1 引言
微电网系统由分布式电源、储能系统、控制器、保护装置和负荷组成,可并网运行和孤岛运行[1 -2 ] 。当微电网系统孤岛运行时,单一的微电源无法满足实际负荷需求,为了提高系统的稳定性以及增大微电网系统的容量,微电网系统不再是单一的微电源系统,而是由多台逆变器并联运行系统。多逆变器并联运行时,由于各台逆变器距离负荷端的线路长度不一致,导致系统出现有功或者无功不精确分配,从而出现功率环流,严重影响并联逆变器的稳定运行。针对这一问题,并联逆变器下垂控制及并联逆变器虚拟同步机(Virtual synchronous generators,VSG)控制策略受到人们的广泛关注。
研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究。文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配。文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大。文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法。文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量。文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定。文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分。文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分。文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分。文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分。文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大。文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配。文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配。
在以上文献对微电网并联逆变器控制策略研究的基础上,针对并联VSG各自距离负荷线路长短不一致,导致功率环流出现,无法实现功率精确分配的问题,本文提出一种基于自适应虚拟阻抗并联VSG控制策略。首先,在分析两并联VSG无功环流产生的基础上,在VSG输出端口电压引入一个补偿电压来弥补线路阻抗不一致产生的那部分压降,利用补偿电压设计自适应虚拟阻抗模块。其次,对并联VSG控制系统进行小参数整定设计。最后,建立基于自适应虚拟阻抗的并联VSG控制系统仿真模型。仿真结果验证了该方法的可行性。
2 并联VSG基本结构及环流分析
2.1 并联VSG基本结构
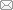
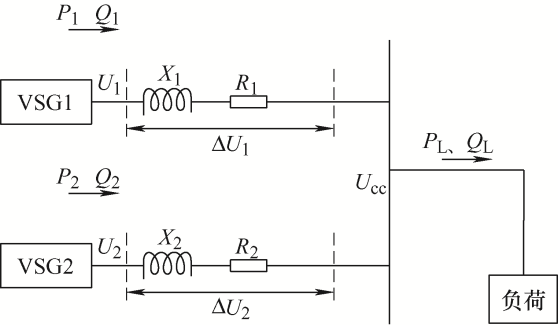
两台并联VSG系统其拓扑结构如图1 所示,由VSG1、VSG2、线路、负载等组成。图1 中,R 、L 、C 分别为滤波器的电阻、电感和电容;V dc 为直流电压。
图1
2.2 功率环流分析
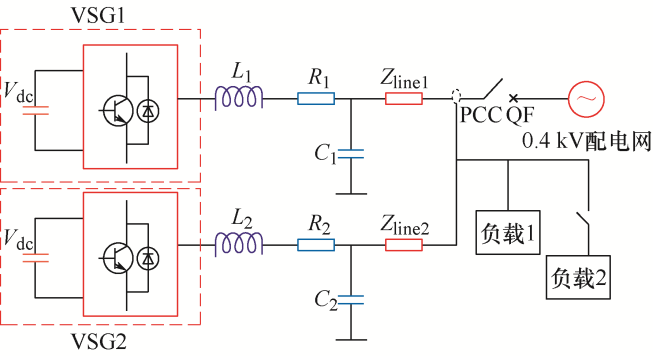
