1 引言
根据微电网的结构特点以及控制要求,微网逆变器控制多采用下垂控制。但传统下垂控制方法采用低通滤波器计算每个工频周期逆变器输出的有功功率和无功功率,存在响应速度慢的缺点[6,7]。同时由于各逆变器输出连接阻抗值存在差异,从而影响功率分配效果[8,9]。文献[9]针对传统下垂控制时逆变器输出电压幅值和频率的不稳定问题,提出了改进的下垂系数自调节方法,减小了微网负荷突变情况下母线电压幅值及频率的波动,但这种方法需要选择合适的控制参数才能较好地实现控制效果。文献[10]把常规高压系统的下垂特性应用到了低压微网中,但缺乏对其应用可行性分析。文献[11]通过控制参数的选取使逆变器的等效输出阻抗呈感性,实现了精确功率解耦,但这种方法参数整定比较困难。
针对传统下垂控制存在系统稳定性降低,功率分配不均等缺点,本文提出了一种基于P-U和Q-f的下垂控制策略,并依据模型预测控制原理,建立三相三线制电压型逆变器数学模型,构建三相三线制电压型逆变器的电流预测模型,并选择预测控制器优化性能指标函数。通过仿真计算对所提出设计方法的正确性和有效性进行了验证。
2 下垂控制策略
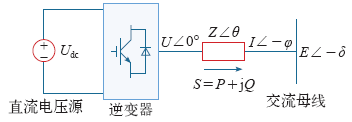
图1
图1
微电源到交流母线的功率传输结构图
Fig.1
Structure diagram on power transmission from micro-source to AC bus
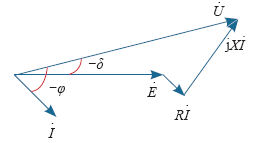
图2
图2
微电源到交流母线的功率传输相量图
Fig.2
Phase diagram on power transmission from micro-source to AC bus
逆变器输出的复功率表达式为
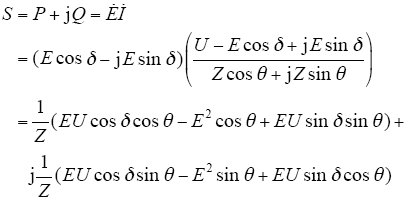
对于低压输电线路下的微网,线路参数RX,电感X可以忽略不计,Z = R,θ = 0°,假设功率角δ很小,sin δ ≈ δ,cos δ ≈ 1,则功率为
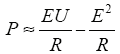
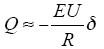
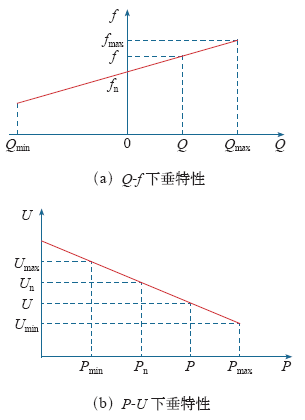
可以得出,低压输电系统有功功率的传输主要决定于电压幅值U,无功功率的传输决定于δ。而微网一般连接在低压配电网侧,此时的下垂特性如图3所示。
图3
基于P-U和Q-f控制的下垂特性,微电源输出电压的幅值和频率为
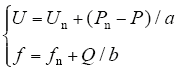
式中,a为有功功率的下垂系数;b为无功功率的下垂系数,其中
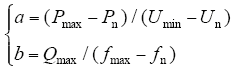
式中,Pmax为微电源在电压下降时允许输出最大功率;Pn为额定有功输出功率;Un为输出额定功率时电压;Umin为电压幅值最小允许值;fn为电网额定频率;fmax为运行频率最大允许值;Qmax为最大允许频率值时的无功功率。
3 模型预测控制器设计
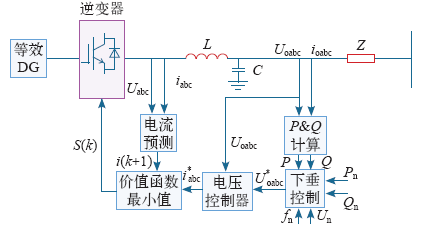
基于下垂特性的模型预测控制原理如图4所示,功率控制器采用下垂控制,并通过电压控制器得出电流参考值。在电流控制器中,假设某一时刻控制逆变器的变量S(k)存在n种可能,且n有限,根据电流预测控制算法,得到下一个采样周期电流的n种预测结果。电流预测的n种结果分别与电流参考变量进行价值函数运算得到n个不同的价值函数值,在下一个采样周期采用使价值函数最小的控制变量值。电流控制器中应用预测控制,使电流参数快速、准确地跟随电流参考值,有效减小电压、频率波动。
