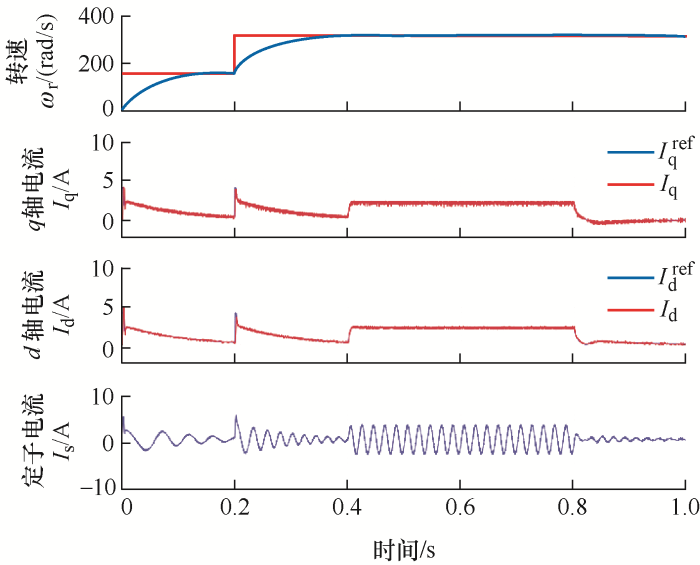
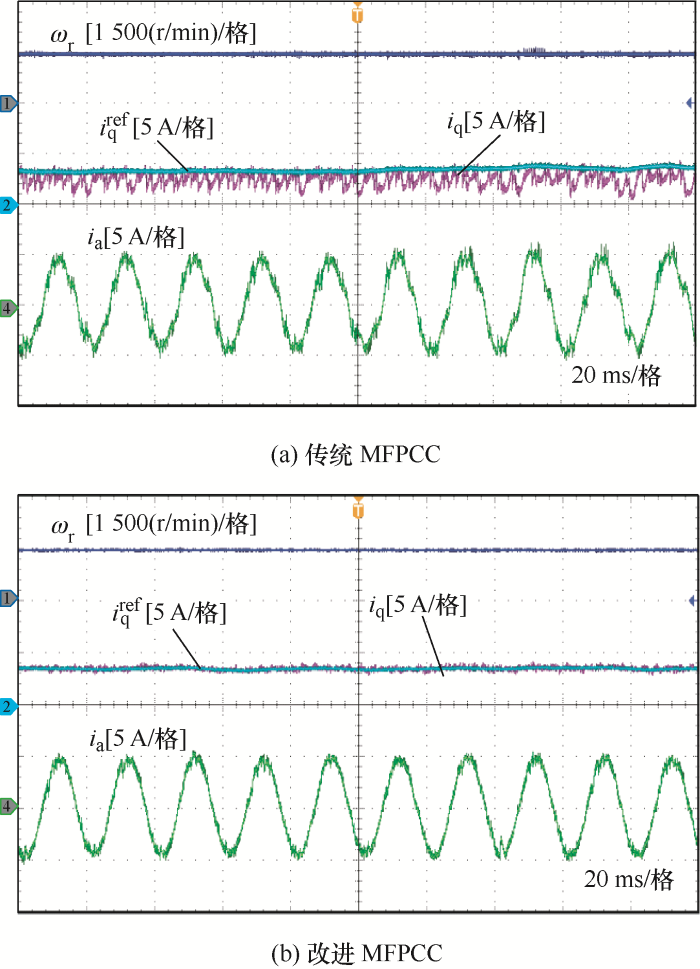
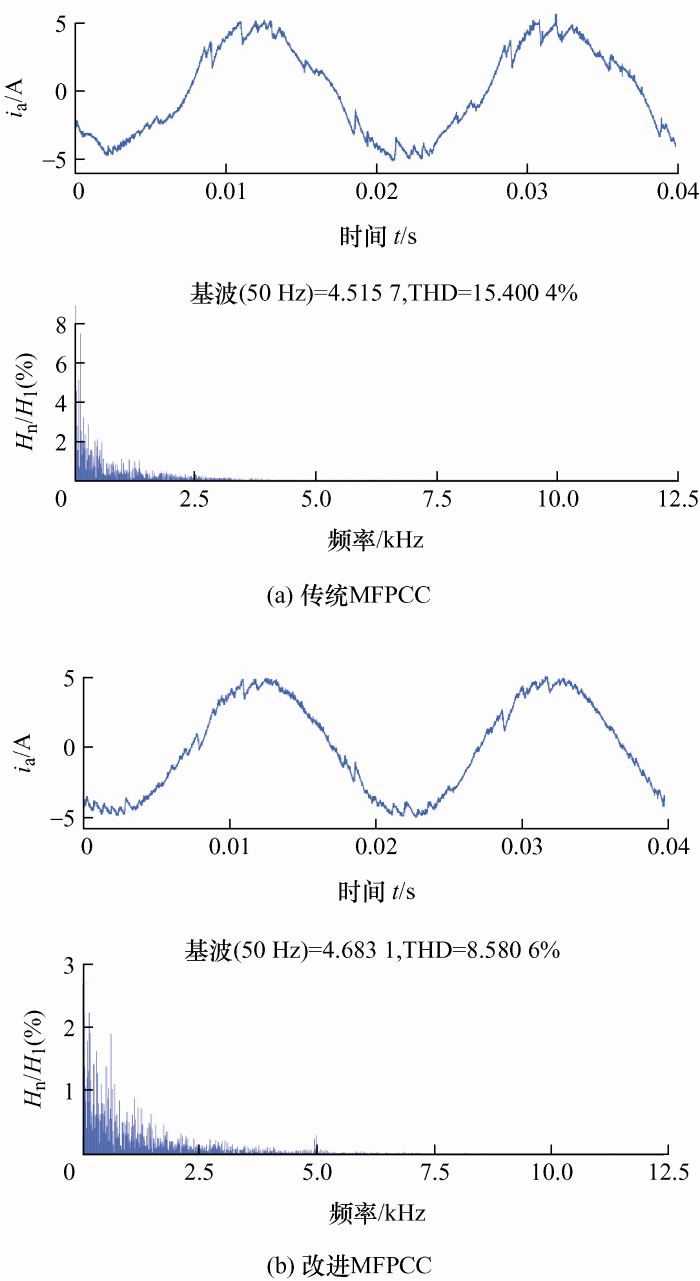
1
2008
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
同步磁阻电机矢量控制研究
1
2015
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Research on vector control of synchronous reluctance motor
1
2015
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
一种新型的交流电机离散电流调节器设计
1
2017
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
A novel design method of AC motor current regulator in discrete-time domain
1
2017
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
轴向叠片各向异性转子同步磁阻电机直接转矩控制的研究
1
2006
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Research on direct torque control of synchronous reluctance motor with axially layered anisotropic rotors
1
2006
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
交流电机控制策略的发展综述
1
2011
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Review of development of AC motor control strategy
1
2011
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Model predictive control for power converters and drives:Advances and trends
1
2017
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Model predictive control of PMSM drives based on general discrete space vector modulation
