1 引言
目前在110kV及以上的高压电力系统中,通常采用电容式电压互感器(Capacitor Voltage Transformer,CVT)作为电压、功率测量、继电保护及载波通信使用[1]。与电磁式电压互感器相比,电容式电压互感器具有绝缘结构合理、造价低及运行可靠性高等优点,因此在超、特高压系统中,电容式电压互感器被广泛应用。
2 故障经过
2017年12月26日21时16分,某站在对一条500kV线路检修后恢复运行。线路带电之后,监控显示两套线路保护装置均为告警信号,检查发现线路三相电压中B相电压明显偏低,且相位比正常状态超前约67°。监控和保护装置显示的线路三相电压见表1。
表1 线路三相电压
Tab.1
| 电压 | A相 | B相 | C相 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 监控设备/kV | 294.95 | 90.85 | 294.63 |
| 保护装置/V | 59.00∠0° | 19.13∠-53° | 59.00∠120° |
通过对CVT本体红外测温发现,线路B相电磁单元为53℃,而A、C同位置温度仅为5℃,B相温度明显高于其他两相,CVT红外测温情况如图1所示。
图1
3 故障排查
3.1 一、二次检查情况
停电后,现场一次检修人员对线路CVT B相包括二次接线盒在内进行了详细的检查,检查了中间变压器低压侧接地情况、末屏接地、二次绕组保护避雷器、二次端子紧固情况、CVT试验小刀开关位置状态、CVT油位等,均未发现明显异常。
二次检修人员对线路CVT端子箱进行了检查,CVT端子箱内无受潮、凝露现象,CVT各二次绕组接地良好,二次线接线情况良好,通压试验无异常,测量各二次绕组绝缘电阻正常,见表2。
表2 CVT各二次绕组对地绝缘电阻
Tab.2
| CVT二次绕组 | 第一绕组 | 第二绕组 | 第三绕组 | 开口三角形绕组 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绝缘电阻/MΩ | ≥2 000 | – | ≥2 000 | ≥2 000 |
| 是否合格 | 合格 | – | 合格 | 合格 |
注:CVT第二绕组未接至CVT端子箱。
3.2 诊断性试验
图2
表3 CVT油化试验数据
Tab.3
| 组分名称 | 含量/(μL/L) |
|---|---|
| H2 | 28.92 |
| CH4 | 4.14 |
| C2H6 | 1.53 |
| C2H4 | 1.16 |
| C2H2 | 0 |
| 总烃 | 6.83 |
| CO | 109.39 |
| CO2 | 485.02 |
表4 “三比值”法结果
Tab.4
| 项 目 | C2H2/ C2H4 | CH4/H2 | C2H4/C2H6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 比值 | 0 | 0.143 | 0.758 |
| 对应编码 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 故障类型 | 低温过热(低于150℃) | ||
根据表4的“三比值”法,可知该电容式电压互感器电磁单元内部存在低温过热(低于150℃)故障,与现场红外测温结果一致。
对异常的B相CVT电容分压器的绝缘电阻、介质损耗及电容量进行试验,试验数据见表5。
表5 CVT元件试验数据
Tab.5
| 电容 | 主绝缘电阻 /MΩ | tgδ(%) | C(实测) /pF | C(初始) /pF | ΔCx(%) | C(总)/pF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C13 | 40 000 | 0.064 | 15 430 | 15 480 | -0.32 | 5 149 |
| C12 | 40 000 | 0.076 | 15 470 | 15 440 | 0.19 | |
| C11 | 40 000 | 0.067 | 17 740 | 17 700 | 0.23 | |
| C2 | 10 000 | 0.106 | 119 000 | 118 900 | 0.08 |
从表5可以看出,CVT各部分主绝缘正常,电容量与初始值比较未见异常,介质损耗值未超过电力设备预防性试验规程,电容分压器运行状态良好。
对电磁单元中间变压器进行直流电阻测试,二次绕组的直流电阻测试结果见表6。
表6 CVT二次绕组直流电阻
Tab.6
| 二次绕组 | 1a-1n | 2a-2n | 3a-3n | da-dn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 直流电阻/mΩ | 25.07 | 46.93 | 51.78 | 157.6 |
