1 引言
有载分接开关(On-load tap-changer,OLTC)在电力系统中承担着调节无功功率、稳定电网电压的重要作用,是有载调压变压器的关键组成部分与唯一可动的部件[1]。在“双碳”背景下,随着有载分接开关在高压直流输电变流变压器、新能源场站升压变压器及传统发电、配电变压器中的大量使用,以及电力系统对电网电压日益精细化调控需求的不断增加,有载分接开关动作频率增加,电弧现象频繁发生,在载流切换调压过程中,容易发生开关触头磨损、烧蚀等现象,故障率升高,影响电网的安全运行。
为了研究电弧放电对电接触材料的损伤机制,近十年来,国内外研究人员已经在电弧放电方面进行了大量研究,主要从电流、滑动速度、法向接触压力等参数方面研究。文献[2]在销盘式摩擦磨损试验机上研究了纯碳带在动态接触力作用下的电弧放电。结果发现电弧放电是随着动态接触力的周期而周期性产生的。文献[3]利用高速摄像机捕捉了电弧放电的动态变化。观察结果表明,电弧放电能够沿滑动方向移动。文献[4]在销盘式摩擦磨损试验机上进行了不锈钢对浸渍铜的金属化碳的电流摩擦和磨损试验,发现在摩擦磨损过程中存在电弧放电的现象。由于摩擦对的振动和高温的作用,电弧的强度随滑动速度和电流的增大而增大。文献[5]研究强电流下滑板与接触网导线的摩擦磨损特性,对比浸铜碳滑板和铜基粉末冶金滑板的摩擦磨损特性,发现两种滑板的摩擦因数和磨耗率随着电流的增大而增大,但载流相同时,浸铜碳滑板的磨耗率要大得多。文献[6]利用试验机在不同的接触压力、滑动速度和接触电流下进行了大量的载流摩擦试验,提出载流效率、摩擦变异系数和电流变异系数,试验发现随着接触压力的增加,磨损率曲线呈U型变化。文献[7]研究刚性接触网/受电弓摩擦副的载流摩擦磨损性能,电弧能量随着法向载荷的增大而减小,当法向载荷Fn>25 N后,电弧能量趋于稳定值。
近年来,仿真软件发展迅速,有限元仿真软件具有精度高、边界适应性好等特点,能够计算出瞬态和稳态的数据,为试验提供了便利,针对电弧的有限元仿真也发展起来。文献[8]针对真空断路器中产生的大电流真空电弧,基于磁流体动力学(Magnetohydrodynamics,MHD)理论建立了电弧等离子体物理模型,并研究了在外界轴向磁场的作用下真空电弧的动态特性。文献[9]以MHD理论为基础,考虑电弧的基本物理特性及电磁效应、热效应和辐射效应,建立了静态弓网电弧二维磁流体动力学模型,仿真计算了电弧的温度场分布,得到了电弧弧柱和两电极内部的温度分布特性。文献[10-11]对弓网系统静态升降弓过程所产生的弓网电弧特性开展了研究,综合电场、热场和磁场的计算,建立了弓网系统静态升降弓时的弓网系统二维模型,仿真分析了不同弓网间隙和不同接触网廓型情况下的电弧温度场分布情况及弓网电弧稳态燃烧特性。以上的电弧研究都是在空气介质中,对绝缘油中电弧放电特性和温度分布的研究较少。
为研究在绝缘油中的电弧放电特性,本文借助COMSOL Multiphysics仿真软件,建立有载分接开关的电弧放电模型,利用仿真的方法分析在绝缘油介质中起弧前和起弧后的触头表面温度分布特性,分析电弧对触头表面的影响,并探究影响电弧温度分布的因素。
2 OLTC触头温度场仿真模型构建
在有载分接开关的运行过程中,分接开关的动触头和静触头由接触到分离,触头间隙会因电压的升高发生击穿,产生电弧。随着触头的分离,隙间电弧逐渐冷却,电弧被拉断,不会发生热击穿,最终电弧熄灭。