1
2021
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
感应电机三矢量模型预测磁链控制
1
2017
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
A three-vectors-based model predictive flux control of induction motor drives
1
2017
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Overview of model predictive control for induction motor drives
1
2016
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Performance evaluation of two-vector-based model predictive current control of PMSM drives
1
2018
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Model predictive control for synchronous reluctance motor drive
1
2017
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Vector control of a synchronous reluctance motor including saturation and iron loss
1
1991
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Review of parameter identification and sensorless control methods for synchronous reluctance machines
1
2020
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Parameter identification and self-commissioning in AC motor drives:A technology status review
1
2019
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Robust model predictive current control based on inductance and flux linkage extraction algorithm
1
2020
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Offset-free direct power control of DFIG under continuous-time model predictive control
2
2017
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
... .文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Zynq implemented Luenberger disturbance observer based predictive control scheme for PMSM drives
2
2020
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
... ]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Adaptive complementary sliding mode control for synchronous reluctance motor with direct-axis current control
1
2022
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
A robust current controller design method for highly nonlinear synchronous reluctance motors
1
2020)
... 同步磁阻电机(Synchronous reluctance motor, SynRM)由于其转子结构简单、成本低、调速范围广的优点在工业传动和电动汽车中得到广泛应用[1].SynRM驱动的控制方法有磁场定向控制(Field oriented control, FOC)[2-3]、直接转矩控制(Direct torque control, DTC)[4]和模型预测控制(Model predictive control, MPC)[5⇓⇓⇓⇓-10]等.在SynRM驱动控制中,为简化系统描述,常假设电机参数固定,不考虑电感磁饱和,而在实际运行工况中,受主磁路饱和与交叉饱和的影响,电机参数并非定值,严重影响电机的高性能控制[11-12].对电机参数进行离线或在线辨识能够减少参数不匹配的影响,但存在计算量大、精确性以及稳定性低的问题[13-14].文献[15]研究了在线电感自适应算法,然而在线多参数识别存在秩不足的问题,因此可能需要额外的信号注入来达到满秩条件.