1 引言
目前,国内外学者提出了大量动力电池SOC估计方法,大致可以分为安时积分法[7]、基于表征参数的方法[8,9,10]、基于电池模型的方法[11,12,13,14]、基于数据驱动的方法[15,16,17,18]。其中,基于模型的SOC估计方法是一种闭环控制的方法,它通过不断地修正SOC估计值,使得算法具有良好的鲁棒性和精准性。该方法是利用电池的电化学模型[19]或等效电路模 型[20],通过状态估计算法实现对电池SOC的估计。电池的电化学模型基于电化学反应原理,通过一系列偏微分方程可以详尽描述电池的内部特性。现应用于电池SOC估计的电化学模型有一维模型、伪二维模型、单粒子模型等。但该类模型的结构复杂,参数繁多且运算量极大[21],往往难以精准建模,不适合用于SOC在线实时估计。而电池的等效电路模型由电阻、电容、电压源等电路元件组成,通过不同的组合构成电路网络来描述电池的外特性,其模型结构相对简单、计算量小[22],具有良好的实时性,在实车BMS中有很好的应用前景。目前,国内外广泛应用的基于等效电路模型的SOC估计方法有卡尔曼滤波算法(Kalman filter,KF)类[23]、滑模观测器法(Sliding mode observers,SMO)[24]、H∞滤波算法(H∞ filter,HIF)[25]以及复合方法[26]等。
鉴于近年来电池技术发展迅猛,关于动力电池SOC估计方法的研究更是层出叠现,有必要对相关技术进行比较和总结,以理清技术难点和关键,并研判相关技术发展动向。为此,本文首先梳理归纳了国内外常见的电池等效电路模型,重点对基于等效电路模型的SOC估计方法进行了总结和比较,分析了影响SOC估计精度的因素及应对策略。最后,对未来SOC估计的研究动向进行了讨论和展望。
2 电池的等效电路模型
建立精准的电池模型是基于模型的方法实现电池SOC估计的前提[27]。除此之外,精准建模有利于更准确地描述电池的外特征,设计可靠的电池状态估计算法,以开发出性能更优良的BMS。因此,对电池模型的研究具有极为重要的意义。由于等效电路模型结构相对简单、计算量小、精准度较好,其应用场景更为广泛,下面对目前常用的5种等效电路模型进行总结和比较。
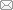
2.1 Rint模型
图1
其状态方程为
该模型简单、易实现,但未考虑电池的极化现象,其适用范围小。当通过电池的电流较大时,其误差也很大。因此,该方法大多是基于电池的OCV-SOC关系,利用参数辨识的算法,实现对电池SOC的估计。
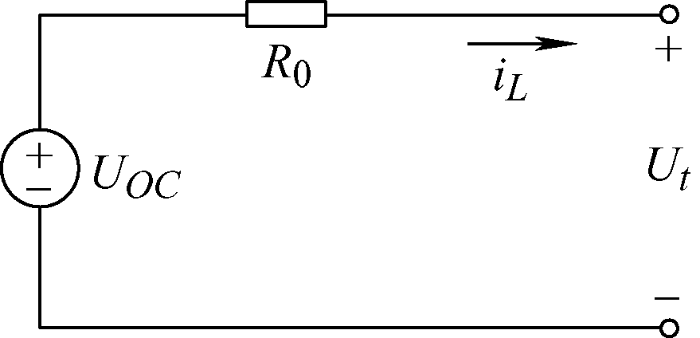
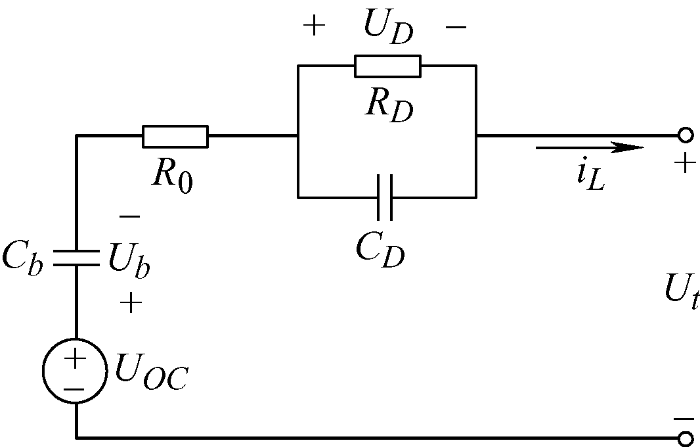
2.2 Thevenin模型
图2
其状态方程为
与Rint模型相比,Thevenin模型考虑了电池的动态特性,因此其准确性更高,并且它的结构也相对简单,计算量不大,具有比较高的应用价值。
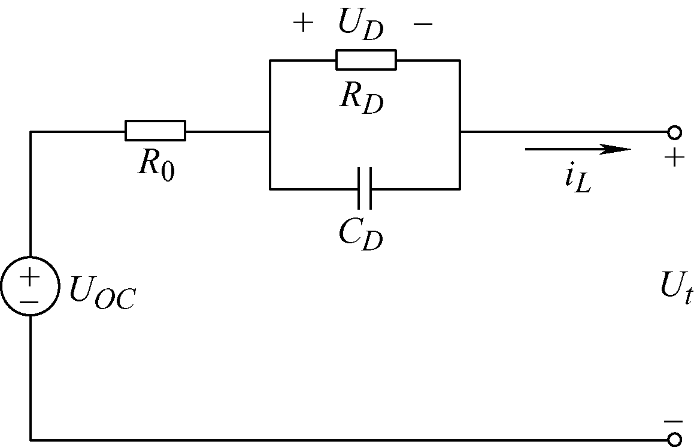
2.3 双极化模型
图3
其状态方程为
由于该模型是由两个RC网络串联而成的,结构更加复杂,但它对电池极化特征的描述更为准确,更能准确模拟电池的实际特性。鉴于上述原因,该模型在估计大倍率工况条件下的电池SOC具有更高的精度。文献[31]则对该模型进行了改进,用受控电压源来表征电池的开路电压,以体现电池的OCV-SOC关系,使模型更加精准。
电池的等效电路模型随着串联RC网络数量的增加,其精准性会更高,更有利于对电池端电压的准确描述。若推广到n个RC网络环节,就构成了电池的n-RC模型[32],但RC环节数量的增加势必会导致计算量的剧增。因此,常用的电池模型是n-RC等效电路模型分别在n=0,n=1和n=2时的特例,即Rint模型、Thevenin模型和双极化模型。
2.4 PNGV 模型
图4
其状态方程为
该模型考虑了负载电流的时间累计对OCV的影响,即SOC变化对OCV的影响,因此既可表示电池电压在某一SOC值下的暂态响应,又可表示电池电压的稳态变化。
2.5 GNL模型
图5
其状态方程为
GNL模型不仅考虑了动力电池SOC变化对OCV的影响,还考虑了电池的自放电现象,是5种等效电路模型中精准性最高的。但其结构也是最复杂的,应用于电池SOC估计时计算成本较高。因此,GNL模型在动力电池SOC估计中的应用性较差。
综上,5种常用的动力电池等效电路模型的比较归纳结论可如表1所示。
表1 电池等效电路模型的比较