触头分离过程中,电弧内部各种粒子在热场、流场、电磁场作用下发生强烈的质量、动量和能量反应,将电磁场、热场、流场构建为磁流体动力学方程组进行求解[12]。在电弧的燃弧过程中,产生大量热量,使绝缘油碳化,绝缘性能下降。为此,建立有载分接开关的有限元仿真模型,模拟电弧对触头的损伤机理。
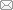
2.1 电弧仿真几何模型及电极材料
图1
一方面因为油浸式有载分接开关的触头材料大多为钨铜合金,其中钨的含量较少,大约为2%;另一方面为了更好地研究电弧对触头的损伤程度,使电弧对触头的损伤更加可视化,选用更易损伤的铜材料作为触头材料,来表征其他材料触头的电弧损伤机理,故动触头和静触头的材料均为铜,材料参数包括相对磁导率、电导率、相对介电常数。具体的模型相关材料参数如表1所示。
变压器油的部分参数随温度的变化而变化,为此设定变压器油的部分参数随温度变化的公式如表2所示。
表2 变压器油的参数
| 参数 | 拟合公式 |
|---|---|
| 动力粘度 | |
| 恒压热容 | |
| 流体密度 | |
| 导热系数 |
开关触头电弧模型的建立是基于磁流体动力学理论,包含流体动力学方程、电磁场方程。在触头电弧产生的区域被认为是局部热力学平衡,电弧产生在绝缘油介质中,其流动区域被认为处于层流状态。不考虑电弧对电极热传导和热辐射造成电极材料相变对电弧特性的影响;不考虑电极内部焦耳热对电弧特性的影响[13]。
(1) 流体动力学方程。流体动力学方程包含流体质量守恒方程、动量守恒方程和能量守恒方程。
流体质量守恒方程
动量守恒方程
能量守恒方程
式中,
(2) 电磁场方程
式中,Qj.v为体积电流源;
2.2 电弧模型边界条件
为了实现准确电弧放电,贴合实际运行情况,必须对模型施加合理的边界条件。有载分接开关的开关触头在切换过程所产生电弧特性的仿真边界条件设置如下,需要对模型的耦合场进行定义。
(1) 温度边界条件。绝缘油的外部边界AB、BC、CD、AD的温度值设置为293.15 K;动触头上表面EF、GH和静触头底部IJ的温度为293.15 K。
(2) 流体流动边界。绝缘油边界AD设置为入口边界,边界BC设置为压力出口边界,压力为0 Pa;绝缘油区域受洛伦兹力影响。
(3) 电磁场边界条件。动触头区域EFGH设置为电流终端,静触头的底部边界IJ设置为接地,初始电势为0 V;动触头边界为阳极,静触头边界为阴极。
(4) 动网格边界条件。边界EFGH和曲线边界EF设置滑动速度v,方向为X轴的正方向;边界KL、KI、IJ和LJ的坐标不变;绝缘油边界AB、BC、CD、AD的坐标均不变。
2.3 网格划分
COMSOL Multiphysics中的网格尺寸属性用来设定网格的大小,包括最大尺寸单元、最小尺寸单元、单元比例、曲率解析度和窄区解析度等,软件中设置了包括极端细化、特别细化、粗化等九种不同的网格划分形式,每种网格划分方式对应于不同的参数设置[14]。在本文中,将几何模型进行网络划分,网格单元数为48 072。为了保证网格的质量,避免因为网格划分粗糙导致几何划分出现错误或出现求解器不收敛的错误。对于绝缘油区域选择“细化”的方式,并设置最小单元网格尺寸为0.15 mm;对于触头部分设置为自由三角形网络,选择“较细化”的方式,以满足计算需求。
3 仿真结果及分析
为了分析油浸式有载分接开关运行中触头的电气烧蚀状况,本文建立有载分接开关触头电弧的仿真模型,采用动网格技术模拟实际的触头滑动,分别仿真了有载分接开关的滑动过程和起弧过程的触头表面温度变化。
3.1 滑动过程中触头表面的温度变化
