1 引言
随着化石能源的逐渐枯竭,风能、太阳能等分布式能源受到了广泛的关注,近年来,国内建立了以逆变器为接口的大型风力、光伏电站[1,2]。一般情况下,分布式电源主要通过并网逆变器接入电网,电网是一个具有转动惯量的系统,常规并网逆变器虽然响应速度快,但缺乏同步发电机的转动惯量与阻尼特性,难以参与电网调节,导致系统有效转动惯量降低,无法为含分布式电源的主动配电网提供必要的电压和频率支撑[3,4,5,6,7,8,9]。同步发电机是商业电能的主要来源,由于同步电机具有对电网天然友好的优势,其转动惯量和阻尼特性能在维持电网稳定运行方面起重要作用[10,11]。若使并网逆变器具有类似同步电机的运行特性,则可以实现分布式电源的友好接入,提高分布式发电系统的稳定性。文献[12]提出了同步逆变器的概念,同步逆变器可实现与同步发电机在内部机理和外部特性上的等效,有望在含分布式电源的主动配电网中发挥重要作用。
同步逆变器通过调节输入的机械功率调节功角继而实现有功调节,通过调节励磁电流来改变感应电动势幅值继而改变无功功率,然而这种调节方式建立的前提是感应电动势和机端电压之间的功角非常小。当同步逆变器的输出阻抗不满足为纯感性且功角较大时,有功和无功不能实现独立控制,引起有功功率和无功功率之间的耦合。这对分布式电源的并网控制、有功无功的出力分配、系统的稳定运行等产生了很大影响[13,14]。为了解决此类问题,文献[15,16]提出下垂参数自适应,利用虚拟阻抗等方法改进下垂控制,但该方法会引起电压跌落;文献[17,18]提出虚拟同步电机功率振荡抑制方法,其基本思想是将有功功率传输方程线性化,并引入线性控制理论,将阻尼因子与转角偏差解耦,以实现有功功率振荡抑制,却忽略了无功功率振荡;文献[19]设计了虚拟同步机非线性阻尼控制器,在无功–电压控制中引入附加励磁控制量,可有效地抑制无功功率振荡,但却忽略了有功功率的振荡;文献[20]提出了电流反馈的思想,能较好地实现功率解耦,但缺乏对同步逆变器功率耦合问题的研究;文献[21]基于同步频率谐振产生机理,采用有源阻尼控制的策略抑制功率耦合引起的谐振问题,但控制算法较为复杂。
针对同步逆变器存在的功率耦合问题,本文提出了一种易于工程实现的功率完全解耦控制策略。首先根据同步逆变器的数学模型,建立了有功功率和无功功率的小信号模型,分析了产生功率耦合的机理;然后将引起动态耦合的功率转化为采用补偿动态电流来实现,使其更加容易调节与控制;同时对加入了反馈电流环的系统进行了稳定性分析,最后通过仿真和实验证明了本文所提方法的可行性和优越性。
2 同步逆变器的功率耦合机理分析
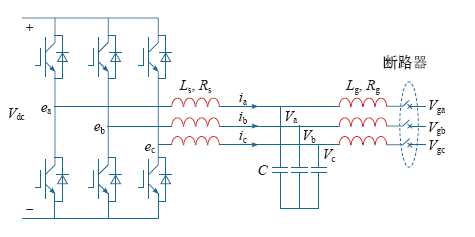
同步逆变器主要由主电路和控制电路组成。同步逆变器的主电路部分如图1所示,其中Lg为线路阻抗。为了便于研究本文提出的同步逆变器解耦控制策略的可行性,假定线路阻抗为纯感性。
同步逆变器主电路的基本思路是将图1中逆变器桥臂的中性点电压ea、eb、ec,电容电压Va、Vb、Vc分别等效为同步发电机感应电动势和机端电压,电感Ls、Ls的内阻Rs模拟同步发电机的定子电感和定子阻抗,并且满足电磁方程,即
图1
控制部分核心算法如图2所示。图中,Dp、Dq为有功、无功阻尼系数,具有频率下垂和阻尼的功能,可以直接实现频率下垂,不需要添加额外的控制环节;Pset为有功功率,可以直接变换为对应的机械转矩Tm;Mf为互感系数;if为励磁电流;
图2
假设采用极对数n = 1的隐极式同步电机,同步逆变器的主要控制方程如下:
励磁电流恒定时,感应电动势的表达式为
转子的机械方程为
电磁转矩方程为
同步逆变器输出的有功功率和无功功率分别为
其中,<,>表示内积。
图3
图3
同步逆变器简化模型及各元素矢量图
Fig.3
Synchronous inverter simplified model and the vector diagram of each element
因此,有
再由|AC| = Xs I sin ϕ = Ecos δ - V,可得
有功功率可以表示为P = VI cos ϕ,结合上式可得到