| 模型 | 优点 | 缺点 | 精准性 | 应用性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rint模型 | 模型结构简单 | 精度低 | 差 | 差 |
| Thevenin模型 | 模型结构较简单考虑了电池动态特性 | 对电池实际特性的描述存在局限 | 较好 | 好 |
| 双极化 模型 | 能准确模拟电池动态特性 | 模型结构复杂 计算成本较高 | 好 | 好 |
| PNGV 模型 | 考虑了电池动态特性;考虑了SOC变化对OCV的影响 | 模型结构较复杂 | 较好 | 较好 |
| GNL模型 | 能准确模拟电池动态特性;考虑了自放电现象 | 模型结构太复杂计算成本高 | 好 | 较差 |
3 基于等效电路模型的估计方法
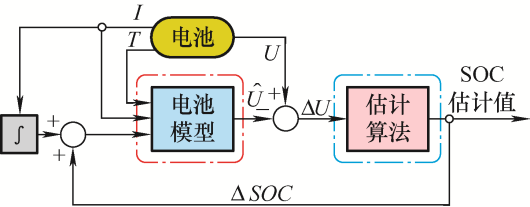
基于等效电路模型SOC估计方法的结构如图6所示,它主要由两个部分组成:电池模型和状态估计算法。该方法中,需要建立一个电池的等效电路模型来预测终端电压,通常是输入电流、SOC和温度。由于模型不能完全等价于实际电池,且测量中存在噪声,SOC估计难免存在误差。为了减小误差,可利用电池模型输出与终端电压之间的偏差来修正每个采样时间内的SOC。然后,修正后的SOC作为电池模型的输入,计算下一个循环的终端电压。因此,该类方法是一种闭环反馈控制的方法,通过不断地修正SOC估计值,使得算法具有良好的鲁棒性和精准性。
图6
目前,国内外学者研究比较多的方法主要有:卡尔曼滤波法、滑模观测器法、H∞滤波法以及复合方法。
3.1 卡尔曼滤波法
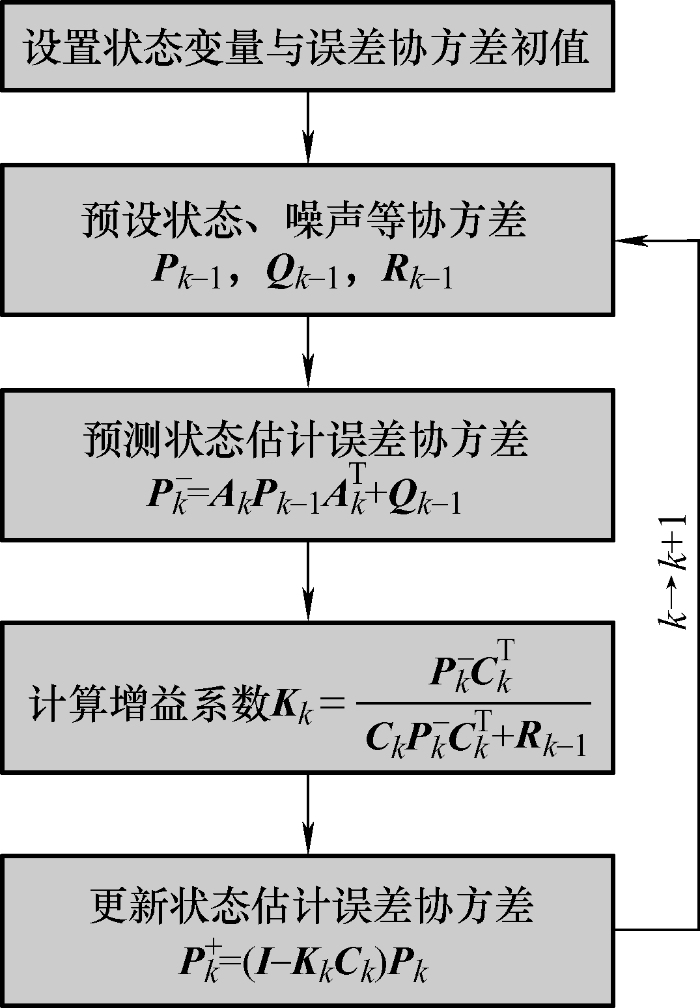
1960年,R. E. Kalman最早提出了卡尔曼滤波算法,它是一种最优化自回归数据处理算法,通过系统输入输出数据,实现对系统状态的最优估计。对于离散系统,其状态方程和观测方程的一般形式如下
式中,x为系统状态矢量;u为系统输入矢量;y为系统输出矢量;$\boldsymbol{\omega}_{k-1}$为系统白噪声,协方差为Qk;vk为测量白噪声,协方差为Rk。
KF算法的计算流程图如图7所示。其中,P为状态估计误差协方差;K为卡尔曼增益矩阵。
图7
3.1.1 扩展卡尔曼滤波法
对于非线性离散系统,其状态方程和观测方程的一般形式如下
式中,$ f\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{k-1}, \boldsymbol{u}_{k-1}\right)$为系统状态方程函数;$h\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{k}, \boldsymbol{u}_{k}\right)$为系统观测方程函数。
EKF对$ f\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{k-1}, \boldsymbol{u}_{k-1}\right)$和$h\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{k}, \boldsymbol{u}_{k}\right)$利用泰勒级数展开,将非线性函数线性化,得到线性化后的状态方程和观测方程为
式中,$\boldsymbol{A}_{k}=\left.\frac{\partial f\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{k}, \boldsymbol{u}_{k}\right)}{\partial \boldsymbol{x}_{k}}\right|_{\boldsymbol{x}_{k}=\hat{x}_{k}}$,$\boldsymbol{C}_{k}=\left.\frac{\partial h\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{k}, \boldsymbol{u}_{k}\right)}{\partial \boldsymbol{x}_{k}}\right|_{\boldsymbol{x}_{k}=\hat{x}_{k}}$;$\hat{\boldsymbol{x}}$为x的估计值。
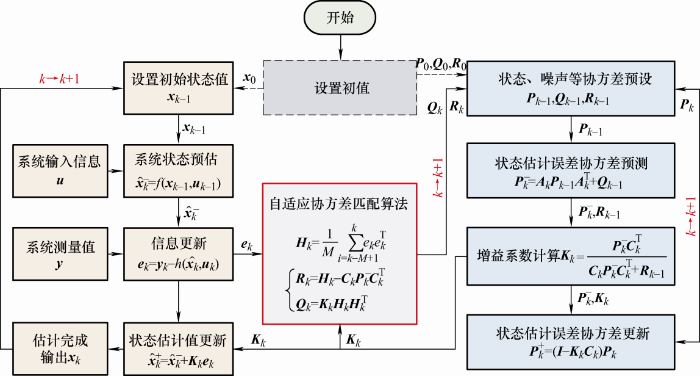
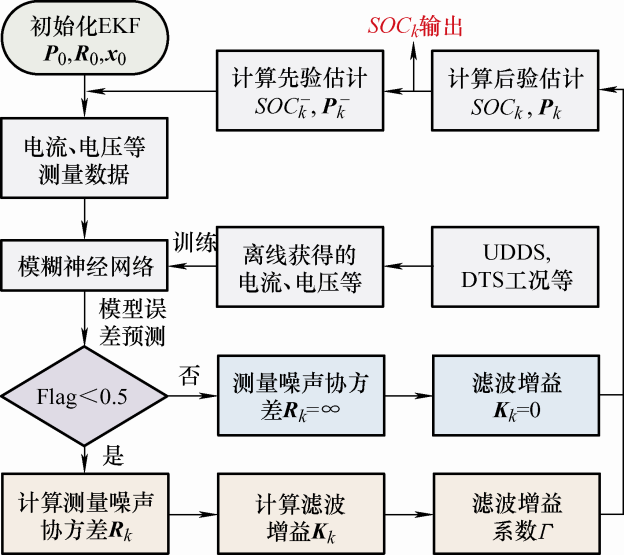