从表6可以看出,中间变压器二次绕组直流电阻数值正常,二次绕组不存在断线情况。
对电磁单元中间变压器进行相关绝缘电阻、交流耐压测试,测试结果见表7。
表7 中间变压器试验数据
Tab.7
| 保护避雷器 | 二次绕组 | N点 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 绝缘电阻/MΩ | 绝缘电阻/MΩ | 交流耐压 | 交流耐压 |
| 0.1 | 8 000 | 2kV/1min | 2kV/1min |
由表7可知,中间变压器二次绕组绝缘电阻及交流耐压试验情况正常,补偿电抗器两端并联的氧化锌避雷器绝缘电阻仅为0.1MΩ,不符合技术要求。
根据以上排查及试验结果,初步断定本次线路CVT B相电压异常的原因可能是补偿电抗器两端并联的保护避雷器故障导致。为进一步明确具体原因,现场对故障CVT进行了更换,并将故障CVT进行返厂解体检查,更换后线路重新投入运行,线路二次电压三相显示正常。
4 解体检查
为了最终确定CVT的故障原因,在日新电机(无锡)厂内对其进行解体检查,电磁单元的内部结构如图3所示。对中间变压器进行感应耐压试验,在150Hz下施加12.5kV试验电压,结果正常。拆开电磁单元封板,检查发现,电磁单元内部绝缘油油色透明清澈,无任何悬浮杂质存在,排油后检查电磁单元内部接线完好,未发现放电、发热痕迹,测量补偿电抗器直流电阻为298Ω,符合厂家设计要求。
图3
图3
故障CVT电磁单元内部结构实物图
Fig.3
Internal structure of the fault CVT electromagnetic unit
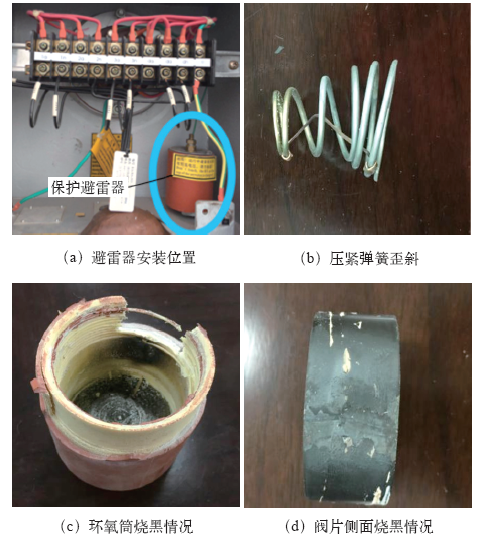
本产品补偿电抗器两端并联的保护避雷器在电磁单元外部,放置在二次接线盒内,如图4a所示,为西安高压电瓷厂生产的HYW-2.0/4.5型保护避雷器,额定电压2kV,持续运行电压1.6kV。
图4
采用1 000V电压测量避雷器绝缘电阻为0MΩ,万用表测量为1 461Ω。对保护避雷器进行解体检查,发现阀片压紧弹簧歪斜,避雷器电阻阀片中部有一处放电痕迹,电阻阀片侧面、避雷器环氧绝缘筒内壁发生沿面放电并烧黑,如图4b~4d所示。
经过上述故障排查、返厂解体检查,可以基本断定造成本次线路CVT二次电压异常的原因是CVT电磁单元中补偿电抗器两端并联的保护用避雷器内部阀片损坏,绝缘降低导致。
5 故障原因分析
5.1 CVT工作原理
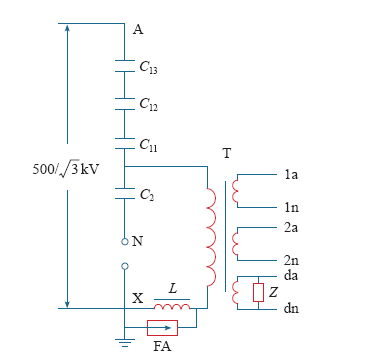
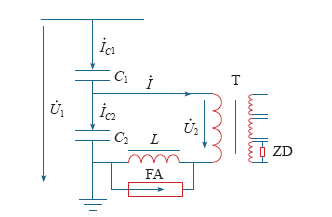
CVT利用阻抗分压原理,电容分压电路如图5所示。
图5
设电容器C1、C2和补偿电抗器L的阻抗为
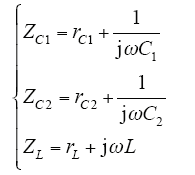
式中,rC1、rC2为电容器C1和C2有功损耗的等效电阻;C1、C2分别为高压电容和中压电容的电容量;rL为补偿电抗器线圈的电阻值;L为补偿电抗器电感值。
由电路定律可得
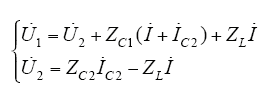
由式(2)可得
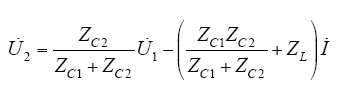
其中,ZC2/(ZC1 + ZC2) ≈ C1/(C1 + C2) = K为CVT的降压比;ZC1ZC2/(ZC1 + ZC2) = ZC = rC + 1/(jωC)为电容分压器的等值阻抗,rC、C为等值电阻和等值电容,且C = C1 + C2。
式(3)可进一步写为
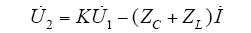
图6
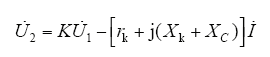
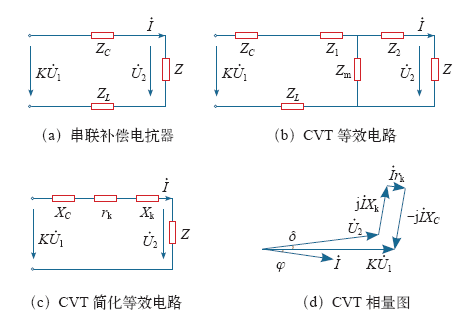
根据式(5)可对电容式电压互感器进行理论分析和相关计算。其对应的相量图如图6d所示。
在补偿电抗器的工程设计上,通常使Xk = XC,以减小电压比误差,相位误差主要来源于电压互感器负载阻抗Z的功率因数,cos ϕ = 1时,
5.2 故障后相量分析
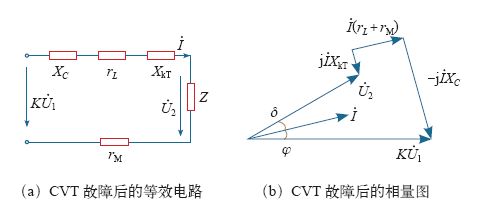
本次补偿电抗器两端并联的避雷器故障后,绝缘电阻为0,失去保护作用,万用表测得避雷器电阻为1 461Ω,远小于补偿电抗器阻抗21.5kΩ,两者并联后近似等效为电阻rM = 1 461Ω,电容器等效电阻(约27Ω)和中间变压器短路电阻数值很小可忽略,等效电路如图7a所示,其中XkT = jωLkT远小于XC,此时对应的电压平衡方程式为