以两台并联VSG之间进行电流环流分析,其等效电路如图2 所示。图2 中,E 1 、E 2 为VSG1和VSG2电源等效电压;δ 1 、δ 2 为VSG1和VSG2系统功角;P 1 、Q 1 为VSG1输出有功和无功功率;P 2 和Q 2 为VSG2输出有功和无功功率;Z 1 、Z 2 为线路1和线路2阻抗;U ˙ 1 U ˙ 2 Z L 为负载阻抗。
图2
(1) I ˙ 1 = E ˙ 1 − U ˙ 1 Z 1 = E 1 ∠ δ 1 − U ∠ 0 ° R 1 + j ω 1 = E 1 cos δ 1 − U + j E 1 sin δ 1 R 1 + j ω L 1
(2) I ˙ 2 = E ˙ 2 − U ˙ 2 Z 2 = E 2 ∠ δ 2 − U ∠ 0 ° R 2 + j ω 2 = E 2 cos δ 2 − U + j E 2 sin δ 2 R 2 + j ω L 2
(3) I ˙ h = I ˙ 1 − I ˙ 2 2 = 1 2 E 1 cos δ 1 − U + j E 1 sin δ 1 R 1 + j ω L 1 - E 2 cos δ 2 − U + j E 2 sin δ 2 R 2 + j ω L 2
当Z 1 =Z 2 ,且线路阻抗整体呈感性,由于VSG的功率角很小,因此sin δ ≈ δ , cos δ ≈ 1
(4) I h = E 1 − E 2 2 X + j E 1 δ 1 − E 2 δ 2 2 X
两并联VSG之间的环流分为两部分,有功环流和无功环流分别为
(5) I hp = E 1 − E 2 2 X I hq = j E 1 δ 1 − E 2 δ 2 X
当两条线路阻抗不同时,它会导致每个VSG产生的励磁电动势的振幅和相位角之间存在差异,进而导致环流出现。
3 自适应虚拟阻抗控制器设计
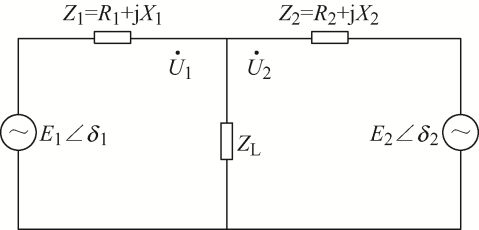
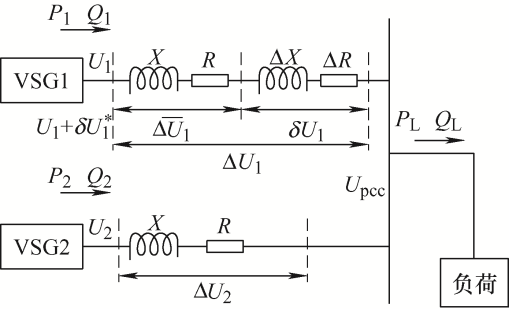
针对线路阻抗不一致导致无功环流出现的问题,通过设计自适应虚拟阻抗来抑制无功环流实现无功功率精确分配。以两台VSG简化等效电路模型来设计自适应虚拟阻抗模块,如图3 所示。图3 中,U 1 、U 2 分别为VSG1和VSG2系统端电压;X 1 、R 1 为线路1的阻抗;X 2 、R 2 为线路2阻抗;P 1 、Q 1 为VSG1系统输出有功和无功功率;P 2 、Q 2 为VSG2系统输出有功和无功功率;ΔU 1 、ΔU 2 为线路1和线路2电压损耗。
图3
(6) Δ U 1 ≈ X 1 Q 1 + R 1 P 1 U 1 Δ U 2 ≈ X 2 Q 2 + R 2 P 2 U 2
(7) Δ X = X 1 − X Δ R = R 1 − R
图4
(8) Δ U 1 ≈ X + Δ X Q 1 + ( R + Δ R ) P 1 U 1 = X Q 1 + R P 1 U 1 + Δ X Q 1 + Δ R P 1 U 1 = Δ U 1 ¯ + δ U 1
式中,δ U 1
(9) U 1 = U pcc + Δ U 1 ¯ + δ U 1 U 2 = U pcc + Δ U 2
通过修正线路1的电压参考值来补偿电压降落,由式(9)可得
(10) U 1 + δ U 1 ∗ = U pcc + Δ U 1 ¯ + δ U 1
(11) δ U 1 * = δ U 1
(12) X v Q 1 + R v P 1 U pcc = Δ X Q 1 + Δ R P 1 U pcc