但在线性化处理中,忽略了高阶项,必然会引起估计结果的误差,并且雅可比矩阵复杂难计算。针对这一问题,许多学者提出了改进的EKF算法。文献[38]设计了一种基于自适应扩展卡尔曼滤波(Adaptive extended Kalman filter,AEKF)算法的SOC估计方法,提升了算法的精度和鲁棒性,其计算流程如图8所示。其中,H是由开窗估计原理得到的新息实时估计协方差函数;M为开窗的大小。文献[39]则用有限差分法取代了EKF算法中非线性函数的偏导运算,提出了一种基于有限差分EKF算法的电池SOC估计方法,降低了模型线性化时所产生的误差,提高了电池SOC估计的精度和鲁棒性。文献[40]进一步提出了一种将灰色预测模型与EKF算法相结合的估计方法,该方法在电池参数急剧变化时仍能准确估算电池的SOC值。
图8
3.1.2 无迹卡尔曼滤波法
与EKF相比,UKF不需要对非线性函数做线性化处理,而是通过无迹变换在估计点附近进行Sigma采样,利用这些采样点表示的高斯密度来近似描述状态概率密度函数。
但UKF算法可能会因为误差协方差矩阵负定等因素造成滤波发散[41]。针对这一问题,文献[42]提出了一种基于平方根UKF算法的SOC估计方法,确保状态协方差的半正定性,提升了算法的稳定性。精准建模是UKF方法对电池SOC准确估计的前提,为此,文献[43]设计了一种基于自适应UKF算法的SOC估计方法,它可以实时估计电池的欧姆内阻并更新电池模型的参数,提升了模型的精度,并且该方法利用欧姆内阻值估算电池的健康状态(State of health,SOH),实现了SOC和SOH的联合估计,进而提升了估算精度。文献[44]则将上述两者相结合,提出了一种自适应平方根UKF算法,并实现了电池SOC和SOH的联合估计,提高了算法的自适应性和精准性。
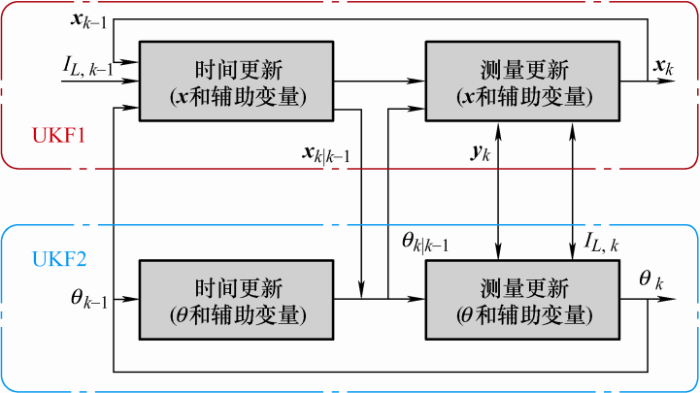
3.1.3 综合型卡尔曼滤波法
图9
3.2 滑模观测器法
滑模观测器用滑模变结构控制代替传统状态观测器中的控制回路,其通过变结构开关高频率切换,使状态的运动点始终在一个平面上小幅度运动,并最终运动到稳定点。由于滑模变结构控制有对参数变化和扰动不敏感的特点,因此,利用滑模观测器进行SOC估计具有较强的鲁棒性。
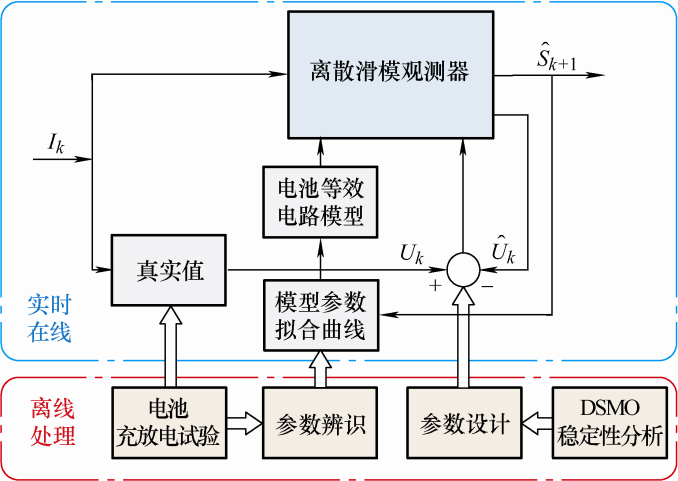
文献[48]设计了一种基于离散滑模观测器(Discrete-time sliding mode observers,DSMO)的SOC估计方法,并验证了其较好的鲁棒性。该方法的系统框图如图10所示,包括两部分:离线处理部分,主要实现电池模型参数辨识和观测器设计;实时在线部分,主要实现对电池状态的实时估计,$\hat{S}_{k+1}$即为电池的实时SOC估计值。但由于滑模观测器采用了离散开关函数,其输出具有抖动。针对这一问题,文献[49]对传统滑模观测器进行改进,摒弃符号函数而采用Sigmoid函数,一定程度上削弱了抖振。文献[50]提出了一种考虑电池容量衰减的滑模观测器SOC估计方法,减小了随着电池老化程度增加可用容量减少对SOC估计造成的误差。
图10
3.3 H∞滤波法
图11
与KF算法不同,H∞滤波算法并不要求预知精确的噪声统计特性[52],并且是最小化最大估计误差。因此,与其他基于等效电路模型的电池SOC估计方法相比,H∞滤波法在各种有色噪声、动力电池建模不精准等情况下具有更强的鲁棒性以及精 准性。
综上,各种基于等效电路模型的SOC估计方法优缺点以及鲁棒性比较见表2。
表2 基于等效电路模型的SOC估计方法比较
| SOC估计方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 鲁棒性 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡尔曼滤波法 | 扩展卡尔曼滤波法 | 克服了传统估计方法的缺点;适用于电流波动剧烈的工况 | 线性化处理产生误差 | 差 |
| 无迹卡尔曼滤波法 | 不需要对非线性函数线性化处理,避免误差 | 异常扰动、初值不确定等因素可能导致系统发散 | 较差 | |
| 综合型卡尔曼滤波法 | 结合了不同卡尔曼滤波算法的优点,估计精度高 | 需要至少两个卡尔曼滤波算法 计算复杂 | 一般 | |
| 滑模观测器法 | 对参数变化和扰动不敏感 | 输出存在抖动 | 较好 | |
| H∞滤波法 | 不要求精准的噪声统计特性,最小化最大估计误差 | 计算复杂 | 好 | |
3.4 复合算法
