 中检测结果表明自适应阈值替代传统先验阈值后进一步缩短攻击检测时间,提高攻击检测性能。
图4
图5
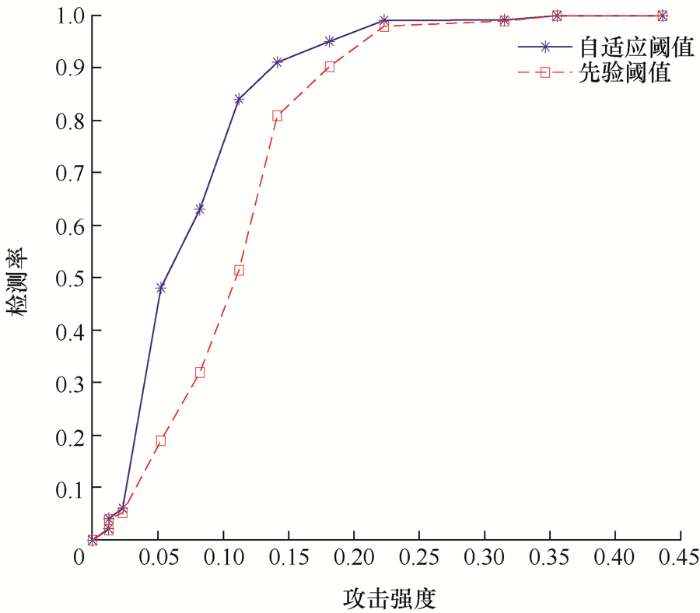
图6 揭示了检测率PD 取决于检测阈值的选取值,即检测阈值越小,检测率越高。在自适应阈值替代先验阈值情况下,可以进一步缩短攻击检测时间,提高攻击的检测率。
图6
5 结论
本文提出基于神经网络观测器的虚假数据攻击检测方法,主要工作总结如下所述。
(1) 考虑虚假数据攻击对内部状态的影响,提出基于内部状态差变化的神经网络观测器残差检测方法,解决了虚假数据攻击欺骗传统基于Kalman的卡方检测方法问题。
(2) 基于状态估计误差和外部扰动的范数上界,设计自适应阈值替代传统的先验阈值,缩短了虚假数据攻击的检测时间。
最后,在IEEE三电机六总线上验证对比了所提攻击检测方法性能的优越性。未来工作中,本文还需要进一步考虑建模时电网模型不确定性对攻击检测的影响,以及针对不同类别的虚假数据攻击的检测与防御研究。
参考文献
View Option
[1]
中华人民共和国国务院新闻办公室 . 新时代的中国能源发展
[N]. 人民日报 ,2020-12-22(010 ).
[本文引用: 1]
The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China . China’s energy development in the new era
[N]. People’s Daily ,2020-12-22(010 ).
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
周建勇 , 陈宝仁 , 吴谦 . 智能电网电力无线宽带专网建设若干关键问题探讨
[J]. 南方电网技术 , 2014 , 8 (1 ):46 -49 .
[本文引用: 1]
ZHOU Jianyong CHEN Baoren WU Qian Discussion on some key problems of power wireless broadband private network construction in smart grid
[J]. Southern Power System Technology , 2014 , 8 (1 ):46 -49 .
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
梅生伟 , 朱建全 . 智能电网中的若干数学与控制科学问题及其展望
[J]. 自动化学报 , 2013 , 39 (2 ):119 -131 .
[本文引用: 1]
MEI Shengwei ZHU Jianquan Some mathematical and control science problems in smart grid and their prospects
[J]. Automatica Sinica , 2013 , 39 (2 ):119 -131 .
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
宋宁宁 , 仝娜 , 严行健 . 智能电网若干问题的探讨
[J]. 电力工程技术 , 2010 , 29 (3 ):82 -84 .
[本文引用: 1]
SONG Ningning TONG Na YAN Xingjian Discussion on some problems of smart grid
[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology , 2010 , 29 (3 ):82 -84 .
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
高鹏 , 陈智雨 , 闫龙川 , 等 . 面向零信任环境的新一代电力数据安全防护技术
[J]. 电力信息与通信技术 , 2021 , 19 (2 ):7 -14 .
[本文引用: 1]
GAO Peng CHEN Zhiyu YAN Longchuan et al . A new generation of power data security protection technology for zero-trust environment
[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology , 2021 , 19 (2 ):7 -14 .
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
刘广一 , 王继业 , 李洋 , 等 . “电网一张图”时空信息管理系统
[J]. 电力信息与通信技术 , 2020 , 18 (1 ):7 -17 .
[本文引用: 1]
LIU Guangyi WANG Jiye LI Yang et al . “One Graph of Power Grid” spatio-temporal information management system
[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology , 2020 , 18 (1 ):7 -17 .
[本文引用: 1]
[7]
郭戈 , 张文安 , 周彬 . “信息物理系统理论、方法及应用”专栏序言
[J]. 控制与决策 , 2019 , 34 (11 ):2273 -2276 .