此外,由于逆变器的非线性和不同参数之间的耦合效应,在低速或小电流工况下难以实现良好的精度.为了获得较好的控制性能,现有文献提出利用扰动观测器的方法来观察由参数误差引起的扰动项并进行补偿[16-17].文献[16]在基于连续时间的预测控制方法中增加了扰动观测器,当电机参数发生变化或外部干扰时,电机驱动仍能保持良好的控制性能.文献[17]则使用龙贝格观测器来估计下一个控制周期的定子电流和电机参数失配引起的扰动.现有文献中还提出了自适应互补滑模控制[18]和鲁棒预测电流控制[19]等控制策略来抑制参数摄动和外部电压扰动的负面影响.然而,这些方法需要较大的计算量,并且其性能取决于观测器参数的设计和调整,这增加了控制器的设计工作. ...
Model-free predictive current control for interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor drives based on current difference detection technique
2
2014
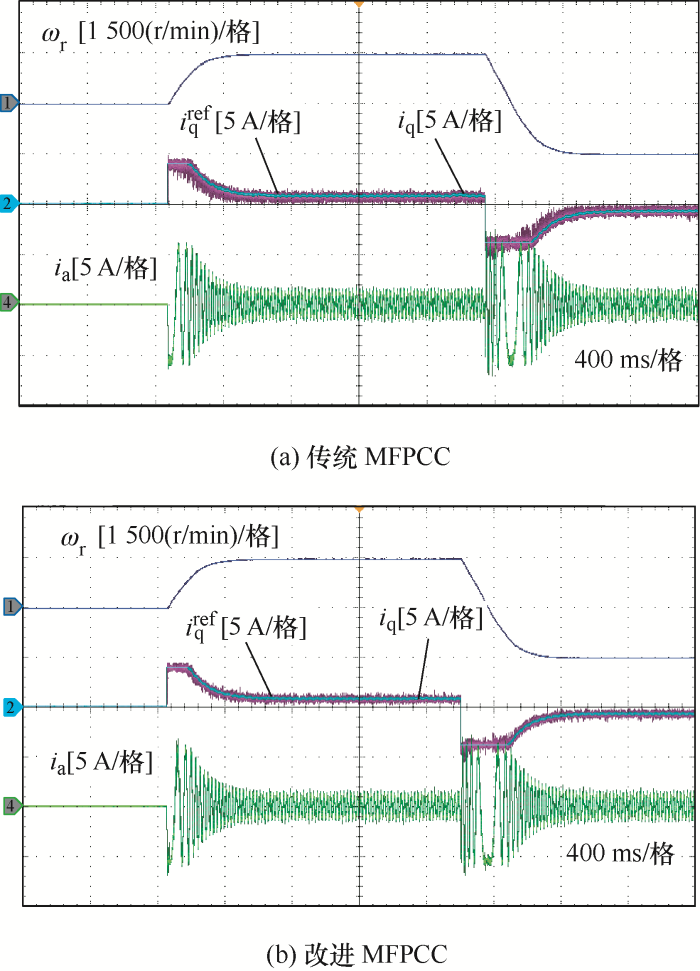
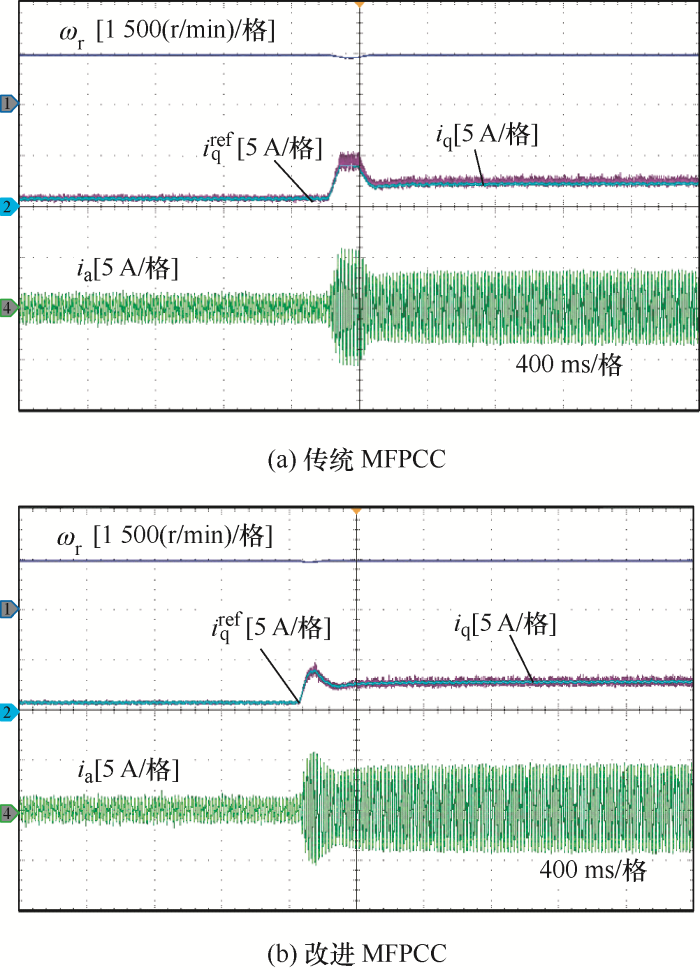
... 针对这种参数不确定性的非线性系统,有学者提出无模型预测电流控制(Model-free predictive current control, MFPCC)方法,基于电流测量和计算的电流差分来预测未来的定子电流,但该方法对电机参数变化和反电动势不敏感[20].传统的MFPCC在一个开关周期内,采用一维查找表(1D-LUT)来存储由逆变器提供的所有基本电压矢量的电流差分,存储的电流差分在线更新,用于MFPCC的电流预测[20],但是要求在一个控制周期内对电流进行两次采样,这增加了硬件采样次数.文献[21]提出在一个控制周期内只需要进行一次电流采样的改进MFPCC,降低了对硬件检测的要求.MFPCC的一个关键参数是LUT的更新频率.如果频率过低,某一特定电压矢量引起的电流差分在较长时间内没有更新,存储的电流差分信息是不可靠的,会影响电流预测精度,长时间的更新停滞甚至会影响系统的稳定性[22].为了解决这个问题,文献[22]提出了一种简单的提高更新频率的方法,对电流差分LUT施加一个较小的刷新频率,如果在预定义的时间周期内没有施加某个电压矢量,它将被强制施加到之后的控制周期.这在一定程度上解决了电流差分更新停滞的问题,但忽略了电压矢量最优检测,以增加电流纹波为代价来获取更新信息.文献[23]采用与最新的三个基本电压矢量对应的电流差分来更新其他电压矢量的电流差分,需要一个序列识别算法和更新规则,将210个可能的向量组合分成6组,但这大大增加了算法的复杂度,并且只有当有三个不同的电压矢量时,才能激活此更新机制. ...