鉴于各种方法存在的不同缺陷,为获取更高的估计精度,将不同方法相融合的复合方法发展迅速。其中,将基于电池模型的方法和基于数据驱动的方法相融合的研究较多。将此两者结合,既能降低基于模型的估计方法对电池模型的依赖程度,又能减少基于数据驱动的估计方法的累计误差,显著提升算法性能。
图12
4 SOC估计误差及应对策略
4.1 温度对SOC估计的影响
为此,可以通过建立全温度范围内的等效电路模型来减小温度变化对SOC估计造成的影响[60]。但实际上传感器只能测量环境温度,电池内部温度无法直接测量。因此,即便建立全温度范围的等效电路模型也会因为无法准确反映电池内部温度而引起SOC估计误差。针对这一问题,文献[61]提出了一种联合扩展卡尔曼滤波的滑模观测器算法,降低了电池内外温差对SOC估计精度的影响。但该方法只是借助滑模观测器补偿电池参数变化引起的建模误差,并没有准确测量电池内部温度,对电池内外温差造成的SOC估计误差消除能力有限。为准确测量电池内部温度,文献[62]研究了一种借助电化学阻抗频谱来实现电池内部温度估计的方法,可以较为准确地测量电池内部温度,但该方法需要复杂的试验装置,不适合应用于SOC的在线实时估计。文献[63]则提出一种基于双扩展卡尔曼滤波算法的电池内部温度估计方法,在不同复杂工况以及初值不确定条件下仍具有较高的精度。尽管这些方法可以准确地测量电池内部温度,但往往都需要独立的试验装置或算法,不能实现SOC的协同估计,相对而言较复杂。
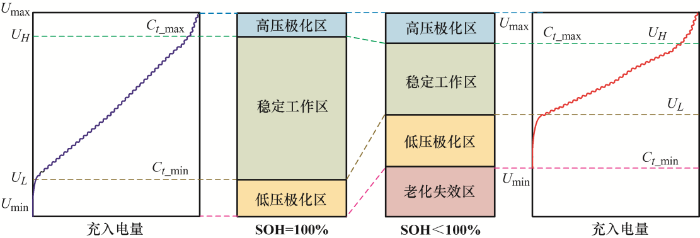
4.2 老化对SOC估计的影响
图13
4.3 模型精度对SOC估计的影响
建立精准的电池模型是基于模型的方法实现电池SOC估计的前提,电池模型不准确,必然会造成SOC估计的误差。为减小模型误差对SOC估计的影响,目前广泛采用以下两类方法。
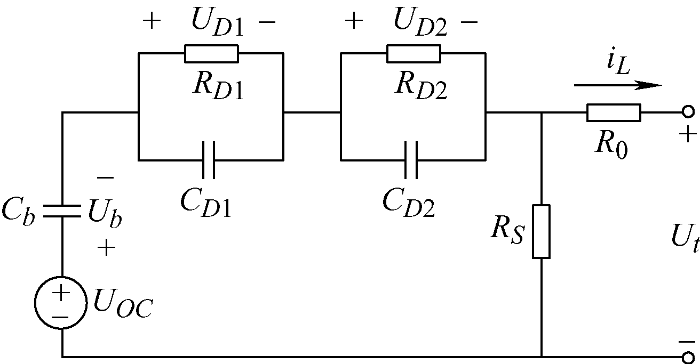
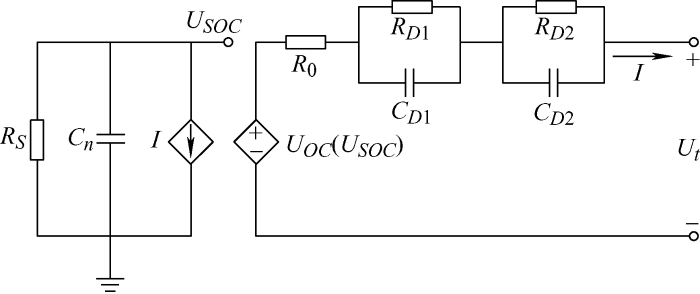
第一类方法是通过改进电池等效电路模型,以提升模型的精度。文献[66]将Butler-Volmer方程与Nernst方程一起嵌入到等效电路模型中,将电化学模型与等效电路模型相结合,提升了模型在大倍率电流下的精度。文献[67]在双极化模型的基础上,提出了一种考虑了SOC变化对OCV影响以及电池自放电现象的等效电路模型,其结构如图14所示。其中,电池的可用容量通过电容Cn和自放电电阻RS表示;电池的开路电压用一个受控电压源表示,其大小与SOC有关。通过对传统模型的改进,可以提升模型精度,但改进后的模型往往会变得复杂。针对这一问题,文献[68]对2阶RC电路模型参数的敏感性展开研究,并在此基础上,通过对非敏感参数的简化处理以达到简化模型的目的,但模型简化必然会牺牲一定的精准度。
图14
另一类方法是借助算法来补偿电池模型的误差,以提升SOC估计的准确性。文献[43, 46, 62]分别采用了无迹卡尔曼滤波,双扩展卡尔曼滤波以及扩展卡尔曼滤波与滑模观测器相结合的方法抑制模型误差对SOC估计的影响。文献[69]提出了一种安时积分法与EKF结合的复合方法,能有效抑制传感器和模型误差对SOC估计造成的负面影响。
4.4 电池组SOC估计
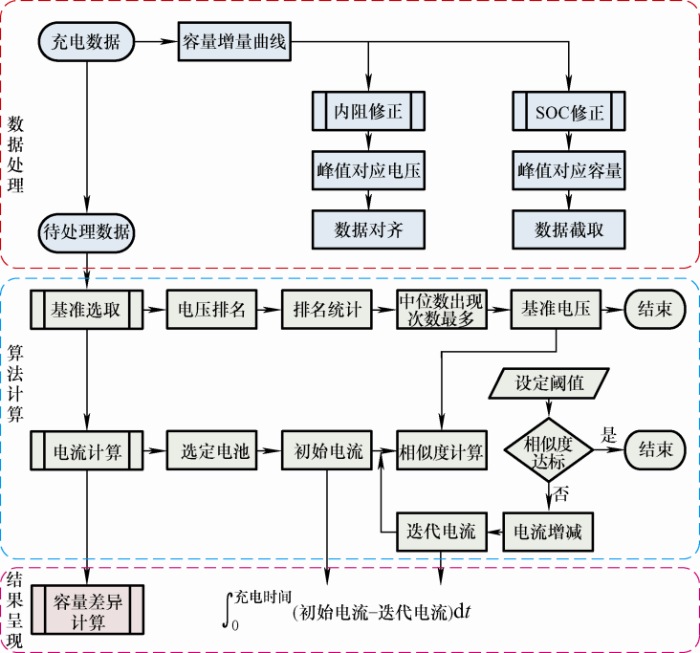
针对电池组中单体电池性能不一致的问题,许多学者提出了电池组均衡控制的策略。文献[72]提出一种将等效电路模型与热模型相融合的电池模型,以实现电池组的均衡控制,但当电池处于电压平台期时,尽管电池组的电压差异较小,其SOC仍具有较大的差异,均衡效果不理想。文献[73]提出了一种基于模糊逻辑控制的均衡方法,以SOC为均衡变量,对Thevenin模型借助EKF得到SOC估计值,然而其均衡结果依赖于电池SOC估计的精确性。文献[74]建立了一种快速容量差异辨识的方法,采用容量增量分析法修正SOC和内阻的估算误差,且仅需要通过一次恒流充电或放电的电池组电压数据即可快速辨识电池组容量的差异,为电池组的均衡控制提供了重要参考,其算法流程如图15所示。
图15
5 讨论与展望
尽管近些年来有关电池SOC估计方法在理论研究及实车应用方面有一定的突破,但仍未出现可同时满足高实时性、准确性、鲁棒性以及电池组均衡管理的高性能估计方法。未来电池SOC估计方法的研究热点和发展动向需重点关注以下几个方面。