载流摩擦过程中,接触面温度热源来自3个方面:摩擦热、接触电阻热和电弧热。在载流摩擦过程中,固定摩擦件和滑动摩擦件之间的接触属于滑动电接触,摩擦副之间的接触区域,是由一些离散的微小接触点所构成,这些接触点不仅支撑载荷,而且承受着脉冲电流[15]。这些微小的接触点实际的接触面积只有几平方毫米,甚至更小,但在这些微小的区域间会传递巨大的能量,摩擦副通过这些微小接触点实现电流的传递。在起弧前,摩擦副的接触面流过电流,因接触电阻的存在,会产生接触电阻热;在洛伦兹力的作用下,相对滑动会产生滑动摩擦热。
在有载分接开关滑动过程中,起弧前的开关触头表面的温度主要来自电阻热和摩擦热。为了研究滑动速度对触头的影响,控制触头间的接触压力为1 N,通入5 A的电流,设置动触头的速度为20 mm/s,触头表面的温度变化如图2所示。
图2
由图2可知,动触头表面的温度随着时间的增长而增大,在固定的距离内,温度从接触点向周围扩散,其最高温度出现在接触点处,形成一个高温区。其原因是随着运行时间的增加,触头接触面之间相互摩擦,摩擦力做功转化为热能,因接触电阻的存在,焦耳热也会随时间增长而增加,最终在电阻热和摩擦热的逐渐积累下,造成接触面的温度上升。
在摩擦热和电阻热的作用下,有载分接开关的开关触头表面温度升高,进而使开关触头的表面氧化;另外由于电应力和力学应力,最终导致材料软化、黏着和剥落,触头表面出现划痕,粗糙度增大,进而使磨损率增大。
3.2 滑动过程中不同速度下触头表面的温度变化
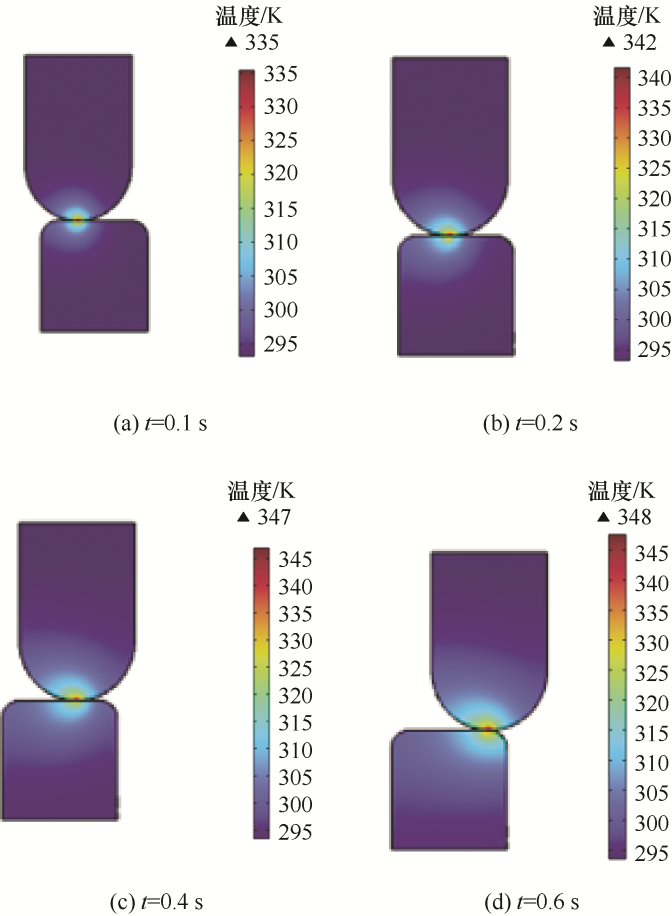
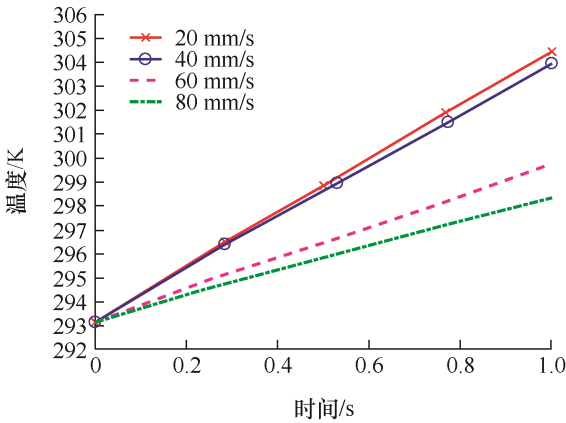
有载分接开关的开关触头尺寸有限,在忽略电弧热的情况下,在一定的距离之内滑动,其触头表面温度受滑动速度的影响很大,为探究在不同的滑动速度下滑动触头表面的温度变化,设置滑动速度分别为20 mm/s、40 mm/s、60 mm/s和80 mm/s,在不同速度下,动触头接触点的温度变化趋势如图3所示。
图3
由于接触电阻的存在,触头表面的温度受电阻热的影响较大。由图3可知,无论速度多大,随着滑动时间的增长,触头表面温度总体呈现上升的趋势;同时,在电弧发生前,随着速度的增大,其触头表面温度下降,温度变化趋势减缓。这是因为在固定的距离内,随着速度增大,电能转化为热能的时间降低,所积累的热量总量降低。在这个过程中,摩擦力做功转化的热能对结果影响不大,对触头表面温度产生影响的主要因素是电阻热。
3.3 不同时刻的电弧温度分布
电弧在燃烧过程中,电场、磁场和热场相互作用,共同影响。电弧等离子体的物性参数包括密度、比热容、热导率和电导率等。当电弧电流一定时,电弧周围电场和磁场相互感应。一方面,电弧电场作用下产生的焦耳热会影响电弧的热场,且电弧焦耳热的值与电弧的电导率相关;另一方面,电弧热传导和热辐射过程会造成电弧热能的耗散,影响电弧热场[13]。
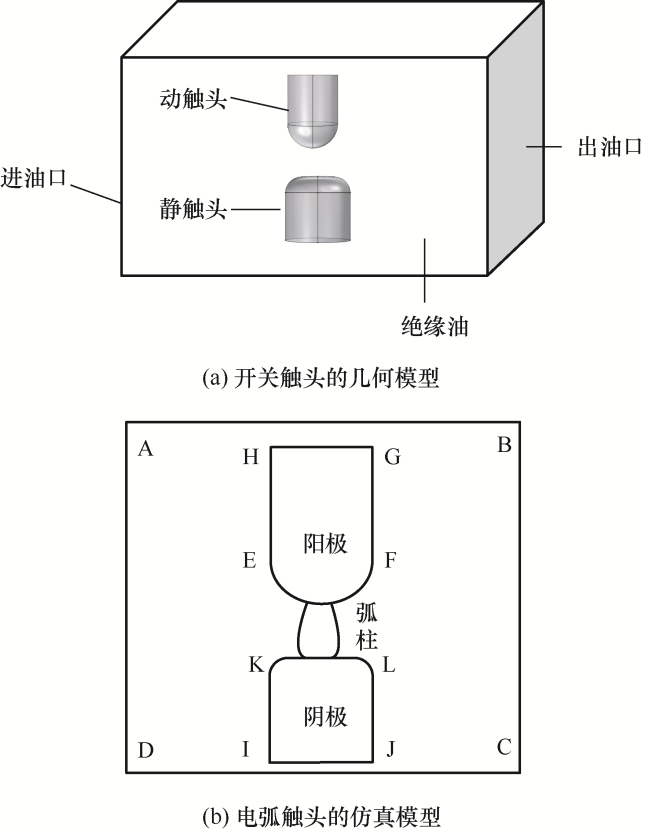
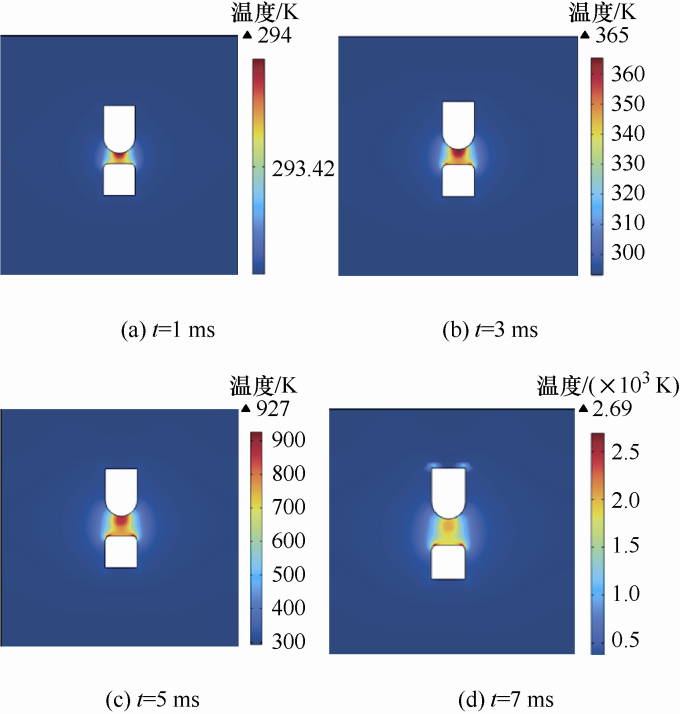
有载分接开关的开关触头在滑动过程中,不可避免地会产生电弧,在电弧的产生过程中,不同时刻其电弧的温度分布也会有所不同,电弧温度的大小与电弧能量密切相关,电弧温度的大小在一定程度上能反映电弧的能量大小以及电弧对触头表面的损伤程度。通过分析电弧的温度分布,可观察到电弧从起弧阶段到燃弧阶段的变化。其变化情况如图4所示,其中滑动速度为20 mm/s。
图4
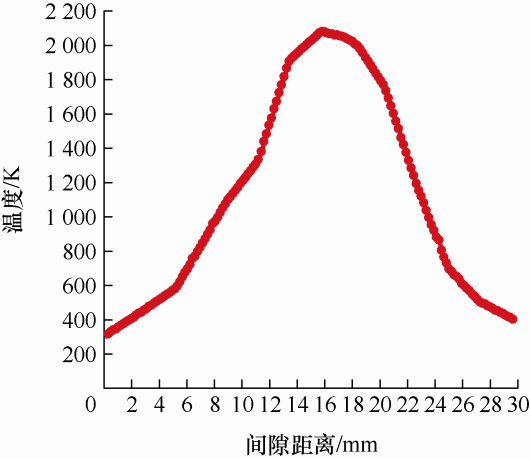
图5
