1 引言
电树枝现象是绝缘材料中由于杂质、气泡等缺陷造成局部电场集中导致局部击穿,进而形成的微米级放电破坏通道,因其形状与树枝相似,被称为电树枝[1]。电树枝一旦产生,就会以极快的速度发展,一旦电树枝生长至穿过绝缘层,就会发生电气故障,从而影响电缆的运行安全[2]。1972年,日本学者在电气绝缘与电介质现象会议上的报道,明确确定了电树枝老化现象是固体电介质绝缘累积破坏的结果,国内外学者围绕这一问题开展了广泛研究[3]。但早期,大部分研究是针对交流电压下的电树枝展开。学者们普遍认为,注入或产生的载流子对聚合物链的直接撞击破坏,以及注入和产生的载流子复合产生的能量是导致聚合物电树枝引发的重要原因[4,5,6]。而在直流电压下,由于极性的单一和波形的长期稳定,注入和产生的载流子不易获得足够能量去撞击分子链,很难产生足够的能引发电树枝的能量。然而,高压直流电缆在运行过程中,除了承受直流额定电压外,还要承受脉冲电压。这些脉冲电压可能是由架空线路引入的雷电脉冲电压,或者是线路故障及十二脉动引起的操作脉冲电压[7,8,9]。当这些脉冲与高压直流电缆中的直流电压相复合时,将产生一个复杂的直流脉冲复合场,导致线路电压急剧变化,加剧电场畸变[10,11,12]。高压直流电缆在运行过程中,由于电压等级高,通过电缆的电流大,持续通过大电流的线芯会产生较多热量,从而导致电缆长期在较高的温度条件下运行[13]。直流电场下电缆绝缘中的电场强度取决于绝缘电阻率,电阻率受温度影响较大,因此电场强度受温度影响。同时,温度的变化还会影响电缆绝缘中电荷的注入和迁移率。随着温度的升高,电荷注入数量增多,载流子迁移率增大[14]。温度的变化影响绝缘中空间电荷的数量[15]。空间电荷的积聚加速电场畸变,引发绝缘老化,导致电树枝的生长,而载流子的运动又与电树枝的生长有着紧密的关系。因此,温度的变化与电树枝的生长特性有着复杂而又紧密的联系。
塑料绝缘电缆因其具有良好的电气、机械和热性能而得到快速推广,其中交联聚乙烯(Cross Linked Polyethylene,XLPE)高压直流电缆性能突出、应用最为广泛[16]。但XLPE电缆的最高工作温度仅为70℃,同时生产 XLPE电缆时用到的交联剂及交联过程中产生的副产物等杂质可能会引入绝缘层内部,使得直流电场下空间电荷积聚更加严重,从而加速绝缘老化。交联过程使聚乙烯从热塑性材料转变成了热固性材料,因此在电缆寿命到期后无法直接回收再利用,将不可避免地产生大量的废弃交联聚乙烯电缆绝缘材料从而产生环保问题[17]。聚丙烯(Polypropylene,PP)绝缘材料具有更高的熔点,可以满足电缆在较高温度下运行的需求。PP具有较高的击穿强度和体积电阻率,对提高电缆运行电压等级和线路载流量意义重大。另外,由于没有交联过程,PP在电缆寿命到期后可以回收再利用,是环保型直流电缆绝缘材料[17,18]。由于PP材料的研究时间还相对较短,对PP材料的老化击穿特性认识不足,因此需要对PP材料在不同条件下的老化击穿特性进行系统研究,为电缆的结构设计和寿命预测提供理论依据。
本文对比了相同条件下PP与XLPE电树枝生长特性,分析了直流脉冲复合场、温度等因素对聚丙烯电树枝生长特性的影响规律,探讨了不同方法抑制电树枝的机理。
2 PP与XLPE电树枝生长特性对比
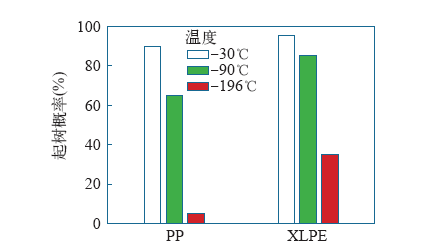
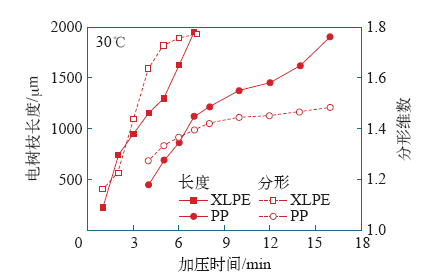
为了对比PP和XLPE的耐电树枝性能,天津大学对相同脉冲电压下的PP和XLPE分别进行了电树枝生长实验[19]。研究发现,PP中的电树枝形态比XLPE更加稀疏,树枝通道更细。同时,在加压时间为10min时,PP中的电树枝起始概率更低,这意味着在PP中电树枝更不易被引发,如图1所示。在相同时间内,PP中电树枝生长速度更慢,分形维数更小,如图2所示。Holto等研究了PP与XLPE中电树枝形态,发现PP中击穿前有单支和多支两类电树枝生长,单支电树枝到达地电极就发生击穿,而多支电树枝要有多个枝干到达地电极才会发生击穿。而XLPE击穿前更易形成丛林状电树枝,如图3所示。同时推测,PP中形成的电树枝区域比XLPE中形成的电树枝区域具有更低的导电性[20,21]。
图1
图2
图3
3 复合场对电树枝的影响研究现状
3.1 直流脉冲电压复合对电树枝生长特性的影响
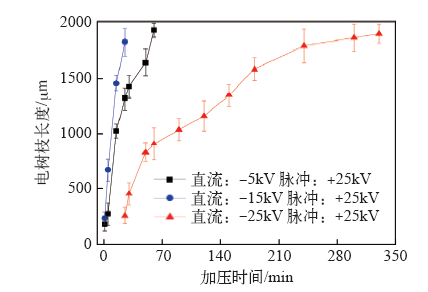
图4
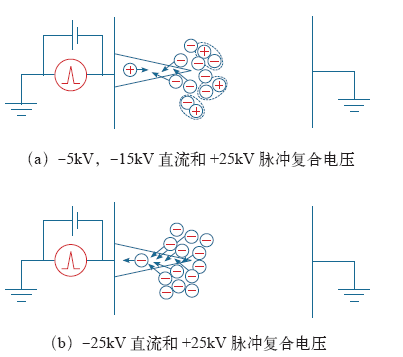
图5
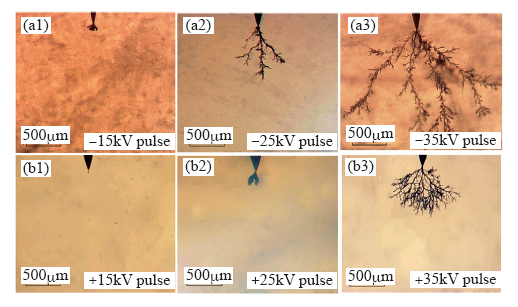