... [20],但是要求在一个控制周期内对电流进行两次采样,这增加了硬件采样次数.文献[21]提出在一个控制周期内只需要进行一次电流采样的改进MFPCC,降低了对硬件检测的要求.MFPCC的一个关键参数是LUT的更新频率.如果频率过低,某一特定电压矢量引起的电流差分在较长时间内没有更新,存储的电流差分信息是不可靠的,会影响电流预测精度,长时间的更新停滞甚至会影响系统的稳定性[22].为了解决这个问题,文献[22]提出了一种简单的提高更新频率的方法,对电流差分LUT施加一个较小的刷新频率,如果在预定义的时间周期内没有施加某个电压矢量,它将被强制施加到之后的控制周期.这在一定程度上解决了电流差分更新停滞的问题,但忽略了电压矢量最优检测,以增加电流纹波为代价来获取更新信息.文献[23]采用与最新的三个基本电压矢量对应的电流差分来更新其他电压矢量的电流差分,需要一个序列识别算法和更新规则,将210个可能的向量组合分成6组,但这大大增加了算法的复杂度,并且只有当有三个不同的电压矢量时,才能激活此更新机制. ...
基于单次电流采样的永磁同步电机无模型预测电流控制
1
2017
... 针对这种参数不确定性的非线性系统,有学者提出无模型预测电流控制(Model-free predictive current control, MFPCC)方法,基于电流测量和计算的电流差分来预测未来的定子电流,但该方法对电机参数变化和反电动势不敏感[20].传统的MFPCC在一个开关周期内,采用一维查找表(1D-LUT)来存储由逆变器提供的所有基本电压矢量的电流差分,存储的电流差分在线更新,用于MFPCC的电流预测[20],但是要求在一个控制周期内对电流进行两次采样,这增加了硬件采样次数.文献[21]提出在一个控制周期内只需要进行一次电流采样的改进MFPCC,降低了对硬件检测的要求.MFPCC的一个关键参数是LUT的更新频率.如果频率过低,某一特定电压矢量引起的电流差分在较长时间内没有更新,存储的电流差分信息是不可靠的,会影响电流预测精度,长时间的更新停滞甚至会影响系统的稳定性[22].为了解决这个问题,文献[22]提出了一种简单的提高更新频率的方法,对电流差分LUT施加一个较小的刷新频率,如果在预定义的时间周期内没有施加某个电压矢量,它将被强制施加到之后的控制周期.这在一定程度上解决了电流差分更新停滞的问题,但忽略了电压矢量最优检测,以增加电流纹波为代价来获取更新信息.文献[23]采用与最新的三个基本电压矢量对应的电流差分来更新其他电压矢量的电流差分,需要一个序列识别算法和更新规则,将210个可能的向量组合分成6组,但这大大增加了算法的复杂度,并且只有当有三个不同的电压矢量时,才能激活此更新机制. ...
Model-free predictive current control for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on single current sampling
1
2017
... 针对这种参数不确定性的非线性系统,有学者提出无模型预测电流控制(Model-free predictive current control, MFPCC)方法,基于电流测量和计算的电流差分来预测未来的定子电流,但该方法对电机参数变化和反电动势不敏感[20].传统的MFPCC在一个开关周期内,采用一维查找表(1D-LUT)来存储由逆变器提供的所有基本电压矢量的电流差分,存储的电流差分在线更新,用于MFPCC的电流预测[20],但是要求在一个控制周期内对电流进行两次采样,这增加了硬件采样次数.文献[21]提出在一个控制周期内只需要进行一次电流采样的改进MFPCC,降低了对硬件检测的要求.MFPCC的一个关键参数是LUT的更新频率.如果频率过低,某一特定电压矢量引起的电流差分在较长时间内没有更新,存储的电流差分信息是不可靠的,会影响电流预测精度,长时间的更新停滞甚至会影响系统的稳定性[22].为了解决这个问题,文献[22]提出了一种简单的提高更新频率的方法,对电流差分LUT施加一个较小的刷新频率,如果在预定义的时间周期内没有施加某个电压矢量,它将被强制施加到之后的控制周期.这在一定程度上解决了电流差分更新停滞的问题,但忽略了电压矢量最优检测,以增加电流纹波为代价来获取更新信息.文献[23]采用与最新的三个基本电压矢量对应的电流差分来更新其他电压矢量的电流差分,需要一个序列识别算法和更新规则,将210个可能的向量组合分成6组,但这大大增加了算法的复杂度,并且只有当有三个不同的电压矢量时,才能激活此更新机制. ...