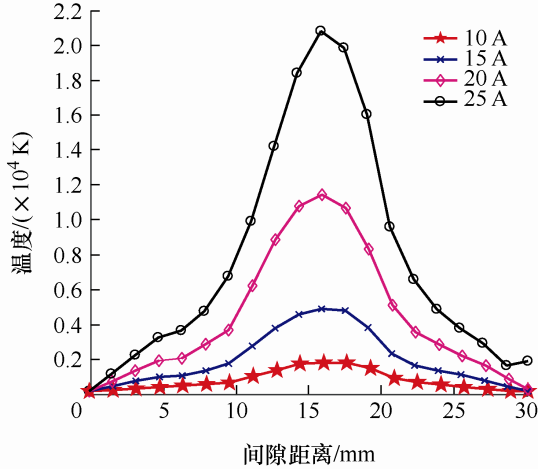
3.4 不同电流下的电弧温度分布
图6
3.5 不同滑动速度下的电弧温度分布
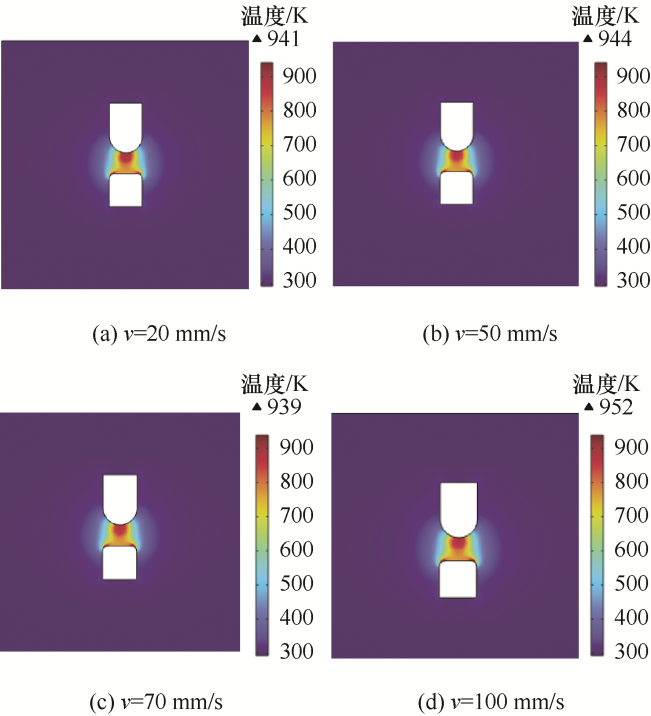
运行速度的大小对载流摩擦性能有一系列复杂影响。随着速度增加,摩擦副间的振动冲击加剧,导致产生离线电弧的概率增大[29]。动静触头在分开时会使绝缘油介质产生电弧,随着触头的移动,弧柱逐渐拉长、弯曲变形,并最终熄灭。在这个过程中,触头间隙或者触头附近会出现重击穿放电的现象,滑动速度的变化影响着重击穿出现的概率。电弧侵蚀对有载分接开关的开关触头损坏严重。为探究滑动速度对电弧温度分布的影响,设定不同的滑动速度为20 mm/s、50 mm/s、70 mm/s、100 mm/s,取电弧电流为5 A,因电弧产生的时间极短,仅仅只有几毫秒,为此设定在8 ms的时间内观察电弧的温度分布情况,获得在不同滑动速度下电弧的温度分布情况,如图7所示。
图7
从图7可以发现,电弧温度向着动触头的上部蔓延,由此将会导致动触头上部表面的损伤程度严重;随着滑动速度的增大,电弧的弧柱半径略微减小,变化幅度较小,电弧的温度呈现先上升后下降的趋势,呈“N”字形变化。在50~70 mm/s存在一个速度值,使电弧达到一个最高的温度。
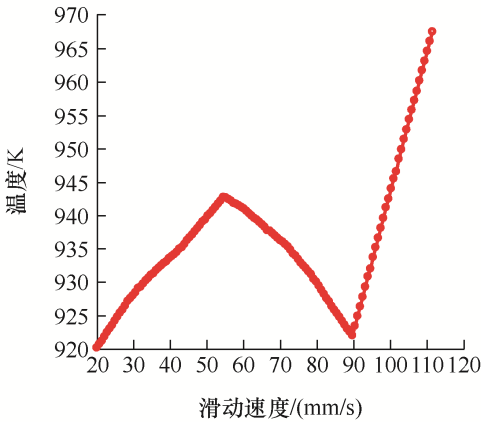
为进一步探究滑动速度对电弧温度分布的影响,在20~100 mm/s进一步细分速度值,测量动触头表面的温度变化,触头表面温度随滑动速度的变化如图8所示。可以发现,滑动速度从20~55 mm/s变化时,触头表面温度一直在上升,55~90 mm/s之间,触头表面温度开始下降,在90 mm/s之后温度又开始上升。由此可知,在滑动速度为55 mm/s时,存在一个相对的最高温度,滑动速度为90 mm/s时,触头表面温度最低,考虑到有载分接开关触头的运行效率和性能,与其他速度相比,此速度是最优的滑动速度。在此速度下,触头表面的温度值最低,电弧对触头表面的侵蚀程度最轻。
图8
进一步探究图8中温度变化的原因发现,在滑动速度55 mm/s之前,随着速度的增加,触头表面温度随之升高,这是因为速度的提高,使触头之间的振荡加剧,产生离线电弧的概率增加,电弧的放电能量增加,触头表面温度升高;在滑动速度55 mm/s之后,由于触头尺寸的限制,有载分接开关的触头滑动过程中,滑动速度越快,其产生电弧存在的时间越短,电弧迅速被拉断,进而造成电弧的传热时间短,在一定的时间内,电弧向外传递的热量不断减少,电弧的最高温度随滑动速度的提高而不断下降。之后,速度继续提高,触头间的振动更加剧烈,电弧的发生频率增大[30-31]。在触头滑动时,接触的时间越短,电弧产生的频率更频繁,温度呈上升趋势。
4 OLTC触头温度场特性试验验证
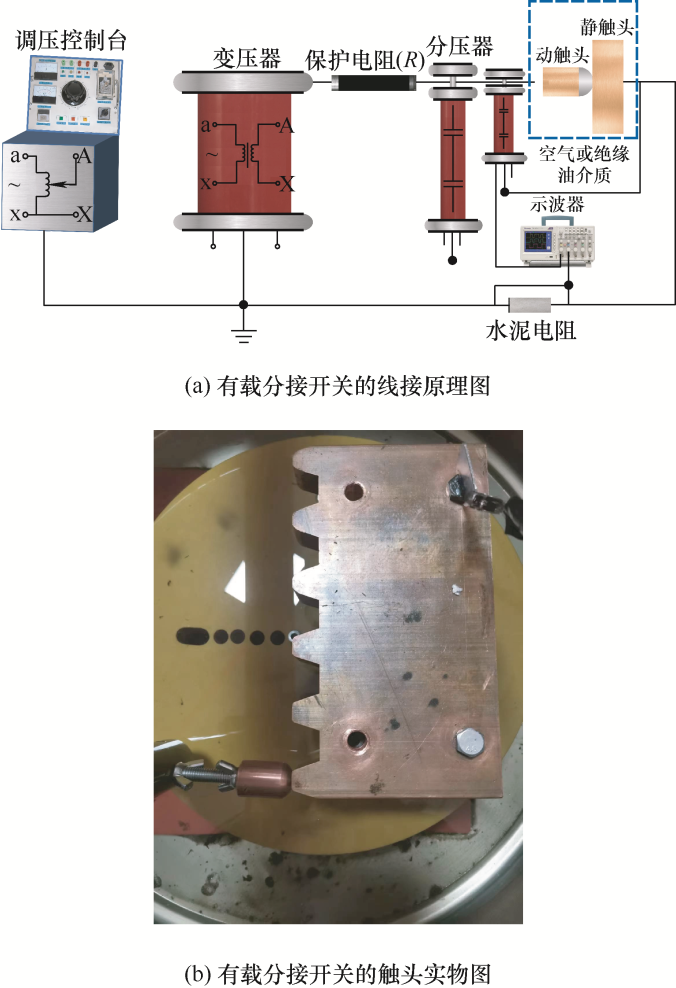
由于电弧等离子体燃烧时温度极高且产生时间短,通过试验的手段来测试电弧的温度分布非常困难。本文基于实验室现有的有载分接开关的载流摩擦试验装置,验证了仿真模型的正确性及有效性,试验装置如图9所示。该试验装置利用伺服电机和滚轴丝杆来驱动触头的滑动,模拟触头的切换过程,通过变压器控制台来调节电压,电压可调范围为0~100 kV,水泥电阻的阻值为50
图9
图10
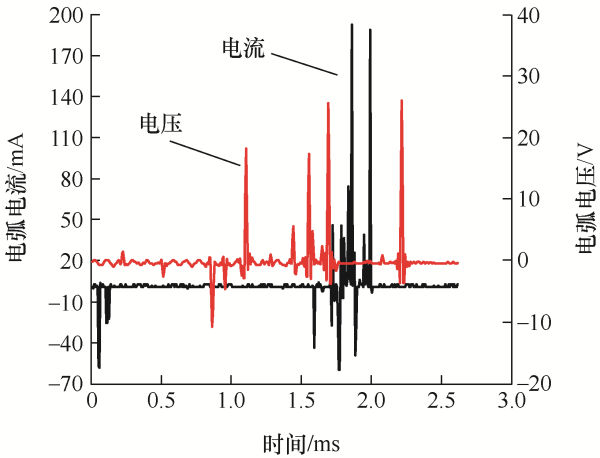