图4
图4中,C、L分别为三相滤波电路的电容、电感,Uabc为三相逆变器PWM模块输出电压瞬时值,iabc为三相滤波电感电流瞬时值,Uoabc为三相逆变器输出负载电压瞬时值,ioabc为三相逆变器输出负载电流瞬时值,U*oabc为三相逆变器输出负载电压参考值,i*abc为三相滤波电感电流参考值。
3.1 逆变器数学模型
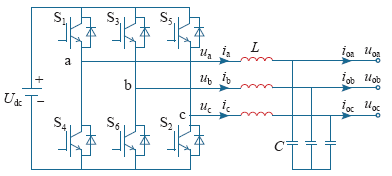
三相三线制电压型逆变器结构如图5所示。三相逆变器通过三相滤波电路向三相负载供电。
图5
图5
三相三线制电压型逆变器结构
Fig.5
Three-phase three-wire system voltage inverter structure
图中,uoa、uob、uoc为三相逆变器输出电压瞬时值,ioa、iob、ioc为三相逆变器输出负载电流瞬时值,ia、ib、ic为三相滤波电感电流瞬时值,ua、ub、uc为三相逆变器PWM模块输出电压瞬时值,S1〜S6为逆变器中6个IGBT单元。
由图5可得三相三线制电压型逆变器交流电压电流方程
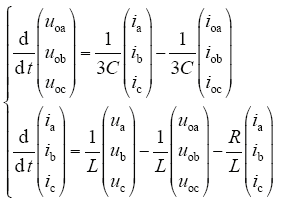
式中,R为三相滤波电路电感的串联等效电阻。
选取状态变量X = (uoauobuociaibic)T,输入量U* = (uaubuc)T及扰动量Us = (ioaiobioc)T,由式(6)定义三相逆变器在abc旋转坐标系的状态方程
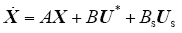
其中
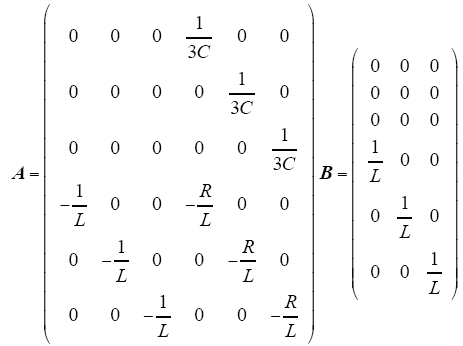
选取输出量为Y = (iaibic)T,则
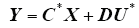
式中,C* = [O3E3]3×6;O3为3维零阵;E3为3维单位阵;D为3维零阵。
设定控制信号si(i = 1,…,n)为逆变器的开关驱动信号,且si的二值逻辑关系为

则三相逆变器PWM模块输出电压瞬时值与控制信号si的关系式为
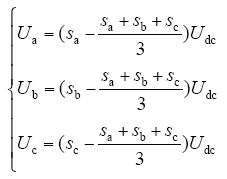
当输入量选为U′ = (sasbsc)T时,三相逆变器在abc旋转坐标系的状态方程变为
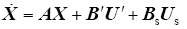
其中
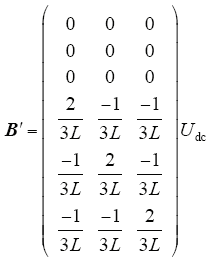
3.2 电流预测模型
假定采样周期Ts远小于电网电压周期,微分di/dt可以近似为
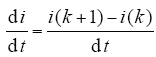
在模型预测中,将式(11)离散化可得
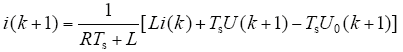
式(12)构成了逆变器的电流预测模型。由于电压U0(k + 1)未知,考虑到采样周期Ts远小于电网电压周期,可以近似地认为其等于在线估算值
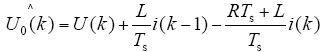
将式(13)代入式(12)得出电流预测模型
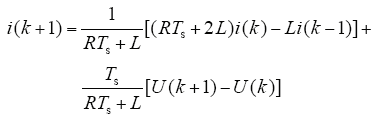
已知电压Uabc与控制信号si的关系,根据控制信号有限的不同组合,可以得到有限的电流预测结果,从而减少计算量。
3.3 优化性能指标函数
由式(14)的电流预测模型可知,对于控制信号的不同组合,可得到不同的电流预测结果。为达到逆变器输出电流对参考电流准确跟踪的控制目的,定义一个价值函数g,使控制性能最优。