由无功功率Q = VI sin ϕ,同理可得
式中,E为同步逆变器桥臂的中性点电压有效值;V为同步逆变器机端电压;Xs = ωLs;δ为功角。
当同步逆变器并网后,根据同步发电机功角特性,存在P-δ、Q-V相对应的调节关系,为了详细分析P-δ、Q-V之间的关系,将式(11)按照小信号模型展开,即
式中,V0、δ0分别为稳态的机端电压和稳态的功角;P0、Q0为稳态有功功率和无功功率;P1、Q1分别为有功功率和无功功率的耦合量。
由式(12)可知,有功不仅与Δδ有关,而且与ΔV有关,因此存在P-V耦合效应;同理可知无功调节存在Q-δ耦合效应。为了能实现消除功率耦合的目的,需要将P-V之间的耦合量P1和Q-δ之间的耦合量Q1消除。
3 功率解耦控制策略
根据以上分析,本文根据相互影响的耦合量P1和Q1,通过动态的补偿相反的-P1和-Q1,达到消除耦合的目的。为了便于实现补偿功率耦合量,本文将补偿动态功率转换成补偿动态电流。
3.1 P-V的解耦控制策略
由式(12)可知,为达到消除P-V耦合的目的,需补偿的有功量为-P1,其表达式为
式中,V0为稳态时机端电压的值;ΔV为机端电压干扰量。
将-P1转化成动态补偿电流,根据文献[22],有功功率又可以表示为
则有
因此,可得需要补偿的电流增量为
3.2 Q-δ的解耦控制策略
由式(12)可知,为消除Q-δ之间的耦合,需要补偿的无功功率为-Q1,其表达式为
其中,Δδ为功角干扰量。
将-Q1转化成补偿电流,即
因此,可得需要补偿的电流增量为
4 电流反馈下的同步逆变器功率解耦控制
由于增加电流环能提高系统的动态响应,并可以限制电流,起到过电流保护的作用。因此本文在原有控制算法的基础上增加了一个反馈电流环,以补偿消除功率耦合量所需要的动态电流。
根据文献[25],可以推导出式(1)在dq坐标中的动态方程为
由式(20)可得电流环的控制框图(见图3),结合式(16)、式(19)可得修正后的电流为
式中,Id*、Iq*为原电流环的给定电流,由参考电流iref经dq变化得到,iref计算式为
综上所述,本文提出解耦控制方法如图4所示。
图4
5 基于动态模型的稳定性分析
图5
图5
增加解耦控制策略的同步逆变器小信号模型
Fig.5
A small signal model of synchronous inverter with decoupling control strategy is added
图5中,iq对e的传递函数为
由图5a可得加入解耦控制策略的有功环的开环环路增益为
由图5b可得加入解耦控制策略的无功环的开环环路增益为
图6
6 仿真验证
为了验证本文提出的解耦控制策略的优越性和可行性,在Matlab14b中搭建仿真平台,并将本文方法与文献[12]在同等情况下进行比较。仿真参数见下表。
表1 仿真参数设计
Tab1
| 参 数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| Ls/mH,Rs /Ω | 0.45,0.27 |
| C /μF | 22 |
| Lg /mH | 0.45 |
| 直流侧电压Vdc /V | 700 |
| 电网电压Ug /V | 220 |
| Dp | 5 |
| Dq | 50 |
| K | 128.066 2 |
| J/kg·m2 | 0.000 405 2 |
| 电流环PI参数 | kp = 2,ki = 30 |
在0~1s断路器断开,同步逆变器与电网预同步,此时输出有功和无功均为0,1s时加入有功功率Pset = 5 000W,2s时加入无功功率Qset = 2 000var,3s时加入电压调节器。
图7
图8
7 结论
本文针对同步逆变器功率耦合控制问题,分析了同步逆变器的功率,建立了小信号模型,详细阐述了产生功率耦合的机理,提出一种基于电流反馈的同步逆变器功率解耦控制策略,并与传统的同步逆变器解耦方法进行比较,得出以下结论:
(1)本文所提方法完全能实现有功功率和无功功率的解耦,使得系统运行更加稳定。