[本文引用: 1]
GUO Ge ZHANG Wenan ZHOU Bin Preface to the column “Theory,method and application of information physical system”
[J]. Control and Decision , 2019 , 34 (11 ):2273 -2276 .
[本文引用: 1]
[8]
孙华东 , 许涛 , 郭强 , 等 . 英国“8·9”大停电事故分析及对中国电网的启示
[J]. 中国电机工程学报 , 2019 , 39 (21 ):6183 -6192 .
[本文引用: 1]
SUN Huadong XU Tao GUO Qiang et al . Analysis on blackout in great Britain power grid on August 9th, 2019 and its enlightenment to power grid in China
[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE , 2019 , 39 (21 ):6183 -6192 .
[本文引用: 1]
[9]
FANG J SU C CHEN Z et al . Power system structural vulnerability assessment based on an improved maximum flow approach
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid , 2018 , 9 (2 ):777 -785 .
DOI:10.1109/TSG.2016.2565619
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
MENG Z CHAO S NING H E et al . False data injection attacks against smart grid state estimation:Construction,detection and defense
[J]. Science China , 2019 , 62 (12 ):2077 -2087 .
[本文引用: 2]
[11]
LIU Y NING P REITERr M K False data injection attacks against state estimation in electric power grids
[J]. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security , 2011 , 14 (1 ):1 -34 .
[本文引用: 1]
[12]
JIN M LAVAEI J JOHANSSON K H Power grid AC-based state estimation:Vulnerability analysis against cyber attacks
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control , 2019 , 64 (5 ):1784 -1799 .
DOI:10.1109/TAC.9
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[13]
RAHMAN M A MOHSENIAN-RAD H False data injection attacks against nonlinear state estimation in smart power grids
[C]// 2013 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting , July 21-25,2013 ,Vancouver,BC,Canada. IEEE, 2013 :1 -5 .
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
刘鑫蕊 , 常鹏 , 孙秋野 . 基于XGBoost和无迹卡尔曼滤波自适应混合预测的电网虚假数据注入攻击检测
[J]. 中国电机工程学报 , 2021 , 41 (16 ):5462 -5476 .
[本文引用: 1]
LIU Xinrui CHANG Peng SUN Qiuye Detection of false data injection attack in power grid based on adaptive hybrid prediction of XGBoost and unscented Kalman filter
[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE , 2021 , 41 (16 ):5462 -5476 .
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
何耀 , 周聪 , 郑凌月 , 等 . 基于扩展卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法
[J]. 中国电力 , 2017 , 50 (10 ):35 -40 .
[本文引用: 1]
HE Yao ZHOU Cong ZHENG Lingyue et al . False data attack detection method based on extended Kalman filter
[J]. Electric Power , 2017 , 50 (10 ):35 -40 .
[本文引用: 1]
[16]
MANANDHAR K CAO X HU F et al . Detection of faults and attacks including false data injection attack in smart grid using Kalman filter
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems , 2014 , 1 (4 ):370 -379 .
DOI:10.1109/TCNS.2014.2357531
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
HOU Lingjie LUO Xiaoyuan WANG Xinyu et al . An adaptive control defense scheme of false data injection attacks in smart grids
[C]// 3rd International Symposium on Autonomous Systems (ISAS) , May 29-31,2019 ,Shanghai,China. IEEE, 2019 :522 -527 .11.
[本文引用: 1]
[18]
BI S ZHANG Y Defending mechanisms against false- data injection attacks in the power system state estimation
[C]// 2011 IEEE GLOBECOM Workshops (GC Wkshps) , December 05-09,2011 ,Houston,TX,USA. IEEE, 2011 :1162 -1167 .
[本文引用: 1]
[19]
KOSUT O JIA L THOMAS R J et al . On malicious data attacks on power system state estimation
[C]// 45th International Universities Power Engineering Conference,August 31-September 03,2010,Cardiff,UK. IEEE , 2010 :1 -6 .
[本文引用: 1]
[20]
王士同 . 神经模糊系统及其应用 [M]. 北京 : 北京航空航天大学出版社 ,1996.
[本文引用: 2]
WANG Shitong Neuro fuzzy system and its application [M]. Beijing : Beihang University Press ,1996.
[本文引用: 2]
[21]
YU W GRIFFITH D GE L et al . An integrated detection system against false data injection attacks in the Smart Grid
[J]. Secur. Commun. Netw. , 2015 , 8 (2 ):91 -109 .