为使电流输出误差最小,选择价值函数为
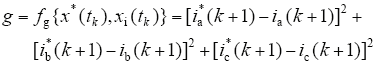
在某一时刻,逆变器的n个控制变量值导致n个不同的价值函数值gi,使价值函数gi最小的控制变量值将在下一个采样周期被应用。此优化过程是在线反复进行,其优化目标随着时间推移变化,仅基于该采样时刻的在线局部优化控制,而不是采用不变的全局优化控制,从而提高了系统的鲁棒性。
4 仿真分析
4.1 仿真模型及参数
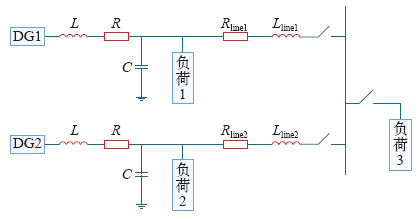
在Matlab中建立如图6所示的双分布式电源微网孤岛运行仿真模型。分别针对传统下垂控制和基于模型预测的下垂控制策略进行仿真实验。
图6
仿真系统中各DG额定功率为PDG1 = 30kW,PDG2 = 20kW,各负荷初始功率为Pload1 = 30kW,Qload1 = 3kvar,Pload2 = 20kW,Qload2 = 2kvar,Pload3 = 30kW,Qload3 = 3kvar。系统其他参数见下表。
表 系统参数
Tab.
| 系统参数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| 电网电压幅值U/V | 380 |
| 直流侧电压Udc/V | 800 |
| 电网频率fn/Hz | 50 |
| 线路参数(Rline/Xline)/(Ω/km) | 0.642/0.083 |
| 滤波电感L/mH | 15 |
| 滤波电容C/mF | 1.6 |
| 滤波电阻R/Ω | 0.01 |
| 下垂系数1/a | 0.002 42 |
| 下垂系数1/b | 0.000 002 |
| 仿真采样周期Ts/μs | 100 |
4.2 仿真结果及分析
对基于模型预测的下垂控制方法进行仿真,并与传统下垂控制方法进行对比和分析。
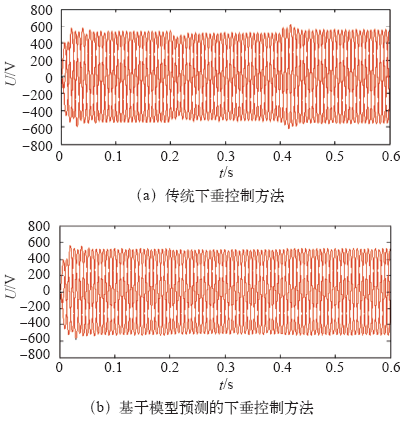
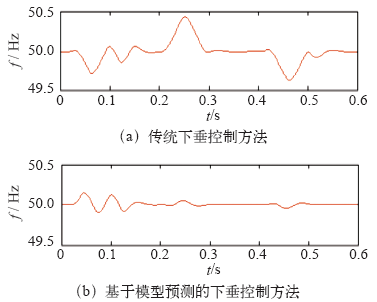
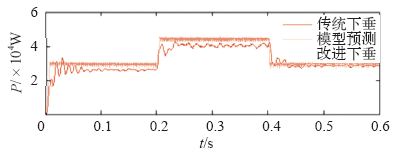
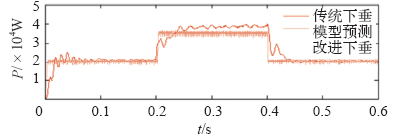
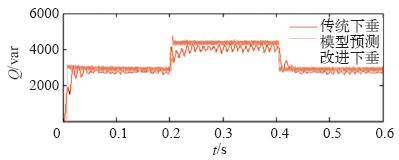
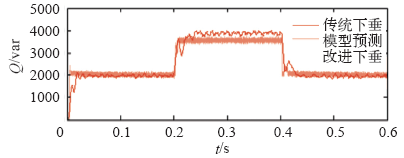
仿真过程中,设定0.2s时接入负荷3,并在0.4s时断开负荷3,恢复到初始状态。分别选取DG1输出电压、频率和DG1、DG2的有功、无功功率进行分析。
图7
图8
图9
图10
图11
图12
上述仿真结果表明,负荷功率变化,传统下垂控制方法下电压和频率发生较大波动,且分布式电源功率分配不均;本文所提出的电流预测控制下垂控制器不仅能更精确平稳地在各分布式电源之间分配负荷,同时在出现较大干扰时能较好地抑制系统电压幅值和频率的波动,保证了系统具有良好的动态特性和稳定性。
5 结论
针对逆变器采用传统下垂控制导致系统稳定性降低,功率分配不均的现象,本文提出了具有模型预测控制的下垂控制方法,并设计了电流预测控制下垂控制器。仿真结果表明:
(1)在系统出现负荷波动时,电流预测控制下垂控制方法比传统下垂控制方法能更好地抑制电压幅值和频率的波动,提高系统稳定性。
(2)相较于传统下垂控制方法,电流预测控制下垂控制方法在稳态运行时能进行更精确的功率分配,且具有跟随快速、稳定性强等优点,可更好地满足微网孤岛模式下系统控制的要求。
参考文献
Autonomous controls of micro-grid
[C].