通过控制器设置不同的滑动速度(20~100 mm/s),当滑动过程中电弧产生时,用示波器同步测量出此时的电压和电流信号,每组数值进行12次试验,求取平均值,得到此时的电弧能量大小。在一定程度上,电弧能量的大小和变化能够反映电弧温度的大小和变化。通过智能运动控制器设定滑动速度在20 mm/s,一次触头间的滑动过程中,其电弧电流和电压变化如图10所示。触头在滑动过程中,由于触头间的振荡与冲击作用,使触头间发生短暂的离线,出现电弧放电的情况。
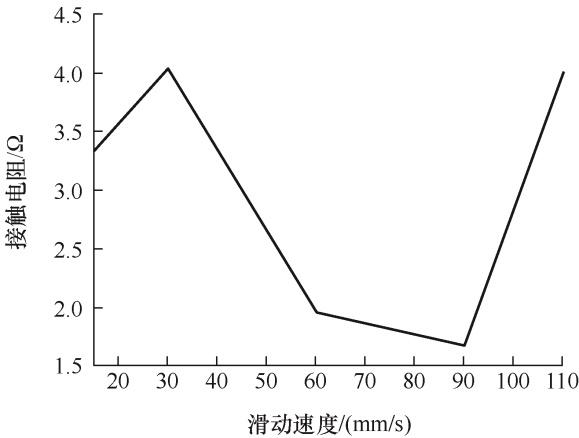
通过电压电流的数值计算得到接触电阻随滑动速度的变化,如图11所示。其中滑动速度为15~30 mm/s时,接触电阻增大,其原因是在这个速度段,电压变化幅度大于电流的变化幅度,电压占据主导地位;在滑动速度为30~90 mm/s时,接触电阻值下降,在起弧中电流慢慢占据主导地位,电弧的产生靠电流来维持。
图11
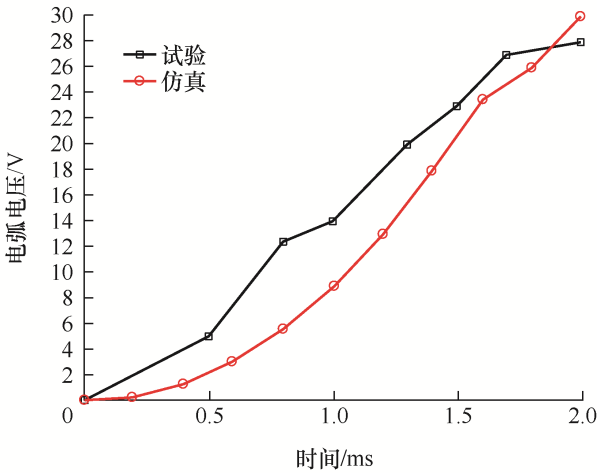
在电弧变化的2 ms内,试验的电弧电压从起弧至达到最大值,电压变化了28 V。同一试验电压下进行电弧仿真,在2 ms内电弧的电压变化了30 V。在滑动速度相同时,试验电弧电压和仿真电弧电压的变化基本一致,其对比如图12所示。
图12
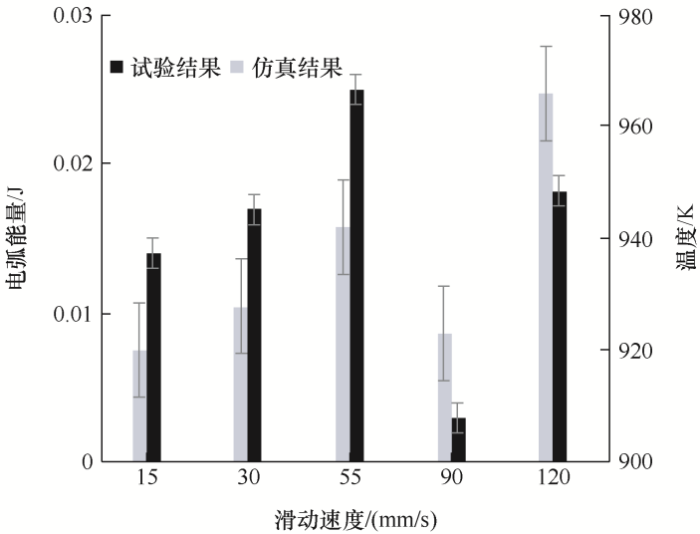
造成这一结果的差异在于仿真中变压器油的电导率是理想数值且数值很小、导电性能差;实际中使用的变压器油有一定的含水量,其电导率数值较大,导电性能较好,使电弧更易发生,从而电压变化更大。图13给出了实际试验中电弧能量随滑动速
图13
度变化以及仿真得到的不同速度下触头表面温度变化曲线,可以看出二者趋势基本相同。这表明搭建的仿真模型在偏差允许的范围内与实际试验情况相符,虽然在边界条件设置时进行了一些假设,但总体上模型是合理有效的。
5 结论
本文通过仿真和试验对有载分接开关滑动触头的电弧温度场特性进行了分析,通过对滑动触头在起弧前和起弧后的表面温度以及电弧温度分布分析,得到以下结论。
(1) 在起弧前,触头表面的温度主要来自电阻热和摩擦热,最高温度出现在接触点处;同时,因为触头尺寸的限制,随着滑动速度的提高,触头表面积累的热量减少,造成温度逐渐下降。
(2) 在起弧的过程中,电弧的温度快速升高,触头间隙逐渐增大,不断拉动电弧,电弧的高温区域不断向动触头表面靠近,使动触头表面烧蚀严重。随着电弧的产生和熄灭,触头表面的温度也随之先上升后下降。
(3) 在滑动速度为55 mm/s时,触头之间的温度达到一个相对最高点,随后开始下降;在滑动速度90 mm/s处,温度达到最低,此后开始上升,在此过程中存在一个相对最优的滑动速度90 mm/s,该速度下电弧对触头的烧蚀最小。
本文研究结论有助于进一步明确有载分接开关触头的电气烧蚀机理,并有利于探索有载分接开关触头最优滑动速度的设计,对延长开关触头的使用寿命具有重要意义。
参考文献
基于卷积神经网络的变压器有载分接开关故障识别
[J].
Fault identification of transformer on-load tap-changer based on convolutional neural network
[J].
Arc discharges of a pure carbon strip affected by dynamic contact force during current-carrying sliding
[J].DOI:10.3390/ma11050796 URL [本文引用: 1]