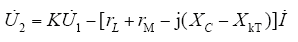
由式(6)可知,故障后CVT等效电路呈容性,电流
图7
图7
故障CVT的等效电路及相量图
Fig.7
The equivalent circuit and phasor diagram of the fault CVT
5.3 故障后定量分析
根据上述故障后的CVT等效电路,忽略和结合本文案例各项试验数据,进行定量计算分析,表8给出了本次计算用参数。
表8 计算用各参数
Tab.8
| 参数 | C1/pF | C2/pF | XC/Ω | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数值 | 5 382 | 119 000 | 25 591 | 0.043 3 |
| 参数 | rL/Ω | rM/Ω | XkT/Ω | U1/kV |
| 数值 | 296 | 1 461 | 5 090 | 295∠-120° |
设中间变压器二次输出电压为
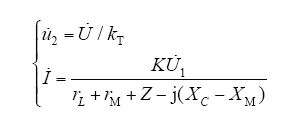
式(7)中kT为中间变压器的电压比,取值为218,根据表8中各参数,结合式(6)和式(7)得
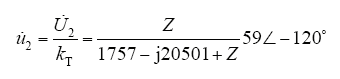
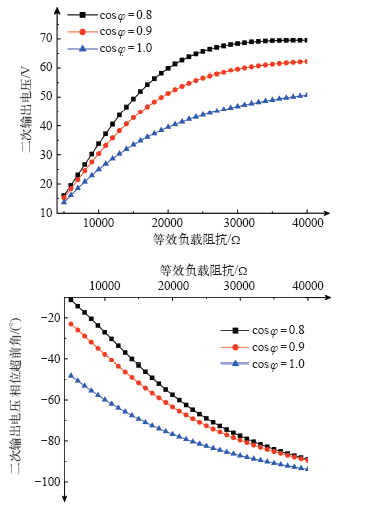
选取不同的等效负载阻抗,利用Matlab软件进行数值仿真计算,计算结果如图8所示。
图8
由图8可以看出,二次输出电压幅值u2随着等效负载阻抗Z的增大而增大,且二次输出电压u2的相位会超前正常的角度(-120°),等效负载阻抗越小,二次输出电压u2的相位超前角越大;等效负载阻抗的功率因数越大,二次输出电压幅值u2越小,u2的相位超前角也越小(与正常角度-120°比较)。
将现场检查的二次电压19.13∠-53°代入式(8),可得Z = 7 229∠0.77°Ω,即等效负载Z为7 229∠0.77°Ω时,将会出现本次案例中二次电压异常情况。
6 结束语
本文根据一起500kV CVT避雷器的故障处理及原因分析,研究了CVT补偿电抗器两端并联的保护避雷器故障,导致互感器二次输出电压异常的原因,得出以下结论:
(1)本次CVT二次输出电压异常的原因为CVT电磁单元中补偿电抗器两端并联的保护用避雷器内部阀片损坏,绝缘降低。
(2)应加强对CVT保护用避雷器的运维措施,加强对运行中CVT二次电压的监测,发现异常及时汇报。
(3)随着交直流混联电网的发展,电网中谐波成分明显复杂,对CVT的各参数配合提出了新的课题,需要组织专业技术人员,优化CVT各参数配置,抑制可能出现的铁磁谐振。
(4)通过相量定性分析了CVT中的保护避雷器故障后,CVT二次输出电压数值偏小、相位超前的原因。
(5)结合本次试验数据,定量分析了CVT中的保护避雷器故障后,CVT二次输出电压随负载的变化情况,并通过计算得出当等效负载Z为7 229∠0.77°Ω时,将会出现二次电压异常情况。
参考文献
电容式电压互感器的安全运行探讨
[J].
Safe operation discussion of capacitor voltage transformer
[J].
电容式电压互感器二次电压异常分析处理
[J].
DOI:10.1002/smll.201906131
URL
PMID:31885140
[本文引用: 1]

Benefiting from the natural abundance and low standard redox potential of potassium, potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) are regarded as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for low-cost energy storage. However, most PIB electrode materials suffer from sluggish thermodynamic kinetics and dramatic volume expansion during K+ (de)intercalation. Herein, it is reported on carbon-coated K2 Ti2 O5 microspheres (S-KTO@C) synthesized through a facile spray drying method. Taking advantage of both the porous microstructure and carbon coating, S-KTO@C