图6为t0时刻(复合电压首次达到最大幅值时)从针尖到地电极的模拟电场分布[27]。当都与+25kV的脉冲电压复合时,-15kV直流电压下的电场峰值更大,表明-15kV时的极性变化作用效果更强。然而,如图4所示,当直流电压从-15kV增加到-25kV时,生长速率降低。+25kV脉冲与-25kV直流电压复合时的电荷输运过程如图5b 所示。在施加脉冲电压后,由于针尖的电势降低,电子被抽出[28]。这种电荷运动使分子链断裂,导致电树枝生长。由于缺乏极性变化过程,同时复合电压的平均值减小, +25kV脉冲与-25kV直流复合电压下的电树枝生长速率小于+25kV脉冲与 -5kV,-15kV直流复合电压下的电树枝生长速率。
图6
图7
研究发现,在电场极性翻转的情况下,由于空间电荷的作用,电场会发生非常严重的畸变[25,26]。Tanaka研究发现,在80kV/mm电场下极化30min后,由于阴极处负电荷的积聚,阴极处的电场降低到约50kV/mm,而阳极的电场增加到约120kV/mm。当外施电压发生极性反转后,由于空间电荷无法突变,所以空间电荷所产生的电场与外加电场共同作用,使阴极处的电场增大到130kV/mm左右[29]。研究发现,极性反转会降低击穿场强。在施加直流电压后,测量试样的正脉冲电压击穿场强,与正极性直流预压下的击穿强度相比,负极性直流预应力下的击穿强度更低[26]。西安交通大学对直流预压后的脉冲电压下的XLPE电树枝起始电压进行了研究。结果表明,电树枝长度主要由脉冲电压的幅值决定,而直流预压的影响不大[30]。Saito等研究了直流预压后脉冲电压下聚乙烯(Polyethylene,PE)中电树枝的引发特性,发现直流预压后不同的停留时间会影响电荷特性从而改变电树枝引发特性[31]。虽然这些研究在一定程度上发现了空间电荷对电树枝生长特性的影响,但在实验中并没有真正实现直流和脉冲电压的叠加而为直流预压。
3.2 其他复合电压对电树枝生长特性的影响
4 温度对电树枝的影响研究现状
表1 11 不同温度及频率下电树枝形态[19]
Tab.1
| 幅值/kV | 频率/Hz | -30℃ | -90℃ | -196℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 400 | 树枝状 | 丛林状 | 树枝状 |
| 15 | 800 | 树枝状 | 丛林状 | 树枝状 |
| 15 | 1 200 | 树枝状 | 丛林状 | 树枝状 |
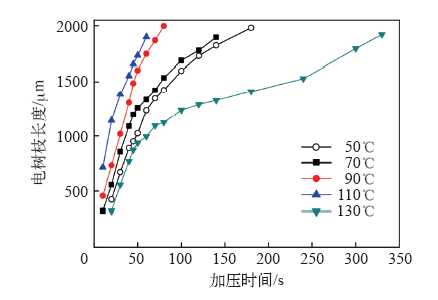
温度的变化影响材料的机械性能。随着温度的降低,PP的弹性模量增加,这意味着PP在-90℃时比-30℃更脆,更容易开裂。在热电子撞击分子链产生电树枝通道的同时,会产生机械裂纹,这些裂纹也作为缺陷存在,雪崩放电也会在这些机械裂纹中产生,形成更加密集的电树枝结构。在PP劣化的过程中,氧气也起了重要的作用。当自由基与氧发生反应时,会产生自氧化反应,聚合物在此过程中被分解。但在-196℃时,氧气液化,自氧化反应不易发生。因此,在-196℃下,PP的分子链极难被打破,形成稀疏的树枝状结构电树。当温度由50℃增大到130℃时,电树枝结构不变,均为树枝状电树,但是随温度升高,电树枝枝干变粗。当温度由50℃增大到110℃时,电树枝生长速度增快,但130℃时的电树枝生长速度比110℃时慢,如图8[34]所示。
图8
脉冲电压施加在针尖后,当外加电压超过注入势垒后,电荷由针尖注入,在电荷的入陷过程中,多余的能量转移给电子,使之成为热电子,热电子撞击分子链,使聚合物降解成自由基,氧气的参与加快了这个过程,不断重复这个过程之后,低密度区形成,在低密度区中碰撞电离,最终导致电树枝的引发。随着温度由50℃升高到110℃,一方面,热能使主链上的单键旋转,并激发分子链的运动。随着温度的升高,分子链的热运动逐渐增大,导致聚合物链段部分松弛,削弱针尖周围的区域,造成电树枝引发概率增大。同时,在高温及高场强的作用下,一些深吸附在聚合物基体中的氧气释放出来参与氧化反应,造成生长速度加快。另一方面,随着温度的升高,部分结晶区域中的大晶体缓慢地融化,非晶区部分增加,自由体积增大。电子在自由体积中加速,获得更大的能量。但由DSC曲线可知,在130 ℃时,晶体融化非常厉害,接近于熔点的温度。此时弹性模量会突然降低,更易形成密集的电树枝区域。随着密集区域的形成,一些注入的电荷被捕获并且分布均匀。空间电荷层将形成一个电场屏蔽,导致在130℃的针尖处电场强度减少。因此,130℃的增长速度比110℃慢。
图9
5 抑制电树枝引发及生长的方法