Dynamic variation of arc discharge during current-carrying sliding and its effect on directional erosion
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.triboint.2015.03.012 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effect of arc discharge on friction and wear behaviors of stainless steel/copper-impregnated metalized carbon couple under electric current
[J].
Research of friction and wear behavior of sliding contacts under strong current conditions
[C]//
Experimental research on current-carrying and friction characteristics of sliding electrical contact
[C]//
Numerical simulation of high-current vacuum arcs with an external axial magnetic field
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPS.2003.818436 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于磁流体动力学模型的弓网电弧温度场仿真
[J].
Simulation of pantograph-catenary arc temperature field based on magnetohydrodynamic model
[J].
高速列车静态升降弓电弧的磁流体动力学仿真研究
[J].
Magnetohydrodynamics simulation of static pantograph arc of high-speed train
[J].
高速列车静态升降弓时弓网电弧稳态特性仿真与分析
[J].
Simulation and analysis of steady-state characteristics of pantograph-catenary arc during static lifting of high-speed train
[J].
带载工况下降弓电弧磁流体建模分析
[J].
Analysis of magnetic fluid modeling of down-bow arc under load conditions
[J].
高速列车弓网电弧温度场特性仿真研究
[J].
Simulation study on temperature field characteristics of pantograph-catenary arc of high-speed train
[J].
利用三维有限元法计算复杂结构线圈电感
[J].
Research on the inductance computing of complicated coil by 3D FEM
[J].
高速载流摩擦接触面温度的特性