(2)将引起耦合的动态功率量转换成动态电流的形式,更便于实现。
(3)增加了电流内环,减少了系统的超调量和过渡时间。
(4)增加了电流内环,使得系统的稳定性能更加优越。
参考文献
欧洲超级电网计划及其对中国电网建设启示
[J].
European supergrid project and its enlightenment to China’s power grid
[J].
下垂控制逆变器的虚拟功角稳定机理分析
[J].
Multi-rate real-time simulation method based on RTDS and FPGA co-simulation platform
[J].
基于虚拟同步发电机的柔性虚拟调速器模型
[J].
Flexible virtual covernor model based on virtual synchronous generator
[J].
Control for grid-connected and intentional islanding operations of distributed power generation
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2010.2049709 URL [本文引用: 1]
独立微电网中基于自适应权重系数的VSG协调控制策略
[J].
VSG coordinated control based on adaptive weight factors in islanded microgrids
[J].
同步控制逆变电源并网预同步过程分析
[J].
Analysis of grid-connecting pre-synchronized process for synchronously controlled inverter power source
[J].
虚拟同步发电机及其在微电网中的应用
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.16.009
URL
[本文引用: 1]

针对分布式电源并网逆变器的虚拟同步发电机控制策略及其在微电网中的应用进行研究。建立并网逆变器用虚拟同步发电机控制方案的数学模型,研究基于虚拟转矩和虚拟励磁的并网有功、无功调节方案,定量分析系统模型参数摄动对并网功率跟踪的影响,详细分析惯性和阻尼参数的整定方法,提出一种基于锁相环的虚拟同步发电机离/并网无缝切换控制策略,可模拟同步发电机的准同期并列装置。最后,针对一个典型微电网系统,利用PSCAD/EMTDC的仿真结果和一台50 kVA样机的实验结果验证所提控制策略的正确性和有效性。结果表明,所提的并网功率调节控制策略具有较好的有功、无功跟踪性能;同时,还能很好地为系统提供惯性和阻尼,提高系统稳定性,此外,还能满足微电网不同运行模式之间的无缝切换。
Virtual synchronous generator and its applications in micro-grid
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.16.009
URL
[本文引用: 1]

针对分布式电源并网逆变器的虚拟同步发电机控制策略及其在微电网中的应用进行研究。建立并网逆变器用虚拟同步发电机控制方案的数学模型,研究基于虚拟转矩和虚拟励磁的并网有功、无功调节方案,定量分析系统模型参数摄动对并网功率跟踪的影响,详细分析惯性和阻尼参数的整定方法,提出一种基于锁相环的虚拟同步发电机离/并网无缝切换控制策略,可模拟同步发电机的准同期并列装置。最后,针对一个典型微电网系统,利用PSCAD/EMTDC的仿真结果和一台50 kVA样机的实验结果验证所提控制策略的正确性和有效性。结果表明,所提的并网功率调节控制策略具有较好的有功、无功跟踪性能;同时,还能很好地为系统提供惯性和阻尼,提高系统稳定性,此外,还能满足微电网不同运行模式之间的无缝切换。
基于参数自适应调节的虚拟同步发电机暂态响应优化控制
[J].