(1) 多约束估计。电池SOC估计受许多因素的影响。环境温度、自身充放电产热、循环次数、放电倍率、自放电以及老化程度等因素都会对SOC的准确估计产生影响。SOC估计要充分考虑这些因素的影响,建立全温度范围以及全寿命周期的SOC估计方法仍会是未来研究的重点。除此之外,目前大多数研究是在实验室进行的,难以真实模拟实车运行中的复杂工况。因此,有必要在自然环境中进行更多的研究,以检查热、冷、雪、雨、湿等不同环境条件的影响。
(2) 电池的多模型融合以及模型的优化与简化。电池的精准建模是基于模型的方法进行SOC估计的前提。对于电池这个复杂系统,单一模型往往很难完全模拟电池的实际运行,将电池电化学模型、等效电路模型、热模型等相融合,得到既能反映内部化学特性又能保持一定的快速动态跟踪能力的复合电池模型会是未来电池建模的趋势。但模型的精度与计算量往往是对立关系,因此,对电池模型的优化改进与简化亦十分重要。
(3) 电池组的均衡控制。电池参数和工作状态的不一致性引起的“短板效应”和“恶性循环”,严重制约了电池组的整体性能。目前的均衡控制研究大多都以SOC作为控制变量,且取得了一定的突破,但建立满足均衡速度、精度以及效率要求的高性能均衡管理系统仍需要进一步研究。
(4) 多状态联合估计与多方法融合估计。电池是一个具有强时变性、非线性等特点的系统,其工作状态之间必然存在复杂的耦合关系,很难独立地对电池某个工作状态进行估计。因此,对电池多状态的协同估计方法需要更深入的研究。此外,在现有研究基础上,将不同估计方法相融合以得到更高效、精准、低成本的复合估计方法仍会是未来的研究热点之一,并且将已有的SOC估计方法与大数据处理以及人工智能算法的结合可能会占据重要 地位。
6 结论
电池SOC估计是BMS最关键的功能之一,是其他状态估计的前提。在众多估计方法中,基于等效电路模型的SOC估计方法具有较好的精准性和鲁棒性,且模型结构简单、计算量相对较小,在电动汽车BMS中应用前景明朗。本文总结了动力电池5种常用的等效电路模型,对其优缺点进行了分析和比较;重点梳理了基于等效电路模型的SOC估计方法,并进行了综合分析与比较;探讨了影响电池SOC估计的主要症结:温度、老化、模型精度以及电池组均衡问题,并对目前的一些应对策略进行了归纳。最后,对SOC未来的发展动向与研究热点进行了讨论与展望。
参考文献
Active equalization control strategy of Li‐ion battery based on state of charge estimation of an electrochemical‐thermal coupling model
[J].
Critical review on the battery state of charge estimation methods for electric vehicles
[J].
Real-time estimation of state-of-charge in lithium-ion batteries using improved central difference transform method
[J].
A review on battery management system from the modeling efforts to its multiapplication and integration
[J].
A novel model-based state of charge estimation for lithium-ion battery using adaptive robust iterative cubature Kalman filter
[J].
State of charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries using hybrid autoencoder and long short term memory neural networks
[J].
A data-driven coulomb counting method for state of charge calibration and estimation of lithium-ion battery
[J].
A novel approach to reconstruct open circuit voltage for state of charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles
[J].