shows excellent rate capability and cycling stability as an anode material for PIBs. Furthermore, the intimate integration of carbon coating through chemical vapor deposition technology significantly enhances the K+ intercalation pseudocapacitive behavior. As a proof of concept, a potassium-ion hybrid capacitor is constructed with the S-KTO@C (battery-type anode material) and the activated carbon (capacitor-type cathode material). The assembled device shows a high energy density, high power density, and excellent capacity retention. This work can pave the way for the development of high-performance potassium-based energy storage devices.
Analysis and treatment on abnormal secondary voltage of capacitor voltage transformers
[J].
DOI:10.1002/smll.201906131
URL
PMID:31885140
[本文引用: 1]

Benefiting from the natural abundance and low standard redox potential of potassium, potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) are regarded as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for low-cost energy storage. However, most PIB electrode materials suffer from sluggish thermodynamic kinetics and dramatic volume expansion during K+ (de)intercalation. Herein, it is reported on carbon-coated K2 Ti2 O5 microspheres (S-KTO@C) synthesized through a facile spray drying method. Taking advantage of both the porous microstructure and carbon coating, S-KTO@C shows excellent rate capability and cycling stability as an anode material for PIBs. Furthermore, the intimate integration of carbon coating through chemical vapor deposition technology significantly enhances the K+ intercalation pseudocapacitive behavior. As a proof of concept, a potassium-ion hybrid capacitor is constructed with the S-KTO@C (battery-type anode material) and the activated carbon (capacitor-type cathode material). The assembled device shows a high energy density, high power density, and excellent capacity retention. This work can pave the way for the development of high-performance potassium-based energy storage devices.
一起CVT故障的处理及分析
[J].