[J].
Temperature characteristics of high-speed current-carrying friction contact surface
[J].
钨/铜载流摩擦副的电弧烧蚀行为
[J].
DOI:10.11973/jxgccl201801004
[本文引用: 1]

在自制载流电弧试验机上进行了钨/铜载流摩擦副的载流电弧烧蚀试验,研究了其电弧烧蚀行为和电弧烧蚀机理。结果表明:随燃弧时间的延长,载流电弧电流下降,电压增加,电场强度则先增后降;载流电弧分为起弧、稳定燃烧和熄弧3个阶段,各阶段的时间间隔分别约占整个燃弧时间的7%,89%和4%,铜试样的严重烧蚀主要发生在起弧阶段和稳定燃烧的初期;随着试验电流的增大,金属蒸气态电弧存在时间延长,铜试样表面的电弧烧蚀坑宽度增加,深度先增后降,这与高熔点钨的沉积加剧有关。
Arc erosion behavior of tungsten/copper current-carrying friction pair
[J].
DOI:10.11973/jxgccl201801004
[本文引用: 1]

Current-carrying arc erosion tests of W/Cu current-carrying frictional pairs were carried out by the home-made current-carrying arc tester. The arc erosion behavior and arc erosion mechanism were studied. The results show that with the arcing time increasing, the current of current-carrying arc decreased, the voltage increased, and the electric field intensity first increased then decreased. The current-carrying arc was divided into three stages of ignition, stable burning and extinction. The time intervals of the three stages were about 7%,89% and 4% of the total arcing time. The serious arc erosion of copper specimen occurred at the ignition stage and at the beginning of stable burning stage. With the increase of test current, the existence time interval of the arc in metallic vapour state extended; the width of arc erosion pit on copper specimen surface increased and the depth first increased then decreased. The results were related to the increasing deposition of tungsten with high melting point.