Optimal control of transient response of virtual synchronous generator based on adaptive parameter adjustment
[J].
虚拟同步发电机技术及展望
[J].
Review and prospect of virtual synchronous generator technologies
[J].
A novel protection scheme for synchronous generator stator windings based on SVM
[J].
DOI:10.4142/jvs.2019.20.e58
URL
PMID:31775185
[本文引用: 1]

The Schmallenberg virus (SBV) is an orthobunyavirus that causes abortions, stillbirths, and congenital defects in pregnant sheep and cattle. Inactivated or live attenuated vaccines have been developed in endemic countries, but there is still interest in the development of SBV vaccines that would allow Differentiating Infected from Vaccinated Animals (DIVA). Therefore, an attempt was made to develop novel DIVA-compatible SBV vaccines using SBV glycoproteins expressed in baculovirus. All vaccines and phosphate buffered saline (PBS) controls were prepared with adjuvant and administered subcutaneously to cattle at 6 month of age. The first trial included 2 groups of animals vaccinated with either carboxyl-terminus glycoprotein (Gc) or PBS and boosted after 2 weeks. In the second trial, 3 groups of cattle were administered either Gc, Gc and amino-terminus glycoprotein (Gn), or PBS with a booster vaccination after 3 weeks. The animals were challenged with SBV 9 days after the booster vaccination in the first study, and 3 weeks after the booster vaccination in the second study. Using a SBV Gc-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, antibodies were first detected in serum samples 14 days after the first vaccination in both trials, and peaked on days 7 and 9 after the booster in the first and second trials, respectively. Low titers of neutralizing antibodies were detected in serum from only 3/6 and 2/4 animals in the first and second trial, respectively, at 14 days after the first vaccination. The titers increased 2 to 3-fold after the booster vaccination. SBV-specific RNA was detected in the serum and selective tissues in all animals after SBV challenge independent of vaccination status. The SBV candidate vaccines neither prevented viremia nor conferred protection against SBV infection.
Virtual synchronous generators: a survey and new perspectives
[J].
DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-53664-7
URL
PMID:31772191
[本文引用: 1]

Neutron detection is crucial for particle physics experiments, nuclear power, space and international security. Solid state neutron detectors are of great interest due to their superior mechanical robustness, smaller size and lower voltage operation compared to gas detectors. Gallium nitride (GaN), a mature wide bandgap optoelectronic and electronic semiconductor, is attracting research interest for neutron detection due to its radiation hardness and thermal stability. This work investigated thermal neutron scintillation detectors composed of GaN thin films with and without conversion layers or rare-earth doping. Intrinsic GaN-based neutron scintillators are demonstrated via the intrinsic 14N(n, p) reaction, which has a small thermal neutron cross-section at low neutron energies, but is comparable to other reactions at high neutron energies (>1 MeV). Gamma discrimination is shown to be possible with pulse-height in intrinsic GaN-based scintillation detectors. Additionally, GaN-based scintillation detector with a 6LiF neutron conversion layer and Gd-doped GaN detector are compared with intrinsic GaN detectors. These results indicate GaN scintillator is a suitable candidate neutron detector in high-flux applications.