DOI:10.1002/smll.201906131
URL
PMID:31885140
[本文引用: 2]

Benefiting from the natural abundance and low standard redox potential of potassium, potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) are regarded as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for low-cost energy storage. However, most PIB electrode materials suffer from sluggish thermodynamic kinetics and dramatic volume expansion during K+ (de)intercalation. Herein, it is reported on carbon-coated K2 Ti2 O5 microspheres (S-KTO@C) synthesized through a facile spray drying method. Taking advantage of both the porous microstructure and carbon coating, S-KTO@C shows excellent rate capability and cycling stability as an anode material for PIBs. Furthermore, the intimate integration of carbon coating through chemical vapor deposition technology significantly enhances the K+ intercalation pseudocapacitive behavior. As a proof of concept, a potassium-ion hybrid capacitor is constructed with the S-KTO@C (battery-type anode material) and the activated carbon (capacitor-type cathode material). The assembled device shows a high energy density, high power density, and excellent capacity retention. This work can pave the way for the development of high-performance potassium-based energy storage devices.
Treatment and analysis of one CVT fault
[J].
DOI:10.1002/smll.201906131
URL
PMID:31885140
[本文引用: 2]

Benefiting from the natural abundance and low standard redox potential of potassium, potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) are regarded as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for low-cost energy storage. However, most PIB electrode materials suffer from sluggish thermodynamic kinetics and dramatic volume expansion during K+ (de)intercalation. Herein, it is reported on carbon-coated K2 Ti2 O5 microspheres (S-KTO@C) synthesized through a facile spray drying method. Taking advantage of both the porous microstructure and carbon coating, S-KTO@C shows excellent rate capability and cycling stability as an anode material for PIBs. Furthermore, the intimate integration of carbon coating through chemical vapor deposition technology significantly enhances the K+ intercalation pseudocapacitive behavior. As a proof of concept, a potassium-ion hybrid capacitor is constructed with the S-KTO@C (battery-type anode material) and the activated carbon (capacitor-type cathode material). The assembled device shows a high energy density, high power density, and excellent capacity retention. This work can pave the way for the development of high-performance potassium-based energy storage devices.
220 kV CVT二次失压故障的分析与试验
[J].
DOI:10.1002/smll.201906131
URL
PMID:31885140
[本文引用: 2]

Benefiting from the natural abundance and low standard redox potential of potassium, potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) are regarded as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for low-cost energy storage. However, most PIB electrode materials suffer from sluggish thermodynamic kinetics and dramatic volume expansion during K+ (de)intercalation. Herein, it is reported on carbon-coated K2 Ti2 O5 microspheres (S-KTO@C) synthesized through a facile spray drying method. Taking advantage of both the porous microstructure and carbon coating, S-KTO@C shows excellent rate capability and cycling stability as an anode material for PIBs. Furthermore, the intimate integration of carbon coating through chemical vapor deposition technology significantly enhances the K+ intercalation pseudocapacitive behavior. As a proof of concept, a potassium-ion hybrid capacitor is constructed with the S-KTO@C (battery-type anode material) and the activated carbon (capacitor-type cathode material). The assembled device shows a high energy density, high power density, and excellent capacity retention. This work can pave the way for the development of high-performance potassium-based energy storage devices.
Fault analysis and test on secondary voltage loss of 220 kV capacitor voltage transforme
[J].
DOI:10.1002/smll.201906131
URL
PMID:31885140
[本文引用: 2]

Benefiting from the natural abundance and low standard redox potential of potassium, potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) are regarded as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for low-cost energy storage. However, most PIB electrode materials suffer from sluggish thermodynamic kinetics and dramatic volume expansion during K+ (de)intercalation. Herein, it is reported on carbon-coated K2 Ti2 O5 microspheres (S-KTO@C) synthesized through a facile spray drying method. Taking advantage of both the porous microstructure and carbon coating, S-KTO@C shows excellent rate capability and cycling stability as an anode material for PIBs. Furthermore, the intimate integration of carbon coating through chemical vapor deposition technology significantly enhances the K+ intercalation pseudocapacitive behavior. As a proof of concept, a potassium-ion hybrid capacitor is constructed with the S-KTO@C (battery-type anode material) and the activated carbon (capacitor-type cathode material). The assembled device shows a high energy density, high power density, and excellent capacity retention. This work can pave the way for the development of high-performance potassium-based energy storage devices.
CVT保护用避雷器故障分析
[J].
Fault analysis on surge arrester of CVT
[J].
电容式电压互感器的谐波传递特性研究
[J].
Harmonic transfer characteristic of capacitor voltage transformer
[J].
500kV电容式电压互感器暂态特性仿真
[J].
Simulations on transient characteristics of 500kV capacitor voltage transformer
[J].