纳米复合材料是指在高分子中均匀添加少量纳米级别(通常为 10%以下)的颗粒后所形成的新型材料,多数学者认为,纳米复合材料中聚合物基体与纳米粒子间形成的界面区域引入了大量陷阱,改变了复合材料的陷阱能级,从而对电树枝的生长产生了重要影响[39]。天津大学研究在PP中添加聚氧化乙烯(Polyoxyethylene,POE)可以提高PP的韧性,但经实验发现,PP/POE共混物的空间电荷积聚增多。在PP/POE中添加纳米ZnO颗粒可以提高抗拉伸强度,同时仍保持了较好的机械韧性。纳米ZnO颗粒使PP/POE的陷阱能级密度增大,减少电荷注入,抑制了空间电荷的积聚。与PP/POE共混物相比,PP/POE/ZnO纳米复合材料的介电常数较小,且击穿强度和体电阻率也得到了提高[40]。Montanari等研究了添加合成蒙脱土(Montmorillonite,MMT)纳米颗粒的iPP和sPP的纳米复合材料的电荷俘获行为特性,与纯PP相比,纳米复合材料的电荷俘获能力明显增强,直流极化电场下空间电荷积聚的减少说明纳米复合材料的绝缘性能得到整体提高[41]。纳米蒙脱土(MMT)具有一维纳米层状结构,哈尔滨理工大学研究发现,在PE和PP中添加适量MMT,可以抑制电树枝的生长[42,43]。分析认为,MMT在PE和PP中抑制电树枝的作用机理相似。一方面,MMT的添加主要抑制电树枝沿电场方向的生长,当电树枝生长至MMT时,无法穿越MMT片层而只能沿着表面生长,而后绕过片层发展。另一方面,MMT通过改变结晶尺寸来提高耐电树枝化特性。同时,MMT的加入将PP的大结晶变为片晶结构,影响结晶区/非结晶区的界面能,增加了电树枝的生长阻力。纳米蒙脱土的引入从物理阻挡及结晶形态改变两个方面解释了对电树枝生长特性的影响,但对层状纳米颗粒及球形纳米颗粒的区别论证较少。
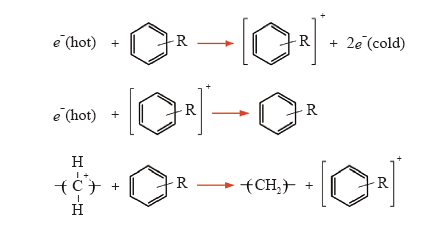
目前的研究表明,在聚合物中加入能够俘获强电场下材料中高能电子的电压稳定剂,可以提高材料的耐电树枝化能力[44,45,46,47]。以芳香族化合物为代表的电压稳定剂的作用机理如图10所示[48]。由于大多数芳香族化合物具有较高的电子亲和能,在强电场作用下,将先受到电子的冲击并被激发或电离,不易再破坏聚合物的分子链,从而提高了绝缘材料的耐电性能;芳香族化合物激发所形成的激发态分子将通过发光或振动将能量以相对无害的形式释放,并还原成初始状态,而电离所形成的阳性游离基将通过与电子作用还原成初始状态。由于大多数芳香族类化合物的电离能都低于聚合物分子链的键能,在高电场作用下,芳香族化合物能与高能电子结合发生电离,从而大幅削弱聚合物中注入的电子能量,提高了聚乙烯绝缘材料的耐电性能。同时,芳香族化合物还能与已发生电离的芳香族化合物发生作用,被还原成初始状态。从机理上分析,这种电压稳定剂不属消耗性,可以一直发挥作用,具有极高的研究价值。但是,现有研究大多数是针对交流电压下的电树枝生长进行研究,对于直流下电树枝的生长是否仍有抑制作用,尤其对于聚丙烯材料电树枝是否有抑制作用,还有待于进一步研究。
图10
S.S. Bamji等学者认为在电树枝引发及生长阶段,在PE无定形相中存在的微量的氧气产生了很重要的作用。氧气与聚合物发生氧化连锁反应,加速分子链的断裂[49]。而抗氧剂的添加,可对聚合物中的氧化连锁反应起到抑制所用,从而抑制电树枝的生长。Y. Sekii[50,51]等研究了酚类和硫类抗氧剂对XLPE直流接地电树枝引发特性的影响。发现酚类抗氧剂对直流接地电树枝起始电压未产生明显影响,而硫类抗氧剂可以提高起始电压。在接地的时候,由于抗氧剂的加入起到了类似陷阱的捕获电荷作用,因此电树枝得到了抑制。目前关于添加抗氧剂的聚丙烯复合绝缘材料电树枝特性的研究较少,对于抗氧剂是否可以对聚丙烯中的电树枝生长起到抑制作用还需进一步深入研究。
6 结论
通过与XLPE对比发现,PP中更不易引发电树枝,电树枝更不易在PP中生长。当直流脉冲复合电压存在极性变化过程时,由空间电荷造成的电场畸变将加剧电树枝生长过程。同时,一定范围内的温度升高将加剧电树枝的生长过程,但接近PP熔融温度时反而会减慢电树枝的生长过程。另外,环境友好型直流电缆料聚丙烯绝缘的电树枝还有不少问题需要深入研究。由于直流电缆运行工况复杂,多物理场耦合作用下的电树枝生长特性及其机理仍有待于进一步研究。同时,目前对于电压稳定剂和抗氧剂的作用及其失效机理仍不清楚,尤其对于直流电压下电树枝的生长是否有效,还有待于进一步探讨。
参考文献
Solid insulation and its deterioration
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acsnano.9b07042
URL
PMID:31697468
[本文引用: 1]