弓网系统电弧的产生及其影响
[J].
Arc generation in pantograph-catenary system and its influence
[J].
弓网电弧磁流体动力学模型
[J].
Magnetohydrodynamic model of pantograph-catenary arc
[J].
大电流对碳滑块/铜银合金接触线载流摩擦磨损性能的影响
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2017.09.011
[本文引用: 1]

在高速载流摩擦磨损试验机上研究速度为150 km/h、接触压力为60~120 N试验工况下,200~500 A大电流对纯碳滑板摩擦磨损性能的影响。结果表明:在低电压大电流的载流条件下,铜银接触线和纯碳滑板间主要以短弧放电为主,放电面积大、电弧输出能量高;碳滑块的磨损形式主要以电弧烧蚀、剥离、熔融、汽化为主,机械磨损较小;碳滑板的磨损量、电弧能量随着电流的增大而急剧上升;摩擦因数随着电流的增加先增加后减小;当电流不变时弓网间的电弧能量随着接触压力增加呈先增加后减小的趋势,磨损量则随着接触压力的增加而减小。
Effect of high current on current-carrying friction and wear properties of carbon slider/copper-silver alloy contact wire
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2017.09.011
[本文引用: 1]

The effect of low-voltage and high-current on the friction and wear behavior of carbon strip/Cu-Ag alloy con-tact wire was studied on a high-speed electric sliding test machine under a constant AC and the sliding velocity of 150 km/h and the contact forces from 60 to 120 N.The results show that under the condition of low-voltage and high-current, the main form of arc discharge between carbon strip/Cu-Ag alloy contact wire is short arc discharge with large arc dis-charge area and high arc energy.The main wear mechanisms of the carbon strip include arc ablation wear,delamination, melting,vaporization and slight mechanical wear.The wear volume of the carbon strip and arc energy is increased sharply with the increasing of the electric current.The friction coefficient is increased first and then decreased with the increasing of electric current.When the current is constant,the arc energy is increased first and then decreased with the increasing of the contact pressure.The wear volume is decreased with the increasing of the contact force.
电弧对弓网系统接触线温度的影响
[J].
Effect of arc on contact wire temperature of pantograph-catenary system
[J].
Simulation on current density distribution of current-carrying friction pair used in pantograph-catenary system
[J].DOI:10.1109/Access.6287639 URL [本文引用: 1]
降雨环境下弓网电弧动态特性研究
[J].
Research on dynamic characteristics of pantograph-catenary arc under rainfall environment
[J].
Study on material transfer in the process of contact strips rubbing against a contact wire with electric current
[J].
DOI:10.1177/1350650115595055
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A series of experimental tests on a block-on-ring tester were carried out to obtain a new understanding of severe material transfer in the process of contact strips rubbing against a contact wire with electric current. Three types of contact strip materials including an aluminum-based strip, a copper-based strip, and a pure carbon strip are tested in electric sliding against two contact wire materials including a pure copper contact wire and a copper–silver alloy contact wire. Test results show that there are serious material transfers in these three different friction couples in electric sliding. The aluminum-based strip has the severest material transfer, followed by the copper-based strip. The pure carbon strip has the minimum material transfer. It is found that the material transfer increases with the increase of the sliding speed, the arc discharge intensity, and the contact pressure. In the presence of electric current, contact strip materials are always transferred to the contact wire.
高速列车弓网电弧模型及其电气特性仿真研究
[J].
Research on pantograph-catenary arc model of high-speed train and its electrical characteristics simulation
[J].
载流摩擦磨损研究进展
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2022.07.022
[本文引用: 1]

载流摩擦磨损是摩擦副在有电流通过时的接触行为。载流摩擦副在工作过程中受力、电、热等多种因素耦合作用,损伤机制复杂多变。综述载流摩擦中的摩擦磨损机制,重点分析服役工况对载流摩擦磨损性能和导电性能的影响,阐述电弧产生的原因及影响因素,并对载流摩擦中的温度场及其仿真模拟研究成果进行归纳,总结载流摩擦材料的应用现状。概括载流摩擦的研究现状及其存在的问题,并指出未来应加强接触副材料在多环境下、多因素耦合作用下的摩擦磨损行为和失效机制研究,并有针对性地研发新型复合材料,以满足具体的工作条件和特殊的性能要求。
Current-carrying friction and wear research progress
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2022.07.022
[本文引用: 1]

The current-carrying friction and wear refers to the contact behavior of friction pair when the current passes through.The damage mechanism of the current-carrying friction pair is complicated and changeable due to the coupling action of force, electricity and heat.The friction and wear mechanism of current-carrying friction was reviewed, the influence of service conditions on current-carrying tribological properties and conductivity was analyzed, the arc generation causes and influencing factors were expounded, the temperature field in current-carrying friction and its simulation research results, and the application status of current-carrying friction material were summarized.The research status and existing problems of current-carrying friction were generalized.It was pointed out that the research on the friction and wear behavior and failure mechanism of contact pair materials under multi environment and multi factor coupling should be strengthened in the future, and new composite materials should be developed to meet the specific working conditions and special performance requirements.
弓网系统滑动电接触特性
[J].
Sliding electrical contact characteristics of pantograph catenary system
[J].