设实际线路阻抗比为α R v 和虚拟电感值L v 为
(13) R v = Δ X Q 1 + Δ R P 1 α Q 1 + P 1 = Δ X + Δ R K r α + K r K r = P 1 Q 1 L v = α R v
(14) Q 1 Q 2 = Q ref 1 Q ref 2 = n
(15) L v = L v0 + ∫ Q 1 − n Q 2 d t
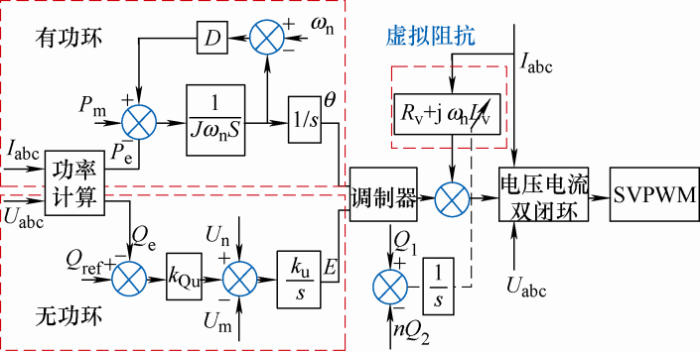
(16) J d ω d t = P m − P e ω − D ω − ω n ω = d δ d t P m = P ref + k pf ω − ω n E = U n + k Qu Q ref − Q e − U m k u s
式中,ω n ω k pf 、k Qu 分别为有功和无功下垂系数;P ref 、Q ref 为有功和无功参考值;P e 、Q e 为电磁功率;D 为阻尼系数;J 为旋转惯量;δ 为系统功角;k u 为积分系数;U n 为额定电压值;U m 为实际电压有效值。
由式(15)、(16)可得自适应虚拟阻抗VSG控制原理框图如图5 所示。
图5
4 并联VSG系统参数整定设计
将S 1 ∶S 2 =n 设为两台VSG的容量比,则两台VSG输出有功和无功也按照该比例分配,即
(17) P 1 ∶ P 2 = n Q 1 ∶ Q 2 = n
(18) δ s = P ref − P e ω s J s + D + ω s
有功实现均分时,两VSG相角一致,同时由终值定理可得
(19) P ref − P e J 1 s + D 1 = n P ref − P e J 2 s + D 2
(20) J 1 J 2 = D 1 D 2 = n
(21) P ref1 + 1 k pf 1 f − f 1 P ref2 + 1 k pf2 f − f 2 = P 1 P 2 = n
(22) k pf 1 k pf 2 = n
(23) k Qu 1 k Qu 2 = 1 n
(24) P 1 = U pcc R 1 E 1 − U pcc X 1 P 2 = U pcc R 2 E 2 − U pcc X 2
(25) R 1 R 2 = X 1 X 2 = 1 n
由式(25)、(27)、(28)、(30)可得并联VSG参数匹配原则为
(26) J 1 J 2 = D 1 D 2 = k pf1 k pf 2 = k Qu1 k Qu2 = R 2 R 1 = X 2 X 1 = n
由LCL电路可知,对于电容的参数整定设计,可根据电容的无功功率来设计。理论上为逆变器单相额定有功的5%左右,但实际工程上取10%~20%。
(27) C ≤ 10 % P ω U m 2 = 10 % P 2 π f U m 2 = 20 μ F
5 仿真分析
根据图1 建立自适应虚拟阻抗并联VSG控制系统仿真模型,并对其进行仿真测试。仿真参数如表1 所示。
5.1 并联VSG孤岛运行情况
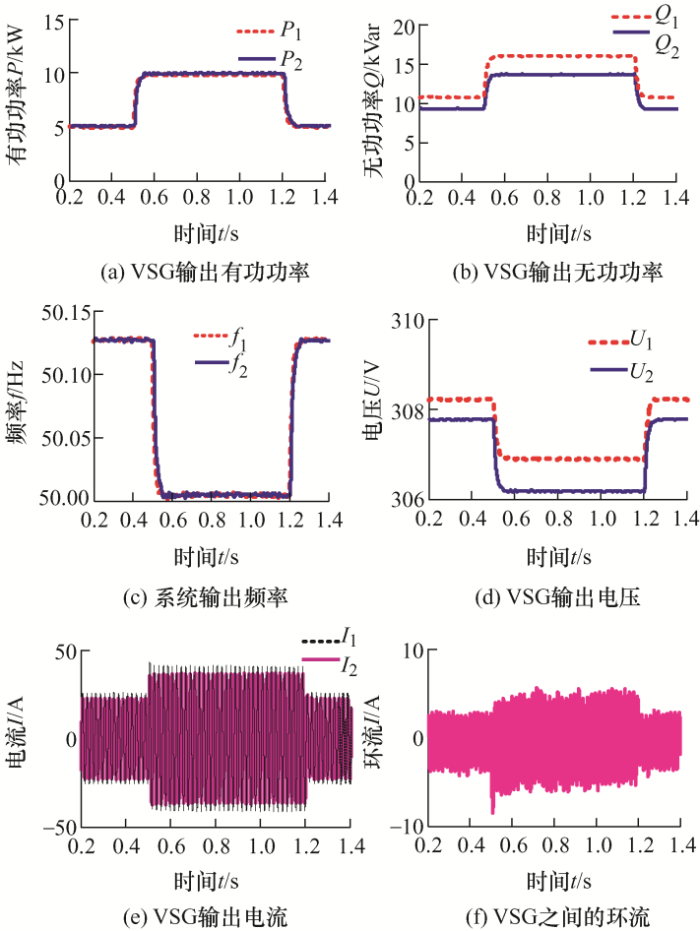
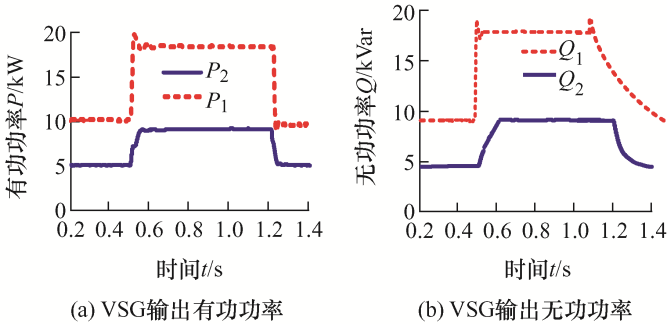
(1) 未加虚拟阻抗运行情况。设置负荷1有功功率P 1 =10 kW,无功功率Q 1 = 20 kVar,负荷2有功功率P 2 =10 kW,无功功率Q 2 =10 kVar,t =[0.5,1.2] s对负荷2进行投切,仿真时间为1.4 s。仿真波形如图6 所示。
图6