The issue of material dissolution is common in aqueous batteries, leading to serious performance deterioration. However, it is difficult to be solved so far. In this study, a single component cathode solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer (CaSO4·2H2O) is observed via in situ electrochemically charging process, as demonstrated in a Ca2MnO4 cathode for an aqueous zinc-ion battery. Density functional theory calculation confirms its electronic insulation and ionic conductor properties, indicating that it is an appropriate SEI film. The material dissolution seems to be effectively suppressed by the presence of the SEI layer on the cathode side. Meanwhile, this in situ formed interface layer is advantageous for lowering impedance, ameliorating interface, and reducing activation energy. As a result, significantly superior rate performance and cycle stability are exhibited. The observation of a protective SEI layer in an aqueous system may provide an insight into the development of high stability aqueous batteries.
Nanocomposites-a review of electrical treeing and breakdown
[J].DOI:10.1109/MEI.2009.5191413 URL [本文引用: 1]
A consideration of treeing breakdown in polymers
Charge transfer and tree initiation in polyethylene subjected to AC voltage stress
[J].DOI:10.1109/14.142702 URL [本文引用: 3]
Evidence of near-ultraviolet emission during electrical-tree initiation in polyethylene
[J].DOI:10.1063/1.338221 URL [本文引用: 1]
Understanding electrical trees in solids: from experiment to theory
[J].
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.011912
URL
PMID:23005457
[本文引用: 1]

Particle-based simulation represents a powerful approach to modeling physical systems in electronics, molecular biology, and chemical physics. Accounting for the interactions occurring among charged particles requires an accurate and efficient solution of Poisson's equation. For a system of discrete charges with inhomogeneous dielectrics, i.e., a system with discontinuities in the permittivity, the boundary element method (BEM) is frequently adopted. It provides the