DOI:10.1002/sec.957
URL
[本文引用: 1]
新时代的中国能源发展
1
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
China’s energy development in the new era
1
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
智能电网电力无线宽带专网建设若干关键问题探讨
1
2014
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
Discussion on some key problems of power wireless broadband private network construction in smart grid
1
2014
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
智能电网中的若干数学与控制科学问题及其展望
1
2013
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
Some mathematical and control science problems in smart grid and their prospects
1
2013
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
智能电网若干问题的探讨
1
2010
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
Discussion on some problems of smart grid
1
2010
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
面向零信任环境的新一代电力数据安全防护技术
1
2021
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
A new generation of power data security protection technology for zero-trust environment
1
2021
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
“电网一张图”时空信息管理系统
1
2020
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
“One Graph of Power Grid” spatio-temporal information management system
1
2020
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
“信息物理系统理论、方法及应用”专栏序言
1
2019
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
Preface to the column “Theory,method and application of information physical system”
1
2019
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
英国“8·9”大停电事故分析及对中国电网的启示
1
2019
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
Analysis on blackout in great Britain power grid on August 9th, 2019 and its enlightenment to power grid in China
1
2019
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
Power system structural vulnerability assessment based on an improved maximum flow approach
1
2018
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
False data injection attacks against smart grid state estimation:Construction,detection and defense
2
2019
... 智能电网作为国家基础设施,其安全性直接影响国家经济以及国民生活.尤其在“十四五”期间面对新能源大规模的接入,重点要确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行[1 ⇓ ⇓ -4 ] .然而,系统的信息-物理融合特性使其面临潜在的信息安全风险,尤其是具有信息-物理协同能力的虚假数据攻击[5 ⇓ -7 ] .这类攻击可以通过注入虚假数据到信息网以掩盖物理系统的内部动态变化,进而造成级联故障引发大面积停电[8 ⇓ -10 ] .例如,2018年,俄罗斯和伊朗基础电力网络攻击事件导致全球20万台路由器遭受影响.2019年,委内瑞拉电力系统网络攻击事件波及全国23个州.因此,迫切需要一种针对虚假数据攻击的检测机制来确保能源转型过程中智能电网系统的安全稳定运行. ...
... 在如图1 所示的IEEE三电机六总线上验证所提攻击检测方法的性能,其中部分相关系统参数可参考文献[10 ].首先通过与传统卡方检测方法的对比,验证所提检测方法的有效性.然后,通过与欧式检测方法对比可知,所提检测方法可以快速检测入侵的虚假数据攻击,提高了攻击的检测率. ...
False data injection attacks against state estimation in electric power grids
1
2011
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
Power grid AC-based state estimation:Vulnerability analysis against cyber attacks
1
2019
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
False data injection attacks against nonlinear state estimation in smart power grids
1
2013
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
基于XGBoost和无迹卡尔曼滤波自适应混合预测的电网虚假数据注入攻击检测
1
2021
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
Detection of false data injection attack in power grid based on adaptive hybrid prediction of XGBoost and unscented Kalman filter
1
2021
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
基于扩展卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法
1
2017
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
False data attack detection method based on extended Kalman filter
1
2017
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
Detection of faults and attacks including false data injection attack in smart grid using Kalman filter
1
2014
... 在2009年,LIU等[11 ⇓ -13 ] 设计了具有隐蔽特性的虚假数据攻击,并揭示了其可以欺骗传统基于测量输出的电网安全机制.为了确保智能电网的安全运行,学者们从多方面开展了对恶意攻击的检测研究.结合系统负荷预测,文献[14 ]提出了基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的虚假数据攻击检测方法.此外,文献[15 ]考虑电网系统模型未知的情况下,给出了基于数据递归的无迹卡尔曼攻击检测策略.进一步考虑噪声特性影响,文献[16 ]提出了基于欧几里得的虚假数据攻击检测方法.基于输出测量数据的改善,以上检测方法可以有效地检测注入到系统中虚假数据攻击,但是缺乏进一步对虚假数据攻击下系统内部状态变化的研究.此外,以上检测方法中检测阈值均为先验阈值,其取值会影响攻击检测性能,例如取值过大会导致攻击的漏检等问题. ...
An adaptive control defense scheme of false data injection attacks in smart grids
1
2019
... 考虑到智能电网的复杂性,在系统中所有部分均可能受到恶意攻击,为简化研究程度,本文研究对象为智能电网的电机侧.考虑电网系统内部状态变化,建立第$i(i=1,2,\cdots,n)$ [17 ] ...
Defending mechanisms against false- data injection attacks in the power system state estimation
1
2011
... 电网中的安全机制是通过输出残差与先验阈值的比较来判断系统是否遭受到外部攻击,其检测表达式如下[18 -19 ] ...
On malicious data attacks on power system state estimation
1
2010
... 电网中的安全机制是通过输出残差与先验阈值的比较来判断系统是否遭受到外部攻击,其检测表达式如下[18 -19 ] ...
2
... 引理3.1[20 ] :给定任意$\varepsilon >0$ L 2 型函数$f:{{\left[ 0,1 \right]}^{n}}\to {{R}^{m}}$ ε 平方误差精度内逼近函数f . ...
... 定理3.1[20 ] :在假设3.1条件下,存在正定矩阵$P>0$ T K
2
... 引理3.1[20 ] :给定任意$\varepsilon >0$ L 2 型函数$f:{{\left[ 0,1 \right]}^{n}}\to {{R}^{m}}$ ε 平方误差精度内逼近函数f . ...
... 定理3.1[20 ] :在假设3.1条件下,存在正定矩阵$P>0$ T K
An integrated detection system against false data injection attacks in the Smart Grid
1
2015
... 为了评价攻击检测性能,本文引入攻击检测率PD 和误报率PF 两个变量,表达式如下[21 ] ...