由图6a 和6b 可知,在线路馈线阻抗不一致的情况下,两台VSG并联逆变器有功能够实现均分,频率也能够保持一致,且频率波动能够满足误差需要。由图6c~6e 可知,两台并联VSG之间出现了无功不均分的现象,由Q -U 关系可知,必然导致两并联VSG输出端口电压不一致以及电流不一致,进而出现较大的无功环流。
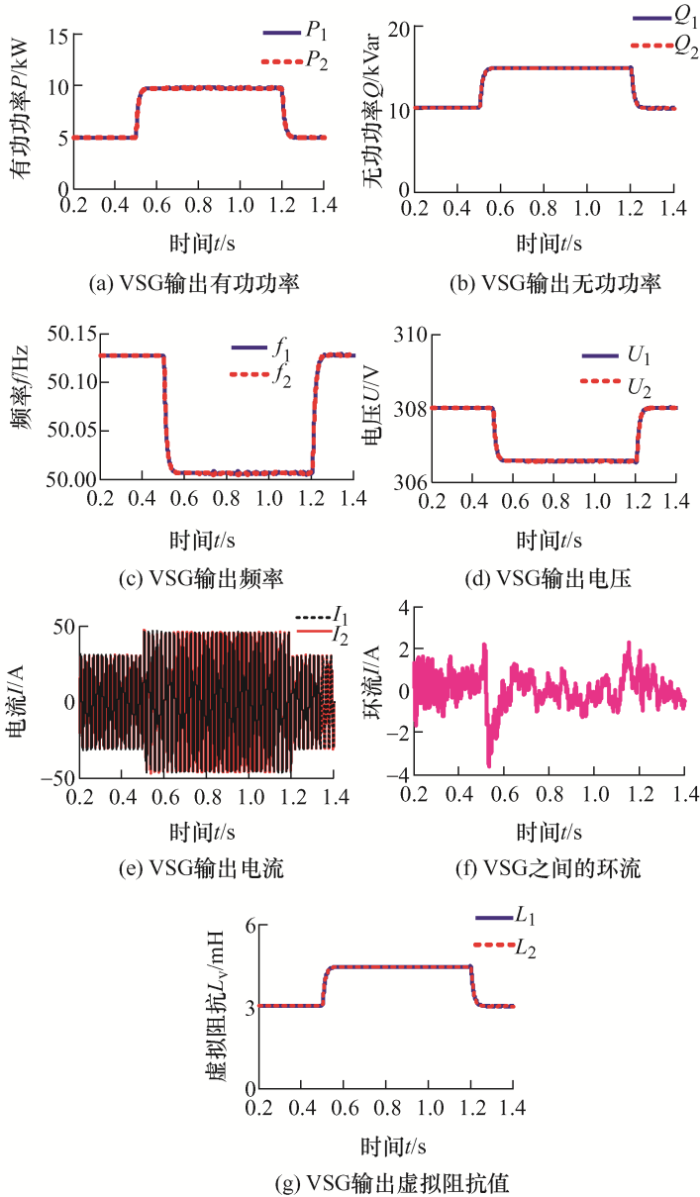
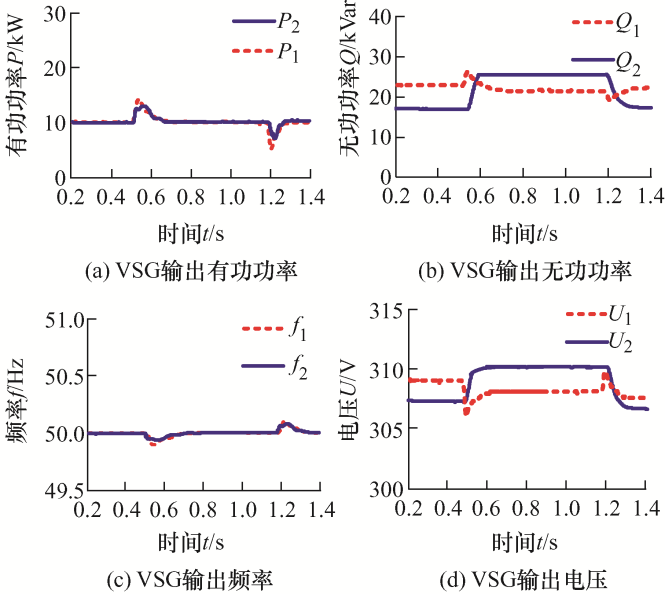
(2) 加入虚拟阻抗运行情况。仿真设置同未加入阻抗时一致,系统容量VSG1和VSG2为1∶1,仿真运行结果如图7 所示。
图7
由图7 可知,引入自适应虚拟阻抗后,在线路馈线阻抗不一致的情况下,两并联VSG能够实现无功和有功的均分,输出端口的电压也能保持一致,形成较小的无功环流。
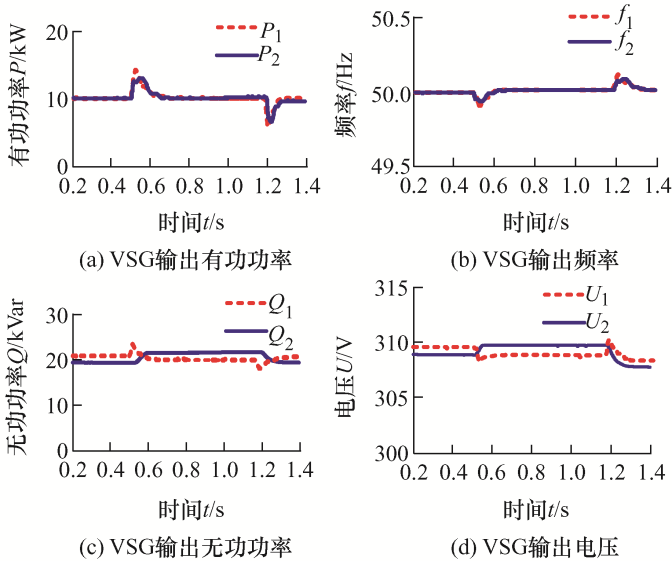
(3) VSG1和VSG2系统容量为2∶1时,设置负荷1有功功率P 1 =15 kW,无功功率Q 1 = 12 kVar,负荷2有功功率P 2 =12 kW,无功功率Q 2 =15 kVar。t =[0.5,1.2] s对负荷2进行投切,仿真时间为1.4 s。仿真波形如图8 所示。
图8
由图8 可知,系统有功和无功按照给定参考比值2∶1的方式承担系统负荷的分配。
5.2 并联VSG并网运行情况
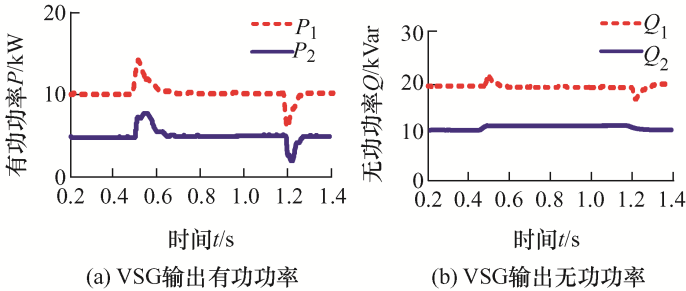
(1) 未引入虚拟阻抗。设置VSG给定有功参考值P 1ref =10 kW,P 2ref =10 kW。无功功率Q 1 =12 kVar,无功功率Q 2 =15 kVar。负荷2在t =[0.5,1.2] s时刻进行投切。仿真波形如图9 所示。
图9
由图9 可知,并联VSG并网运行时,VSG1和VSG2都按照给定参考输出,有功和频率输出完全一致。由于线路阻抗不一致,系统输出无功和电压与给定参考值之间有较大的误差,无法实现无功均分。
(2) 引入虚拟阻抗。VSG1和VSG2额定容量为1∶1时,仿真条件设置同并网运行时未引入虚拟阻抗运行情况,仿真时间为1.4 s,仿真波形如图10 所示。
图10
由图10 可知,相比于未引入虚拟阻抗,两VSG的无功和电压与参考值之间的偏差较小,基本能够跟随给定。
(3) 当VSG1和VSG2的额定容量为2∶1时,仿真设置同上,系统仿真波形如图11 所示。
图11
由图11 可知,并联VSG并网运行时,系统按给定容量之比输出有功和无功功率。
6 结论
为了使并联VSG逆变器之间的环流得到抑制及实现无功功率的精确分配,提出自适应虚拟阻抗的方法。建立两台并联VSG自适应虚拟阻抗控制系统进行仿真测试,分别对并联VSG孤岛运行(未加入虚拟阻抗和加入虚拟阻抗)、并联VSG并网运行(未加入虚拟阻抗和加入虚拟阻抗)情况进行仿真测试。仿真测试得出结论如下所述。
(1) 并联VSG孤岛运行时,引入自适应虚拟抗并联VSG系统相比于未引入自适应虚拟阻抗并联VSG系统,虚拟阻抗能够自适应变化抑制无功环流,系统能够按照给定指令(1∶1和2∶1)承担系统负荷的精确分配。
(2) 并联VSG并网运行时,自适应虚拟抗并联VSG系统相比于未引入自适应虚拟阻抗并联VSG系统,VSG逆变器输出功率能够按照给定指令(1∶1和2∶1)实现功率的精确分配。
参考文献
View Option
[1]
张建华 , 黄伟 . 微电网运行控制与保护技术 [M]. 北京 : 中国电力出版社 , 2012 .