分布式电源并网逆变器典型控制方法综述
[J].
Overview of typical control methods for grid-connected inverters of distributed generation
[J].
Improvement of stability and load sharing in an autonomous micro-grid using supplementary droop control loop
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRS.2009.2032049 URL [本文引用: 1]
Operation of a multi-agent system for micro-grid control
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRS.2005.852060 URL [本文引用: 1]
A mas architecture for micro-grid control
[C].
UPS无互联并联中基于结构控制的下垂特性控制方案
[J].
Modeling and stability analysis for parallel operation of UPS with no control interconnection basing on droop characteristic
[J].
SPWM逆变电源的无互联信号线并联控制技术
[J].
Parallel operation of sinusoid without control interconnections
[J].
Output impedance design of parallel-connected UPS inverters with wireless load-sharing control
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2005.851634 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于改进下垂法的微电网逆变器并联控制技术
[J].This paper analyzes the active and reactive power circulating current model of the paralleling inverters in typical microgrid and presents an improved adaptive droop controller to improve the performance of parallel-connected inverters. With the proposed control strategy, large fluctuations of bus voltage and system frequency caused by load variation can be avoided. It uses an adaptive integral loop gain to improve the dynamic performance of parallel systems. It also reduces unreasonable reactive power flow between the inverters in a microgrid, therefore avoids unnecessary power losses and additional equipment capacity. Simulation and experimental results confirm the validity of the proposed control technique.
Paralleling control technique of micro-grid inverters based on improved droop method
[J].This paper analyzes the active and reactive power circulating current model of the paralleling inverters in typical microgrid and presents an improved adaptive droop controller to improve the performance of parallel-connected inverters. With the proposed control strategy, large fluctuations of bus voltage and system frequency caused by load variation can be avoided. It uses an adaptive integral loop gain to improve the dynamic performance of parallel systems. It also reduces unreasonable reactive power flow between the inverters in a microgrid, therefore avoids unnecessary power losses and additional equipment capacity. Simulation and experimental results confirm the validity of the proposed control technique.
基于储能的微电网并网和孤岛运行模式平滑切换综合控制策略
[J].Microgrid is an effective approach to solve the grid-connection of distributed generations, and the hybrid microgrid composed of wind farm, photovoltaic generation and energy storage system possesses the feature that the clean energy can be fully utilized and its operation is reliable. The smooth switching between grid-connected operation mode and islanded operation mode of microgrid is an important measure to ensure the secure and reliable operation of microgrid. For this reason, a synthetical control strategy integrating new type of master-slave control with peer-to-peer control is adopted to control the operation mode transition between grid-connected operation mode and islanded operation mode of microgrid. A model of microgrid composed of complementary wind farm, photovoltaic generation and energy storage system is constructed on DigSILENT/PowerFactory platform, and the feasibility of the proposed control strategy is verified by simulation results. Besides, simulation results also show that the improved control strategy can ensure power balance of microgrid before and after the switching and keep the voltage of the bus connected with microgrid and frequency of the microgrid within the allowed range.
Synthetical control strategy for smooth switching between grid-connected and islanded operation model of micro-grid based on energy storage system
[J].Microgrid is an effective approach to solve the grid-connection of distributed generations, and the hybrid microgrid composed of wind farm, photovoltaic generation and energy storage system possesses the feature that the clean energy can be fully utilized and its operation is reliable. The smooth switching between grid-connected operation mode and islanded operation mode of microgrid is an important measure to ensure the secure and reliable operation of microgrid. For this reason, a synthetical control strategy integrating new type of master-slave control with peer-to-peer control is adopted to control the operation mode transition between grid-connected operation mode and islanded operation mode of microgrid. A model of microgrid composed of complementary wind farm, photovoltaic generation and energy storage system is constructed on DigSILENT/PowerFactory platform, and the feasibility of the proposed control strategy is verified by simulation results. Besides, simulation results also show that the improved control strategy can ensure power balance of microgrid before and after the switching and keep the voltage of the bus connected with microgrid and frequency of the microgrid within the allowed range.