Synchronverters: inverters that mimic synchronous generators
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TIE.2010.2048839
URL
[本文引用: 4]

In this paper, the idea of operating an inverter to mimic a synchronous generator (SG) is motivated and developed. We call the inverters that are operated in this way synchronverters. Using synchronverters, the well-established theory/algorithms used to control SGs can still be used in power systems where a significant proportion of the generating capacity is inverter-based. We describe the dynamics, implementation, and operation of synchronverters. The real and reactive power delivered by synchronverters connected in parallel and operated as generators can be automatically shared using the well-known frequency- and voltage-drooping mechanisms. Synchronverters can be easily operated also in island mode, and hence, they provide an ideal solution for microgrids or smart grids. Both simulation and experimental results are given to verify the idea.
采用势函数法的微电网无功控制策略
[J].由于受到微电网线路阻抗特性等因素的影响,传统的下垂控制存在无功出力难以按照下垂增益分配的问题。分析分布式电源无功出力与空载输出电压之间的关系,并在此基础上提出基于二级控制的微电网无功控制策略。该方案利用无功出力分配关系和空载输出电压的偏离程度构造势函数。微电网中央控制器根据势函数对各分布式电源的空载输出电压进行集中调整,达到改善无功出力分配的目的。仿真结果表明该方案具有良好的动态响应特性和稳态性能。此外,用正则环流无功概念来考察不同负荷水平对分布式电源无功出力分配的影响,进一步验证了所提方案的有效性。
Reactive power control strategy of microgird using potential function method
[J].由于受到微电网线路阻抗特性等因素的影响,传统的下垂控制存在无功出力难以按照下垂增益分配的问题。分析分布式电源无功出力与空载输出电压之间的关系,并在此基础上提出基于二级控制的微电网无功控制策略。该方案利用无功出力分配关系和空载输出电压的偏离程度构造势函数。微电网中央控制器根据势函数对各分布式电源的空载输出电压进行集中调整,达到改善无功出力分配的目的。仿真结果表明该方案具有良好的动态响应特性和稳态性能。此外,用正则环流无功概念来考察不同负荷水平对分布式电源无功出力分配的影响,进一步验证了所提方案的有效性。
基于相对增益分析的目标函数对角化微网功率解耦控制方法
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.13.004
URL
[本文引用: 1]

微网技术可有效整合不同类型新能源及可再生能源分布式发电的优势, 为新能源及可再生能源分布式并网发电的规模化应用提供有效可行的技术途径. 微网多样的运行方式与高质量的电力服务, 离不开灵活与稳定的控制系统, 而对微电源输出有功、无功的独立控制问题亟待研究. 针对微网线路参数特点引起的有功无功耦合问题, 提出了基于相对增益分析的目标函数对角化微网功率解耦控制方法, 将相对增益分析方法应用于低压微网线路功率模型的配对选择, 量化控制通道耦合度, 应用目标函数对角化的解耦方法, 最终实现微网线路有功功率和无功功率的独立控制. 仿真实验表明, 提出的解耦方法解决了微网线路功率耦合问题, 可实现微网系统有功、无功功率的独立灵活调节.
Objective function diagonalization decoupling control of microgrid power based on relative gain analysis
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.13.004
URL
[本文引用: 1]

微网技术可有效整合不同类型新能源及可再生能源分布式发电的优势, 为新能源及可再生能源分布式并网发电的规模化应用提供有效可行的技术途径. 微网多样的运行方式与高质量的电力服务, 离不开灵活与稳定的控制系统, 而对微电源输出有功、无功的独立控制问题亟待研究. 针对微网线路参数特点引起的有功无功耦合问题, 提出了基于相对增益分析的目标函数对角化微网功率解耦控制方法, 将相对增益分析方法应用于低压微网线路功率模型的配对选择, 量化控制通道耦合度, 应用目标函数对角化的解耦方法, 最终实现微网线路有功功率和无功功率的独立控制. 仿真实验表明, 提出的解耦方法解决了微网线路功率耦合问题, 可实现微网系统有功、无功功率的独立灵活调节.