A systematic model-based degradation behavior recognition and health monitoring method for lithium-ion batteries
[J].
Enhanced online model identification and state of charge estimation for lithium-ion battery under noise corrupted measurements by bias compensation recursive least squares
[J].
Sequential Monte Carlo filter for state-of-charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on auto regressive exogenous model
[J].
Learning of battery model bias for effective state of charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries
[J].
A high-order state-of-charge estimation model by cubature particle filter
[J].
State of charge estimation of a lithium-ion battery based on adaptive Kalman filter method for an equivalent circuit model
[J].
Reliable state of charge estimation of battery packs using fuzzy adaptive federated filtering
[J].
Online state-of-health estimation for Li-ion battery using partial charging segment based on support vector machine
[J].
Hybrid state of charge estimation for lithium-ion battery under dynamic operating conditions
[J].
Lithium-ion batteries state of charge prediction of electric vehicles using RNNs-CNNs neural networks
[J].
State of charge estimation for lithium-ion battery using an electrochemical model based on electrical double layer effect
[J].
Quadrature Kalman filter-based state of charge estimation for lithium-ion battery
[J].
一种高精度锂离子电池建模方案研究
[J].
Research on a high-precision modeling scheme for lithium-ion battery
[J].
平方根采样点卡尔曼滤波在磷酸铁锂电池组荷电状态估算中的应用
[J].
Application of square root sigma point Kalman filter to SOC estimation of LiFePO4 battery pack
[J].
Online parameters identification and state of charge estimation for lithium-ion capacitor based on improved cubature Kalman filter
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.est.2019.100810 URL [本文引用: 1]
Robust estimation for state-of-charge and state-of-health of lithium-ion batteries using integral-type terminal sliding-mode observers
[J].