一种微电网多逆变器并联运行控制策略
[J].在微电网多逆变器并联系统中,由于逆变器的输出阻抗以及与公共连接点的线路阻抗存在差异,应用传统下垂控制法会导致逆变器间的环流较大及功率均分精度较低。在分析多逆变器并联系统中传统下垂控制法及逆变器输出阻抗对系统性能的影响基础上,通过引入感性虚拟阻抗,提出一种适合微网多逆变器并联的电压电流双环下垂控制策略。虚拟阻抗的引入使输出阻抗仅由滤波电感值决定,减少了逆变器输出电阻的影响;考虑线路阻抗的影响,提出一种新型改进下垂控制算法,通过对下垂系数进行修正,减弱了线路阻抗差异对并联均流的影响,提高了多逆变器并联性能。仿真与实验结果表明了该控制策略的正确性和有效性。
A control strategy for parallel operation of multi-inverters in micro-grid
[J].在微电网多逆变器并联系统中,由于逆变器的输出阻抗以及与公共连接点的线路阻抗存在差异,应用传统下垂控制法会导致逆变器间的环流较大及功率均分精度较低。在分析多逆变器并联系统中传统下垂控制法及逆变器输出阻抗对系统性能的影响基础上,通过引入感性虚拟阻抗,提出一种适合微网多逆变器并联的电压电流双环下垂控制策略。虚拟阻抗的引入使输出阻抗仅由滤波电感值决定,减少了逆变器输出电阻的影响;考虑线路阻抗的影响,提出一种新型改进下垂控制算法,通过对下垂系数进行修正,减弱了线路阻抗差异对并联均流的影响,提高了多逆变器并联性能。仿真与实验结果表明了该控制策略的正确性和有效性。
Model predictive direct torque control-part II: implementation and experimental evaluation
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2008.2007032 URL [本文引用: 1]
Model predictive control-a simple and powerful method to control power converters
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2008.2008349 URL [本文引用: 1]
一种多步预测的变流器有限控制集模型预测控制算法
[J].变流器有限控制集模型预测控制(finite control set model predictive control,FCS-MPC)算法是一种变流器优化控制算法。该算法具有动态响应快、处理系统约束灵活且无需PWM调制器和相关参数设计等优点,但仅可确保所选开关函数组合在一个控制周期内的最优,这样将使得系统控制趋于保守,而影响系统控制性能。分析传统变流器FCS-MPC算法的保守性,提出一种在一个控制周期内同时考虑最优开关函数组合及次优开关函数组合,并确保在两个控制周期内所选开关函数组合最优的多步预测的FCS-MPC算法(finite control set model predictive control with multi-step prediction,FCS-MPCMSP);进行采用该算法的两电平三相电压型逆变器在空载、带阻感性负载、带非线性负载及负载投入等工况下的仿真和实验。仿真及实验结果表明:采用该算法的三相电压型逆变器输出电压与给定电压的差值明显小于采用传统FCS-MPC算法的情况,改善了逆变器输出电压质量,从而验证了该算法的有效性及可行性。
A model predictive control scheme of multi-step prediction finite control set for conveners
[J].变流器有限控制集模型预测控制(finite control set model predictive control,FCS-MPC)算法是一种变流器优化控制算法。该算法具有动态响应快、处理系统约束灵活且无需PWM调制器和相关参数设计等优点,但仅可确保所选开关函数组合在一个控制周期内的最优,这样将使得系统控制趋于保守,而影响系统控制性能。分析传统变流器FCS-MPC算法的保守性,提出一种在一个控制周期内同时考虑最优开关函数组合及次优开关函数组合,并确保在两个控制周期内所选开关函数组合最优的多步预测的FCS-MPC算法(finite control set model predictive control with multi-step prediction,FCS-MPCMSP);进行采用该算法的两电平三相电压型逆变器在空载、带阻感性负载、带非线性负载及负载投入等工况下的仿真和实验。仿真及实验结果表明:采用该算法的三相电压型逆变器输出电压与给定电压的差值明显小于采用传统FCS-MPC算法的情况,改善了逆变器输出电压质量,从而验证了该算法的有效性及可行性。
Model predictive control of an inverter with output LC filter for UPS applications
[J].