改进型微源下垂控制策略研究
[J].The conventional microsource wireless droop control base on “power-voltage-current” close loop is widely used. The power sharing performance of this method is significantly affected by the resistive line impedance. This paper analyzes the effectiveness of two existing solutions: the adjustment method by choosing proper control parameters has limited regulating range, which means a poor performance; the virtual impedance control method has a wide range. But it has the problem of voltage sag, this paper provides an improved method with no Q-V power close loop. This method simulates the virtual impedance as the virtual synchronous generator inductance; uses the virtual impedance voltage to realize the microsource Q-V voltage droop characteristic, which can save the microsource voltage sag amplitude. Finally, simulation results and experimental results on the parallel inverter are provided to prove the performance of this new control method.
Research on improved microsource droop control method
[J].The conventional microsource wireless droop control base on “power-voltage-current” close loop is widely used. The power sharing performance of this method is significantly affected by the resistive line impedance. This paper analyzes the effectiveness of two existing solutions: the adjustment method by choosing proper control parameters has limited regulating range, which means a poor performance; the virtual impedance control method has a wide range. But it has the problem of voltage sag, this paper provides an improved method with no Q-V power close loop. This method simulates the virtual impedance as the virtual synchronous generator inductance; uses the virtual impedance voltage to realize the microsource Q-V voltage droop characteristic, which can save the microsource voltage sag amplitude. Finally, simulation results and experimental results on the parallel inverter are provided to prove the performance of this new control method.
自适应调节下垂系数的微电网控制策略
[J].
DOI:10.7500/AEPS201203084
URL
[本文引用: 1]

For conventional droop control,it is difficult to keep rated frequency or voltage amplitude within small deviations in island operation mode when the load changes,and it is also difficult to keep constant power output in the grid-connected operation mode when the frequency or voltage amplitude of the grid fluctuates.To address these problems,a droop controller with adaptive drooping coefficient adjustment is designed to remove static deviations in frequency and maintain small deviations in voltage amplitude in island mode and to maintain constant power output in grid-connected mode.Moreover,a multiple master-slave control strategy is proposed based on the droop controller to overcome the shortcomings of the master-slave microgrid system control and the multiple master microgrid system control based on V/f.MATLAB/Simulink simulation shows that the proposed droop controller and multiple master-slave control strategy are feasible and effective.
A microgrid control strategy based on adaptive drooping coefficient adjustment
[J].
DOI:10.7500/AEPS201203084
URL
[本文引用: 1]

For conventional droop control,it is difficult to keep rated frequency or voltage amplitude within small deviations in island operation mode when the load changes,and it is also difficult to keep constant power output in the grid-connected operation mode when the frequency or voltage amplitude of the grid fluctuates.To address these problems,a droop controller with adaptive drooping coefficient adjustment is designed to remove static deviations in frequency and maintain small deviations in voltage amplitude in island mode and to maintain constant power output in grid-connected mode.Moreover,a multiple master-slave control strategy is proposed based on the droop controller to overcome the shortcomings of the master-slave microgrid system control and the multiple master microgrid system control based on V/f.MATLAB/Simulink simulation shows that the proposed droop controller and multiple master-slave control strategy are feasible and effective.
Power system stabilization using virtual synchronous generator with alternating moment of inertia
[J].
DOI:10.1109/JBHI.2019.2954003
URL
PMID:31751255
[本文引用: 1]

Cranial base procedures involve manipulation of small, delicate and complex structures in the fields of otology, rhinology, neurosurgery and maxillofacial surgery. Critical nerves and blood vessels are in close proximity of these structures. Augmented reality is an emerging technology that can revolutionize the cranial base procedures by providing supplementary anatomical and navigational information unified on a single display. However, the awareness and acceptance of possibilities of augmented reality systems in cranial base domain is fairly low. This article aims at evaluating the usefulness of augmented reality systems in cranial base surgeries and highlights the challenges that current technology faces and their potential solutions. A technical perspective about different strategies employed in development of an augmented realty system is also presented. The current trend suggests an increase in interest towards augmented reality systems that may lead to safer and cost-effective procedures. However, several issues need to be addressed before it can be widely integrated into routine practice.