An adaptive fusion estimation algorithm for state of charge of lithium-ion batteries considering wide operating temperature and degradation
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228132 URL [本文引用: 1]
Disturbance observer-based state-of-charge estimation for Li-ion battery used in light electric vehicles
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.est.2019.101144 URL [本文引用: 1]
State of charge estimation method based on the extended Kalman filter algorithm with consideration of time‐varying battery parameters
[J].DOI:10.1002/er.v44.13 URL [本文引用: 1]
一种动力电池动态特性建模
[J].
A modeling method for power battery dynamics
[J].
基于STF&LM算法的串联锂离子电池组不一致性辨识与状态估计
[J].
Inconsistency identification and state estimation of series-connected lithium-ion battery pack based on STF&LM algorithm
[J].
Parameter sensitivity analysis and simplification of equivalent circuit model for the state of charge of lithium-ion batteries
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2019.135239 URL [本文引用: 1]
锂离子电池建模及其参数辨识方法研究
[J].
Research on lithium-ion battery modeling and model parameter identification methods
[J].
A novel approach of battery pack state of health estimation using artificial intelligence optimization algorithm
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.11.068 URL [本文引用: 1]
Overview of model-based online state-of-charge estimation using Kalman filter family for lithium-ion batteries
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.rser.2019.06.040 URL [本文引用: 1]
Overview of lithium-ion battery modeling methods for state-of-charge estimation in electrical vehicles
[J].DOI:10.3390/app8050659 URL [本文引用: 1]
Current profile optimization for combined state of charge and state of health estimation of lithium ion battery based on Cramer-Rao bound analysis
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.63 URL [本文引用: 1]
State of charge and online model parameters co-estimation for liquid metal batteries
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.05.032 URL [本文引用: 1]
State of charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on adaptive dual Kalman filter
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.apm.2019.09.011 URL [本文引用: 1]
Online estimation of model parameters and state-of-charge of LiFePO4 batteries in electric vehicles
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.08.005
URL
[本文引用: 1]

The accurate estimation of internal parameters and state-of-charge (SoC) of battery, which greatly depends on proper models and corresponding high-efficiency, high-accuracy algorithms, is one of the critical issues for the battery management system. A model-based online estimation method of a LiFePO(4) battery is presented for application in electric vehicles (EVs) by using an adaptive extended Kalman filter (AEKF) algorithm. The Thevenin equivalent circuit model is selected to model the LiFePO(4) battery and its mathematics equations are deduced to some extent. Additionally, an implementation of the AEKF algorithm is elaborated and employed for the online parameters' estimation of the LiFePO(4) battery model. To illustrate advantages of the online parameters' estimation, a comparison analysis is performed on the terminal voltages between the online estimation and the offline calculation under the Hybrid pulse power characteristic (HPPC) test and the Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (UDDS) test. Furthermore, an efficient online SoC estimation approach based on the online estimation result of open-circuit voltage (OCV) is proposed. The experimental results show that the online SoC estimation based on OCV-SoC can efficiently limit the error below 0.041. (C) 2011 Elsevier Ltd.
基于有限差分扩展卡尔曼滤波的锂离子电池SOC估计
[J].锂离子电池荷电状态的快速准确估计是电池管理系统的关键技术。针对锂离子电池这一动态非线性系统,以二阶RC等效电路模型为基础,采用递推最小二乘法估算模型参数,运用有限差分扩展卡尔曼滤波算法对电池荷电状态进行估算。仿真结果表明,该模型能较好地体现电池的动态特性,有限差分扩展卡尔曼滤波算法在估算过程中能保持很好的精度,并可以有效地减小由模型误差引入的荷电状态估计误差。
Estimation of state of charge of lithium-ion battery based on finite difference extended Kalman filter
[J].
基于灰色扩展卡尔曼滤波的锂离子电池荷电状态估算
[J].
Estimation of lithium-ion battery state of charge based on grey prediction model-extended Kalman filter
[J].
Parameter identification and state of charge estimation of NMC cells based on improved ant lion optimizer
[J].
基于平方根无迹卡尔曼滤波的锂电池状态估计
[J].
State-of-charge estimation based on square root unscented Kalman filter algorithm for Li-ion batteries
[J].
基于自适应无迹卡尔曼滤波算法的锂离子动力电池状态估计
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.03.016
URL
[本文引用: 1]

应用传统的无迹卡尔曼滤波(unscented Kalman filter, UKF)算法估计电动汽车锂离子动力电池核电状态(state of charge, SOC)时, 常会出现由于电池模型参数不准确而造成估计误差增大的问题, 该文采用了自适应无迹卡尔曼滤波(adaptive unscented Kalman filter, AUKF)算法解决该问题。AUKF算法是一种循环迭代算法, 可以实时估计电池模型中的欧姆内阻, 提高电池模型准确性, 从而提高电池SOC估计精度。另外, 电池的欧姆内阻可以表征电池的健康状态(state of health, SOH), 因此还可以根据电池的欧姆内阻估计出电池的SOH。在设定工况下对电池做充放电实验, 实验分析表明, 与UKF相比, AUKF提高了电池SOC估计的精度, 并能准确的估计出电池的欧姆内阻。
States estimation of Li-ion power batteries based on adaptive unscented Kalman filters
[J].
基于自适应平方根无迹卡尔曼滤波算法的锂离子电池SOC和SOH估计
[J].
State of charge and state of health estimation of Li-ion batteries based on adaptive square-root unscented Kalman filters
[J].
A normal‐gamma‐based adaptive dual unscented Kalman filter for battery parameters and state‐of‐charge estimation with heavy‐tailed measurement noise
[J].DOI:10.1002/er.v44.5 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于综合型卡尔曼滤波的锂离子电池荷电状态估算
[J].
Li-ion battery state of charge estimation based on comprehensive Kalman filter
[J].