[本文引用: 1]
ZHANG Jianhua HUANG Wei Micro-grid operation control and protection technology [M]. Beijing : China Electric Power Press , 2012 .
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
袁健 , 杨伟 . 独立微网中多虚拟同步机功率精确分配控制策略
[J]. 电力系统保护与控制 , 2019 , 47 (4 ):35 -42 .
[本文引用: 1]
YUAN Jian YANG Wei Precise power allocation control strategy of multi-virtual synchronous machines in independent microgrid
[J]. Power System Protection and Control , 2019 , 47 (4 ):35 -42 .
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
王晓寰 , 王书光 , 刘聪哲 , 等 . 下垂控制并联系统中功率精确分配的控制策略
[J]. 电力电子技术 , 2019 , 53 (8 ):4 -7 .
[本文引用: 1]
WANG Xiaohuan WANG Shuguang LIU Congzhe et al. Control strategy of accurate power distribution in droop control parallel system
[J]. Power Electronics Technology , 2019 , 53 (8 ):4 -7 .
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
李红萍 , 杨洪耕 , 曾巧燕 , 等 . 孤岛型微电网中改进下垂控制策略
[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报 , 2017 , 29 (4 ):49 -54 .
[本文引用: 1]
LI Hongping YANG Honggeng ZENG Qiaoyan et al. Improved droop control strategy in isolated microgrid
[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA , 2017 , 29 (4 ):49 -54 .
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
贾东强 , 及洪泉 , 于希娟 , 等 . 基于改进下垂控制的多微网并联运行控制策略研
[J]. 电力电容器与无功补偿 , 2021 , 42 (1 ):199 -204 .
[本文引用: 1]
JIA Dongqiang JI Hongquan YU Xijuan et al. Research on multi microgrid parallel operation control strategy based on improved droop control
[J]. Power Capacitor and Reactive Power Compensation , 2021 , 42 (1 ):199 -204 .
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
张泽正 , 文传博 . 虚拟复阻抗下的低压并联逆变器改进下垂控制策略
[J]. 智慧电力 , 2020 , 48 (10 ):70 -77 .
[本文引用: 1]
ZHANG Zezheng WEN Chuanbo Improved droop control strategy of low voltage parallel inverter under virtual complex impedance
[J]. Smart Power , 2020 , 48 (10 ):70 -77 .
[本文引用: 1]
[7]
王施珂 , 刘增 , 刘进军 . 基于端口特性的并联下垂逆变器系统的小信号建模与稳定性分析
[J]. 电源学报 , 2020 , 18 (2 ):83 -94 .
DOI:10.13234/j.issn.2095-2805.2020.2.83
[本文引用: 1]
孤岛交流微电网中,并联下垂逆变器系统被广泛应用。基于有功功率-基波频率的下垂控制原理,逆变器之间的动态相互作用不仅体现在母线电压和输出电流之间,也体现在变化的系统基波频率上,从而引发小信号稳定性问题。建立了下垂逆变器的端口特性小信号模型,除传统的输出阻抗和输入导纳之外,提出一种新型端口特性以表征基波频率动态;进一步基于单个模块的端口特性,建立了多台逆变器并联系统的小信号模型;基于广义奈奎斯特稳定性判据,计算由阻抗导纳乘积与基波频率端口特性乘积之和组成的回率矩阵的特征轨迹,对并联系统的稳定性做出判断。最后,实验结果证明了所提小信号模型和稳定性判据的有效性。
WANG Shike LIU Zeng LIU Jinjun Small signal modeling and stability analysis of parallel droop inverter system based on port characteristics
[J]. Journal of Power Supply , 2020 , 18 (2 ):83 -94 .
DOI:10.13234/j.issn.2095-2805.2020.2.83
[本文引用: 1]
Parallel droop-controlled inverter system is widely employed in islanded AC microgrids. Since the active power-fundamental frequency droop control principle is applied, the dynamic interactions among inverters exist not only in the bus voltage and transmitted current but also in the variable system fundamental frequency, thereby causing small-signal stability issues. A small-signal model for the terminal characteristics of a droop-controlled inverter is established. Besides the conventional output impedance and input admittance, a novel set of terminal characteristics is proposed to characterize the dynamics of fundamental frequency. Furthermore, a small-signal model of parallel droop-controlled inverter system is constructed based on the terminal characteristics of individual inverters. According to the generalized Nyquist criterion(GNC), a stability prediction approach is proposed for the parallel system by calculating the characteristic loci of return ratio matrix, which is the sum of the product of impedance and admittance and that of fundamental frequency terminal characteristics. Finally, experimental results validated the effectiveness of the proposed small-signal models as well as the stability criterion.