solution of Poisson's equation, accounting for polarization effects due to the discontinuity in the permittivity by computing the induced charges at the dielectric boundaries. In this framework, the total electrostatic potential is then found by superimposing the elemental contributions from both source and induced charges. In this paper, we present a comparison between two BEMs to solve a boundary-integral formulation of Poisson's equation, with emphasis on the BEMs' suitability for particle-based simulations in terms of solution accuracy and computation speed. The two approaches are the collocation and qualocation methods. Collocation is implemented following the induced-charge computation method of D. Boda et al. [J. Chem. Phys. 125, 034901 (2006)]. The qualocation method is described by J. Tausch et al. [IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 20, 1398 (2001)]. These approaches are studied using both flat and curved surface elements to discretize the dielectric boundary, using two challenging test cases: a dielectric sphere embedded in a different dielectric medium and a toy model of an ion channel. Earlier comparisons of the two BEM approaches did not address curved surface elements or semiatomistic models of ion channels. Our results support the earlier findings that for flat-element calculations, qualocation is always significantly more accurate than collocation. On the other hand, when the dielectric boundary is discretized with curved surface elements, the two methods are essentially equivalent; i.e., they have comparable accuracies for the same number of elements. We find that ions in water--charges embedded in a high-dielectric medium--are harder to compute accurately than charges in a low-dielectric medium.
DC overvoltage control during loss of converter in multiterminal voltage-source converter-based HVDC (M-VSC-HVDC)
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2003.813888 URL [本文引用: 1]
A study of temporary overvoltage at HVDC rectifier stations
[C].