Oscillation damping of a distributed generator using a virtual synchronous generator
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2013.2281359
URL
[本文引用: 1]

These days, distributed generators (DGs), such as photovoltaic, wind turbine, and gas cogeneration systems have attracted more attention than in the past. DGs are often connected to a grid by power inverters. The inverters used in DGs are generally controlled by a phase-locked loop (PLL) in order to be synchronized with the grid. In a stability point of view, the power system will be significantly affected if the capacity of inverter-based DGs becomes larger and larger. The concept of the virtual synchronous generator (VSG), which is used to control inverters to behave like a real synchronous generator, can be considered as a solution. The VSG can produce virtual inertia from energy storage during a short operation time, and the active power can be produced by a VSG similar to a synchronous generator. In this paper, an oscillation damping approach is developed for a DG using the VSG. The method is confirmed analytically, and verified through computer simulations. Finally, some laboratory experiments are conducted using 10-kW inverters and a transmission-line simulator.
Mohamed A R I. Integrating VSCs to weak grids by nonlinear power damping controller with self-synchronization capability
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPWRS.2013.2280659
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper presents a new control topology to enable effective integration of voltage source converters (VSCs) in weak grids. The controller has two main parts. The first part is a linear power-damping and synchronizing controller which automatically synchronizes a VSC to a grid by providing damping and synchronizing power components, and enables effective full power injection even under very weak grid conditions. The controller adopts cascaded angle, frequency and power loops for frequency and angle regulation. The controller emulates the dynamic performance of synchronous machines, which eases grid integration and provides a virtual inertia control framework for VSCs to damp power and frequency oscillations. Although the linear controller offers stable and smooth operation in many cases, it cannot ensure system stability in weak grids, where sudden large disturbances rapidly drift system dynamics to the nonlinear region. To overcome this difficulty, a supplementary nonlinear controller is developed to assist the linear controller and enhance system performance under large-signal nonlinear disturbances, such as self-synchronization, disturbances in grid frequency and angle, high power injection in very weak grids and fault-ride-through conditions.
A power decoupling control strategy for droop controlled inverters and virtual synchronous generators
虚拟同步发电机的功率动态耦合机理及同步频率谐振抑制策略
[J].
Power dynamic coupling mechanism and resonance suppression of synchronous frequency for virtual synchronous generators
[J].
Power system dynamics. stability and control
[M].
具有同步发电机特性的微电网逆变器控制
[J].With the help of energy storage, synchronous generator model used in conventional power system being applied in renewable energy generation is called virtual synchronous generator (VSG) and presented in this paper. Through designing prime motor controller and excitation controller , renewable energy station with VSG can obtain the well-known frequency and voltage drooping mechanisms, and mimics a characteristic of system dynamic performance influenced by rotor inertia. It can solve the problems of low output impedance and low damp on conventional power converter, and improve the stability of renewable power generation system. The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed VSG algorithm is suitable to micro grid.(The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed VSG can simulate the characteristics of real synchronous generator.)
Control strategy of micro grid converters with synchronous generator characteristic
[J].With the help of energy storage, synchronous generator model used in conventional power system being applied in renewable energy generation is called virtual synchronous generator (VSG) and presented in this paper. Through designing prime motor controller and excitation controller , renewable energy station with VSG can obtain the well-known frequency and voltage drooping mechanisms, and mimics a characteristic of system dynamic performance influenced by rotor inertia. It can solve the problems of low output impedance and low damp on conventional power converter, and improve the stability of renewable power generation system. The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed VSG algorithm is suitable to micro grid.(The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed VSG can simulate the characteristics of real synchronous generator.)
A study of the use of synchronverters for grid stabilization using simulations in SimPower
[D].
Almost global asymptotic stability of a constant field current synchronous machine connected to an infinite bus
[C].