[8]
沈超 , 帅智康 , 程慧婕 . 虚拟同步机并联电流控制型变换器系统暂态同步稳定性分析
[J]. 电力系统自动化 , 2021 , 45 (10 ):115 -123 .
[本文引用: 1]
SHEN Chao SHUAI Zhikang CHENG Huijie Transient synchronization stability analysis of virtual synchronous machine parallel current controlled converter system
[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems , 2021 , 45 (10 ):115 -123 .
[本文引用: 1]
[9]
涂春鸣 , 谢伟杰 , 肖凡 , 等 . 多虚拟同步发电机并联系统控制参数对稳定性的影响分析
[J]. 电力系统自动化 , 2020 , 44 (15 ):77 -86 .
[本文引用: 1]
TU Chunming XIE Weijie XIAO Fan et al. Analysis of influence of control parameters on stability of multi virtual synchronous generator parallel system
[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems , 2020 , 44 (15 ):77 -86 .
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
马文涛 , 王金梅 , 王永奇 . 虚拟阻抗对不同电压等级逆变器并联系统的稳定性影响分析
[J]. 中国电力 , 2021 , 54 (9 ):135 -142 ,175.
[本文引用: 1]
MA Wentao WANG Jingmei WANG Yongqi Analysis of the influence of virtual impedance on the stability of inverter parallel systems with different voltage level
[J]. Electric Power , 2021 , 54 (9 ):135 -142 ,175.
[本文引用: 1]
[11]
WANG X H QING H Y HUANG P et al. Modeling and stability analysis of parallel inverters in island microgrid
[J]. Electronics , 2020 , 9 (3 ):463 .
DOI:10.3390/electronics9030463
URL
[本文引用: 1]
The island microgrid is composed of a large number of inverters and various types of power equipment, and the interaction between inverters with different control methods may cause system instability, which will cause the power equipment to malfunction. Therefore, effective methods for analyzing the stability of the microgrid system have become particularly important. Generally, impedance modeling methods are used to analyze the stability of power electronic converter systems. In this paper, the impedance models of a PQ-controlled inverter and droop-controlled inverter are established in d-q frame. In view of the difference of output characteristics between the two control methods, the island microgrid is equivalent to a double closed-loop system. The impedance model of the parallel system is derived and the open loop transfer function of the system is extracted. Based on the generalized Nyquist criterion (GNC), the stability of parallel system working in island microgrid mode is analyzed using this proposed impedance model. The simulation and experiment results are presented to verify the analysis.
[12]
周宁博 , 叶佳卓 , 邓双喜 , 等 . 孤岛微网中VSG并联运行功率精确分配控制策略
[J]. 电工电能新技术 , 2020 , 39 (8 ):47 -55 .
DOI:10.12067/ATEEE1909027
[本文引用: 1]
孤岛微网中,使用VSG控制策略控制逆变器,可以有效增加系统惯性与阻尼,提高孤岛微网系统稳定性。多VSG并联运行时不能按下垂系数精确分配无功功率。针对此问题,本文提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略。通过分布式二次控制器获取各VSG无功功率值,根据所需无功功率大小,自适应调整VSG定子电抗值,间接控制逆变器无功出力实际值,达到无功功率精确分配的目标。此控制策略不需要线路阻抗信息,在网络通讯故障的情况下仍具有较强鲁棒性,且在实际应用中可降低对通信网络带宽需求。同时给出了并联运行VSG参数匹配方法。最后在Matlab/Simulink中搭建了三台VSG并联仿真模型,仿真结果验证了所提控制策略的有效性和可行性。
ZHOU Ningbo YE Jiazhuo DENG Shuangxi et al. Precise power distribution control strategy for VSG parallel operation in isolated island microgrid
[J]. New Electric Energy Technology , 2020 , 39 (8 ):47 -55 .
[本文引用: 1]
[13]
赵金鑫 , 苗虹 , 曾成碧 . 基于改进虚拟同步发电机控制技术的低压微电网功率分配策略
[J]. 电力建设 , 2020 , 41 (7 ):42 -48 .
DOI:10.12204/j.issn.1000-7229.2020.07.006
[本文引用: 1]
低压微电网中,采用虚拟同步发电机(virtual synchronous generator,VSG)策略控制多台逆变器并联运行时,由于线路阻抗差异较大,无法实现输出功率的按容量精确分配。针对这一问题,文章提出一种改进的VSG控制技术,在无功电压控制环中引入公共点电压反馈和积分环节,消除线路阻抗对无功分配的影响;并在虚拟阻抗环引入无功功率反馈,根据系统运行情况实时调整虚拟阻抗的阻值。在Matlab/Simulink环境下搭建了仿真模型,仿真结果表明,所提改进控制策略实现了有功和无功功率的精确分配,降低了逆变器输出电压幅值跌落,并且具有较强的鲁棒性。
ZHAO Jinxin MIAO Hong ZENG Chengbi Low voltage microgrid power distribution strategy based on improved virtual synchronous generator control technology
[J]. Power Construction , 2020 , 41 (7 ):42 -48 .
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
温春雪 , 黄耀智 , 胡长斌 , 等 . 虚拟同步发电机接口变换器并联运行虚拟阻抗自适应控制
[J]. 电工技术学报 , 2020 , 35 (S2 ):494 -502 .
[本文引用: 1]
WEN Chunxue HUANG Yaozhi HU Changbin et al. Virtual impedance adaptive control for parallel operation of virtual synchronous generator interface converter
[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society , 2020 , 35 (S2 ):494 -502 .