Improved model-free predictive current control for synchronous reluctance motor drives
2
2016
... 针对这种参数不确定性的非线性系统,有学者提出无模型预测电流控制(Model-free predictive current control, MFPCC)方法,基于电流测量和计算的电流差分来预测未来的定子电流,但该方法对电机参数变化和反电动势不敏感[20].传统的MFPCC在一个开关周期内,采用一维查找表(1D-LUT)来存储由逆变器提供的所有基本电压矢量的电流差分,存储的电流差分在线更新,用于MFPCC的电流预测[20],但是要求在一个控制周期内对电流进行两次采样,这增加了硬件采样次数.文献[21]提出在一个控制周期内只需要进行一次电流采样的改进MFPCC,降低了对硬件检测的要求.MFPCC的一个关键参数是LUT的更新频率.如果频率过低,某一特定电压矢量引起的电流差分在较长时间内没有更新,存储的电流差分信息是不可靠的,会影响电流预测精度,长时间的更新停滞甚至会影响系统的稳定性[22].为了解决这个问题,文献[22]提出了一种简单的提高更新频率的方法,对电流差分LUT施加一个较小的刷新频率,如果在预定义的时间周期内没有施加某个电压矢量,它将被强制施加到之后的控制周期.这在一定程度上解决了电流差分更新停滞的问题,但忽略了电压矢量最优检测,以增加电流纹波为代价来获取更新信息.文献[23]采用与最新的三个基本电压矢量对应的电流差分来更新其他电压矢量的电流差分,需要一个序列识别算法和更新规则,将210个可能的向量组合分成6组,但这大大增加了算法的复杂度,并且只有当有三个不同的电压矢量时,才能激活此更新机制. ...
... .为了解决这个问题,文献[22]提出了一种简单的提高更新频率的方法,对电流差分LUT施加一个较小的刷新频率,如果在预定义的时间周期内没有施加某个电压矢量,它将被强制施加到之后的控制周期.这在一定程度上解决了电流差分更新停滞的问题,但忽略了电压矢量最优检测,以增加电流纹波为代价来获取更新信息.文献[23]采用与最新的三个基本电压矢量对应的电流差分来更新其他电压矢量的电流差分,需要一个序列识别算法和更新规则,将210个可能的向量组合分成6组,但这大大增加了算法的复杂度,并且只有当有三个不同的电压矢量时,才能激活此更新机制. ...
An effective model-free predictive current control for synchronous reluctance motor drives
1
2019
... 针对这种参数不确定性的非线性系统,有学者提出无模型预测电流控制(Model-free predictive current control, MFPCC)方法,基于电流测量和计算的电流差分来预测未来的定子电流,但该方法对电机参数变化和反电动势不敏感[20].传统的MFPCC在一个开关周期内,采用一维查找表(1D-LUT)来存储由逆变器提供的所有基本电压矢量的电流差分,存储的电流差分在线更新,用于MFPCC的电流预测[20],但是要求在一个控制周期内对电流进行两次采样,这增加了硬件采样次数.文献[21]提出在一个控制周期内只需要进行一次电流采样的改进MFPCC,降低了对硬件检测的要求.MFPCC的一个关键参数是LUT的更新频率.如果频率过低,某一特定电压矢量引起的电流差分在较长时间内没有更新,存储的电流差分信息是不可靠的,会影响电流预测精度,长时间的更新停滞甚至会影响系统的稳定性[22].为了解决这个问题,文献[22]提出了一种简单的提高更新频率的方法,对电流差分LUT施加一个较小的刷新频率,如果在预定义的时间周期内没有施加某个电压矢量,它将被强制施加到之后的控制周期.这在一定程度上解决了电流差分更新停滞的问题,但忽略了电压矢量最优检测,以增加电流纹波为代价来获取更新信息.文献[23]采用与最新的三个基本电压矢量对应的电流差分来更新其他电压矢量的电流差分,需要一个序列识别算法和更新规则,将210个可能的向量组合分成6组,但这大大增加了算法的复杂度,并且只有当有三个不同的电压矢量时,才能激活此更新机制. ...
Model-free control and intelligent PID controllers:Towards a possible trivialization of nonlinear control
1
2009
... 另外,FLIESS等[24]在2009年提出基于超局部模型的MFPCC,基于系统短时间内的输入和输出数据建立超局部模型,其中系统的不确定项可以通过微分代数方法[25⇓-27]或扩展状态观测器[28-29]得到.然而,在超局部模型中系统输入的增益是假定已知的或基于经验程序获得的,调优工作不可避免. ...