Dual EKF-based state and parameter estimator for a LiFePO4 battery cell
[J].DOI:10.6113/JPE.2017.17.2.398 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于离散滑模观测器的锂电池荷电状态估计
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.01.023
URL
[本文引用: 1]

锂电池的荷电状态(state of charge,SOC)估计是电池管理系统的重要组成部分,针对锂电池非线性的特性,提出了采用离散滑模观测器估计锂电池荷电状态的方法,给出了离散滑模观测器的设计方法及其稳定性证明。基于锂电池的戴维南等效电路模型,给出了该方法的设计过程,在不同的充放电电流倍率和环境温度下,进行了锂电池模型的参数辨识,通过与常用的扩展卡尔曼滤波法相比较,分析了离散滑模观测器对锂电池SOC估计的精度、鲁棒性和算法复杂度等方面的性能。实验结果表明,采用该算法可实现锂电池SOC快速精确地估计,误差可控制在约3%,验证了该方法的可行性。
Charge state estimation of Li-ion batteries based on discrete-time sliding mode observers
[J].
基于改进滑模观测器的锂离子电池荷电状态估计方法
[J].
Improved sliding mode observer for state of charge estimation of lithium-ion battery
[J].
State of charge estimation of vanadium redox flow battery based on sliding mode observer and dynamic model including capacity fading factor
[J].DOI:10.1109/TSTE.2017.2699288 URL [本文引用: 1]
Online capacity estimation for lithium-ion batteries through joint estimation method
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113817 URL [本文引用: 1]
一种锂离子电池荷电状态估计与功率预测方法
[J].
Method for estimation of state of charge and power prediction of lithium-ion battery
[J].
基于模糊神经网络优化扩展卡尔曼滤波的锂离子电池荷电状态估计
[J].
State of charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on extended Kalman filter optimized by fuzzy neural network
[J].
基于门控循环单元神经网络和Huber-M估计鲁棒卡尔曼滤波融合方法的锂离子电池荷电状态估算方法
[J].
A hybrid approach to lithium-ion battery SOC estimation based on recurrent neural network with gated recurrent unit and Huber-M robust Kalman filter
[J].
基于自适应回归扩展卡尔曼滤波的电动汽车动力电池全生命周期的荷电状态估算方法
[J].
State of charge estimation method of electric vehicle power battery life cycle based on auto regression extended Kalman filter
[J].
基于神经网络和MS-AUKF算法的蓄电池荷电状态估计
[J].
SOC estimation of battery by MS-AUKF algorithm and BPNN
[J].
Disturbance observer-based state-of-charge estimation for Li-ion battery used in light electric vehicles
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.est.2019.101144 URL [本文引用: 1]
A multi‐timescale adaptive dual particle filter for state of charge estimation of lithium‐ion batteries considering temperature effect
[J].
Analysis of the heat generation of lithium-ion battery during charging and discharging considering different influencing factors
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s10973-013-3599-9
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Operating temperature of lithium-ion battery is an important factor influencing the performance of electric vehicles. During charging and discharging process, battery temperature varies due to internal heat generation, calling for analysis of battery heat generation rate. The generated heat consists of Joule heat and reaction heat, and both are affected by various factors, including temperature, battery aging effect, state of charge (SOC), and operation current. In this article, a series of experiments based on a power-type lithium manganese oxide/graphite battery was implemented under different conditions. The parameters for Joule heat and reaction heat are determined, and the Joule heat, reaction heat as well as total heat generation rate is detailed and analyzed considering the influence of temperature, aging, SOC, and current. In order to validate the accuracy of heat generation rate, a lumped battery heat transfer model is applied to calculate the temperature variation, and the estimated temperature variation shows good correspondence with experimental results under different currents and aging conditions. Due to its simplicity, the temperature variation estimation method is suitable for real time applications.
温度和老化意识融合驱动的电动车辆锂离子动力电池电量和容量协同估计
[J].
Co-estimation of lithium-ion battery state-of-charge and capacity through the temperature and aging awareness model for electric vehicles
[J].
联合扩展卡尔曼滤波的滑模观测器SOC估算算法研究
[J].
Research on the SOC estimation algorithm of combining sliding mode observer with extended Kalman filter
[J].
基于电化学阻抗谱的锂离子电池内部温度在线估计方法研究
[J/OL].
On-line estimation method for internal temperature of lithium-ion battery based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
[J].
基于双卡尔曼滤波算法的动力电池内部温度估计
[J].
Battery internal temperature estimation method through double extended Kalman filtering algorithm
[J].
Lithium-ion battery health prognosis based on a real battery management system used in electric vehicles
[J].DOI:10.1109/TVT.25 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于模型参数辨识的储能电池状态估算
[J].
Energy storage battery state estimation based on model parameter identification
[J].
A temperature and current rate adaptive model for high-power lithium-titanate batteries used in electric vehicles
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.41 URL [本文引用: 1]
Accurate electrical battery model capable of predicting runtime and I-V performance
[J].DOI:10.1109/TEC.2006.874229 URL [本文引用: 1]
Parameter sensitivity analysis and simplification of equivalent circuit model for the state of charge of lithium-ion batteries
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2019.135239 URL [本文引用: 1]
A hybrid state-of-charge estimation method based on credible increment for electric vehicle applications with large sensor and model errors
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.est.2019.101106 URL [本文引用: 1]
电池组分段混合均衡控制策略
[J].
Segmented hybrid equalization control strategy for battery packs
[J].
面向整组寿命最大化的电动汽车电池一致性变化规律及其均衡策略
[J].
Consistency variation law and equalization strategy of electric vehicle battery for maximizing the life of the battery pack
[J].
Integrated equivalent circuit and thermal model for simulation of temperature-dependent LiFePO4 battery in actual embedded application
[J].DOI:10.3390/en10010085 URL [本文引用: 1]
Equalization of lithium-ion battery pack based on fuzzy logic control in electric vehicle
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.41 URL [本文引用: 1]
锂离子电池组容量差异辨识方法研究
[J/OL].
Research on capacity difference identification method of lithium-ion battery pack
[J/OL].