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
澎湃 . 基于虚拟阻抗的微电网下垂控制策略研究
[J]. 供用电 , 2018 , 35 (6 ):60 -65 .
[本文引用: 1]
PENG Pai Research on droop control strategy in micro-grid based on virtual impedance
[J]. Distribution & Utilization , 2018 , 35 (6 ):60 -65 .
[本文引用: 1]
[16]
朱作滨 , 黄绍平 , 李振兴 . 孤岛型微网并联逆变器下垂控制策略研究
[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报 , 2020 , 32 (2 ):119 -124 .
[本文引用: 1]
ZHU Zuobin HUANG Shaoping LI Zhenxing Research on droop control strategy of parallel inverters for isolated microgrid
[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA , 2020 , 32 (2 ):119 -124 .
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
ZHANG B LI D X WANG Y K et al. Self-adaptable reactive power-voltage controller for virtual synchronous generators
[J]. The Journal of Engineering , 2019 , 2 (16 ):2969 -2973 .
[本文引用: 1]
[18]
LIU J MIURA Y BEVRANI H et al. Enhanced virtual synchronous generator control for parallel inverters in microgrids
[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid , 2017 , 8 (5 ):2268 -2277 .
DOI:10.1109/TSG.2016.2521405
URL
[本文引用: 1]
[19]
YAN X W CUI Y CUI S Control method of parallel inverters with self-synchronizing characteristics in distributed microgrid
[J]. Energies , 2019 , 12 (20 ):3874 .
DOI:10.3390/en12203874
URL
[本文引用: 1]
A high level of insulation moisture in a transformer increases the breakdown probability and forces a reduction of its load. Therefore, there is a need to dry the transformer insulation. For technical reasons, there are some restrictions on the use of common drying methods for cellulose insulation available on the market. The aim of the research was to check the possibility of using synthetic ester for effective drying of cellulose materials of various thickness and an evaluation of the drying dynamics. The replacement of mineral oil with a synthetic ester caused a reduction of moisture in paper and thin pressboard by one percentage point. It was possible in the case of drying these materials for seven days at a temperature of 70 °C. The effects of drying were much smaller in the case of thicker cellulose samples. This paper also shows the complex problem of simultaneously drying materials of different thicknesses. Drying thin paper and thick pressboard at the same time significantly slows down the drying process of the pressboard. Presented results will be used to develop a procedure for drying the transformer insulation system using a synthetic ester.
[20]
YAN X W MA H B JIA J X et al. Precise reactive power-voltage droop control of parallel virtual synchronous generators that considers line impedance
[J]. Electronics , 2021 , 10 (11 ):1344 .
DOI:10.3390/electronics10111344
URL
[本文引用: 1]
Problems such as high power coupling, low distribution accuracy, and insufficient reactive power-voltage droop accuracy occur when distributed generators are operated in parallel due to the influence of line impedance. The precise control of output reactive power and voltage is difficult to achieve using traditional virtual synchronous generator (VSG) control. Taking this into consideration, this study proposes a virtual synchronous generator reactive power-voltage integrated control strategy that considers line parameters to solve this problem. First, the impedance voltage drop of the line is compensated for in accordance with local information control to ensure the consistency of the control voltage in parallel operation of distributed generators and to realize the precise droop control of reactive power and the voltage of the point of common coupling (UPCC). Second, virtual negative impedance control is added to change the equivalent output impedance characteristics of the system and achieve power decoupling. On this basis, the active frequency and reactive voltage decoupling control effect of the improved control strategy is quantified and analyzed using the relative gain matrix. The accuracy of reactive power distribution and droop control is theoretically derived and analyzed by establishing a small-signal model of a two-machine parallel system. Finally, the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed integrated control strategy are verified via a simulation model and an experimental platform for parallel operation. Results show that the proposed integrated control strategy can effectively solve the problems of power decoupling and accurate distribution, reduce system loop current, and realize accurate reactive power-voltage droop. Compared with the traditional VSG control strategy, the dynamic deviation of UPCC is reduced by at least 40% when a large-scale load disturbance occurs.
1
2012
... 微电网系统由分布式电源、储能系统、控制器、保护装置和负荷组成,可并网运行和孤岛运行[1 -2 ] .当微电网系统孤岛运行时,单一的微电源无法满足实际负荷需求,为了提高系统的稳定性以及增大微电网系统的容量,微电网系统不再是单一的微电源系统,而是由多台逆变器并联运行系统.多逆变器并联运行时,由于各台逆变器距离负荷端的线路长度不一致,导致系统出现有功或者无功不精确分配,从而出现功率环流,严重影响并联逆变器的稳定运行.针对这一问题,并联逆变器下垂控制及并联逆变器虚拟同步机(Virtual synchronous generators,VSG)控制策略受到人们的广泛关注. ...
1
2012
... 微电网系统由分布式电源、储能系统、控制器、保护装置和负荷组成,可并网运行和孤岛运行[1 -2 ] .当微电网系统孤岛运行时,单一的微电源无法满足实际负荷需求,为了提高系统的稳定性以及增大微电网系统的容量,微电网系统不再是单一的微电源系统,而是由多台逆变器并联运行系统.多逆变器并联运行时,由于各台逆变器距离负荷端的线路长度不一致,导致系统出现有功或者无功不精确分配,从而出现功率环流,严重影响并联逆变器的稳定运行.针对这一问题,并联逆变器下垂控制及并联逆变器虚拟同步机(Virtual synchronous generators,VSG)控制策略受到人们的广泛关注. ...