“Intelligent” controllers on cheap and small programmable devices
1
2013
... 另外,FLIESS等[24]在2009年提出基于超局部模型的MFPCC,基于系统短时间内的输入和输出数据建立超局部模型,其中系统的不确定项可以通过微分代数方法[25⇓-27]或扩展状态观测器[28-29]得到.然而,在超局部模型中系统输入的增益是假定已知的或基于经验程序获得的,调优工作不可避免. ...
Model-free control
1
2013
... 另外,FLIESS等[24]在2009年提出基于超局部模型的MFPCC,基于系统短时间内的输入和输出数据建立超局部模型,其中系统的不确定项可以通过微分代数方法[25⇓-27]或扩展状态观测器[28-29]得到.然而,在超局部模型中系统输入的增益是假定已知的或基于经验程序获得的,调优工作不可避免. ...
Model-free predictive current control of PMSM drives based on ultra-local model
1
2019
... 另外,FLIESS等[24]在2009年提出基于超局部模型的MFPCC,基于系统短时间内的输入和输出数据建立超局部模型,其中系统的不确定项可以通过微分代数方法[25⇓-27]或扩展状态观测器[28-29]得到.然而,在超局部模型中系统输入的增益是假定已知的或基于经验程序获得的,调优工作不可避免. ...
Model-free predictive current control of PMSM drives based on extended state observer using ultra-local model
1
2021
... 另外,FLIESS等[24]在2009年提出基于超局部模型的MFPCC,基于系统短时间内的输入和输出数据建立超局部模型,其中系统的不确定项可以通过微分代数方法[25⇓-27]或扩展状态观测器[28-29]得到.然而,在超局部模型中系统输入的增益是假定已知的或基于经验程序获得的,调优工作不可避免. ...
基于扩展滑模扰动观测器的永磁同步电机新型无模型滑模控制
1
2022
... 另外,FLIESS等[24]在2009年提出基于超局部模型的MFPCC,基于系统短时间内的输入和输出数据建立超局部模型,其中系统的不确定项可以通过微分代数方法[25⇓-27]或扩展状态观测器[28-29]得到.然而,在超局部模型中系统输入的增益是假定已知的或基于经验程序获得的,调优工作不可避免. ...
New model-free sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on extended sliding mode disturbance observer
1
2022
... 另外,FLIESS等[24]在2009年提出基于超局部模型的MFPCC,基于系统短时间内的输入和输出数据建立超局部模型,其中系统的不确定项可以通过微分代数方法[25⇓-27]或扩展状态观测器[28-29]得到.然而,在超局部模型中系统输入的增益是假定已知的或基于经验程序获得的,调优工作不可避免. ...
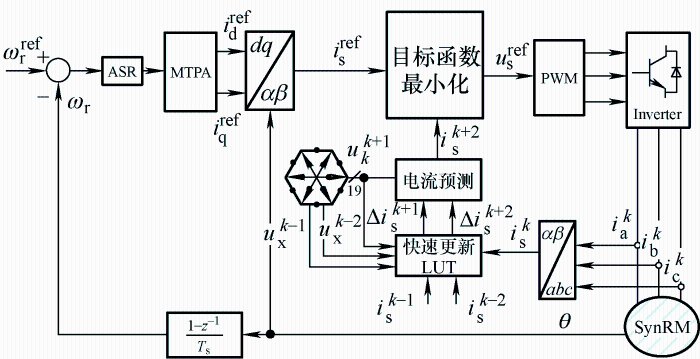
Finite-control-set model predictive direct torque control with extended set of voltage space vectors
1
... 为获得更精确的电压矢量,文献[30]提出扩展电压矢量方案,通过调整逆变器的开关切换状态扩展电压矢量,可以获取更多的候选电压矢量,明显加快了响应速度,减小了电流纹波,但其还是基于MPC方法,未在MFPCC上应用. ...
Robust predictive current control of induction motors based on linear extended state observer
1
2021
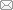
... 在
坐标系下,建立SynRM的超局部数学模型为
[31] ...