独立微网中多虚拟同步机功率精确分配控制策略
1
2019
... 微电网系统由分布式电源、储能系统、控制器、保护装置和负荷组成,可并网运行和孤岛运行[1 -2 ] .当微电网系统孤岛运行时,单一的微电源无法满足实际负荷需求,为了提高系统的稳定性以及增大微电网系统的容量,微电网系统不再是单一的微电源系统,而是由多台逆变器并联运行系统.多逆变器并联运行时,由于各台逆变器距离负荷端的线路长度不一致,导致系统出现有功或者无功不精确分配,从而出现功率环流,严重影响并联逆变器的稳定运行.针对这一问题,并联逆变器下垂控制及并联逆变器虚拟同步机(Virtual synchronous generators,VSG)控制策略受到人们的广泛关注. ...
Precise power allocation control strategy of multi-virtual synchronous machines in independent microgrid
1
2019
... 微电网系统由分布式电源、储能系统、控制器、保护装置和负荷组成,可并网运行和孤岛运行[1 -2 ] .当微电网系统孤岛运行时,单一的微电源无法满足实际负荷需求,为了提高系统的稳定性以及增大微电网系统的容量,微电网系统不再是单一的微电源系统,而是由多台逆变器并联运行系统.多逆变器并联运行时,由于各台逆变器距离负荷端的线路长度不一致,导致系统出现有功或者无功不精确分配,从而出现功率环流,严重影响并联逆变器的稳定运行.针对这一问题,并联逆变器下垂控制及并联逆变器虚拟同步机(Virtual synchronous generators,VSG)控制策略受到人们的广泛关注. ...
下垂控制并联系统中功率精确分配的控制策略
1
2019
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Control strategy of accurate power distribution in droop control parallel system
1
2019
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
孤岛型微电网中改进下垂控制策略
1
2017
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Improved droop control strategy in isolated microgrid
1
2017
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
基于改进下垂控制的多微网并联运行控制策略研
1
2021
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Research on multi microgrid parallel operation control strategy based on improved droop control
1
2021
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
虚拟复阻抗下的低压并联逆变器改进下垂控制策略
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Improved droop control strategy of low voltage parallel inverter under virtual complex impedance
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
基于端口特性的并联下垂逆变器系统的小信号建模与稳定性分析
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Small signal modeling and stability analysis of parallel droop inverter system based on port characteristics
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
虚拟同步机并联电流控制型变换器系统暂态同步稳定性分析
1
2021
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Transient synchronization stability analysis of virtual synchronous machine parallel current controlled converter system
1
2021
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
多虚拟同步发电机并联系统控制参数对稳定性的影响分析
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Analysis of influence of control parameters on stability of multi virtual synchronous generator parallel system
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
虚拟阻抗对不同电压等级逆变器并联系统的稳定性影响分析
1
2021
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Analysis of the influence of virtual impedance on the stability of inverter parallel systems with different voltage level
1
2021
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Modeling and stability analysis of parallel inverters in island microgrid
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
孤岛微网中VSG并联运行功率精确分配控制策略
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Precise power distribution control strategy for VSG parallel operation in isolated island microgrid
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
基于改进虚拟同步发电机控制技术的低压微电网功率分配策略
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Low voltage microgrid power distribution strategy based on improved virtual synchronous generator control technology
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
虚拟同步发电机接口变换器并联运行虚拟阻抗自适应控制
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Virtual impedance adaptive control for parallel operation of virtual synchronous generator interface converter
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
基于虚拟阻抗的微电网下垂控制策略研究
1
2018
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Research on droop control strategy in micro-grid based on virtual impedance
1
2018
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
孤岛型微网并联逆变器下垂控制策略研究
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Research on droop control strategy of parallel inverters for isolated microgrid
1
2020
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Self-adaptable reactive power-voltage controller for virtual synchronous generators
1
2019
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Enhanced virtual synchronous generator control for parallel inverters in microgrids
1
2017
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Control method of parallel inverters with self-synchronizing characteristics in distributed microgrid
1
2019
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...
Precise reactive power-voltage droop control of parallel virtual synchronous generators that considers line impedance
1
2021
... 研究人员对微电网并联逆变器控制策略进行了大量的研究.文献[3 ]提出一种逆变器输出无功功率反馈控制及鲁棒下垂控制的方法,实现了无功功率的精确分配.文献[4 ]提出了一种改进的下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分,但是输出电压无法实现一致,偏差较大.文献[5 ]提出一种改进下垂控制方法,仿真验证了离并网时系统电压振荡和频率波动,对多微源并联之间的有功和无功均分问题未提供解决方法.文献[6 ]提出一种基于虚拟复阻抗的改进下垂控制策略,实现了无功均分和提高了电压质量.文献[7 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ -11 ]对并联下垂/VSG控制系统进行小信号建模,并分析了系统的稳定性及相应参数整定.文献[12 ]提出了一种基于分布式二次控制器的电压补偿策略,自动调整各VSG定子电抗值,实现了无功功率均分.文献[13 ]提出了基于虚拟电感的自适应VSG并联控制策略,实现了功率均分.文献[14 ]对线路首末端的电压值和线路损耗进行信息实时监测,从而实时计算出精确的虚拟阻抗,通过增加/减少虚拟阻抗来动态调节,实现功率均分.文献[15 -16 ]提出自适应虚拟阻抗下垂控制策略,实现了并联逆变器有功均分.文献[17 ]提出一种自适应无功电压控制策略,通过无功功率差调节电压系数,但其负载电压波动仍然比较大.文献[18 -19 ]利用VSG的下垂特性来实现系统功率控制,通过调节VSG外部下垂特性来实现并联VSG功率的精确分配.文献[20 ]提出考虑线路阻抗的无功电压综合控制策略,对电压进行补偿同时增加虚拟负阻抗改变系统的输出等效阻抗特性并实现功率去耦,有效抑制系统回路环流,实现功率精确分配. ...