Transient overvoltage on a bipolar HVDC overhead line caused by DC line faults
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPAS.1970.292606 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effects of direct fluorination on space charge accumulation in HTV silicone rubber
[J].
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.011912
URL
PMID:23005457
[本文引用: 1]

Particle-based simulation represents a powerful approach to modeling physical systems in electronics, molecular biology, and chemical physics. Accounting for the interactions occurring among charged particles requires an accurate and efficient solution of Poisson's equation. For a system of discrete charges with inhomogeneous dielectrics, i.e., a system with discontinuities in the permittivity, the boundary element method (BEM) is frequently adopted. It provides the solution of Poisson's equation, accounting for polarization effects due to the discontinuity in the permittivity by computing the induced charges at the dielectric boundaries. In this framework, the total electrostatic potential is then found by superimposing the elemental contributions from both source and induced charges. In this paper, we present a comparison between two BEMs to solve a boundary-integral formulation of Poisson's equation, with emphasis on the BEMs' suitability for particle-based simulations in terms of solution accuracy and computation speed. The two approaches are the collocation and qualocation methods. Collocation is implemented following the induced-charge computation method of D. Boda et al. [J. Chem. Phys. 125, 034901 (2006)]. The qualocation method is described by J. Tausch et al. [IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 20, 1398 (2001)]. These approaches are studied using both flat and curved surface elements to discretize the dielectric boundary, using two challenging test cases: a dielectric sphere embedded in a different dielectric medium and a toy model of an ion channel. Earlier comparisons of the two BEM approaches did not address curved surface elements or semiatomistic models of ion channels. Our results support the earlier findings that for flat-element calculations, qualocation is always significantly more accurate than collocation. On the other hand, when the dielectric boundary is discretized with curved surface elements, the two methods are essentially equivalent; i.e., they have comparable accuracies for the same number of elements. We find that ions in water--charges embedded in a high-dielectric medium--are harder to compute accurately than charges in a low-dielectric medium.
Review of high voltage direct current cables
[J].
DOI:10.1002/hbm.24389
URL
PMID:30240499
[本文引用: 1]

Data-driven methods have been widely used in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data analysis. They extract latent factors, generally, through the use of a simple generative model. Independent component analysis (ICA) and dictionary learning (DL) are two popular data-driven methods that are based on two different forms of diversity-statistical properties of the data-statistical independence for ICA and sparsity for DL. Despite their popularity, the comparative advantage of emphasizing one property over another in the decomposition of fMRI data is not well understood. Such a comparison is made harder due to the differences in the modeling assumptions between ICA and DL, as well as within different ICA algorithms where each algorithm exploits a different form of diversity. In this paper, we propose the use of objective global measures, such as time course frequency power ratio, network connection summary, and graph theoretical metrics, to gain insight into the role that different types of diversity have on the analysis of fMRI data. Four ICA algorithms that account for different types of diversity and one DL algorithm are studied. We apply these algorithms to real fMRI data collected from patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls. Our results suggest that no one particular method has the best performance using all metrics, implying that the optimal method will change depending on the goal of the analysis. However, we note that in none of the scenarios we test the highly popular Infomax provides the best performance, demonstrating the cost of exploiting limited form of diversity.
Space charge and electric field in thermally aged multilayer joints model
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2015.005363 URL [本文引用: 1]
Electrical tree at high temperature in XLPE and effect of oxygen
Effect of temperature on space charge detrapping and periodic grounded DC tree in cross-linked polyethylene
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2016.005986 URL [本文引用: 1]
Space charge measurement of cross-linked polyethylene at low temperatures polyethylene
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2017.006689 URL [本文引用: 1]
高压直流交联聚乙烯电缆应用与研究进展
[J].
Application and re-search progress of HVDC XLPE cables
[J].
Space charges and initiation of electrical trees
[J].DOI:10.1109/14.19869 URL [本文引用: 2]
环保型高压直流电缆绝缘材料研究进展
[J].
Research progress of environ-ment-friendly HVDC power cable insulation materials
[J].
Effect of low temperature on electrical treeing of polypropylene with repetitive pulse voltage
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2016.7556462 URL [本文引用: 8]
Electrical treeing in extruded polypropylene high voltage cable insulation
Characteristics of electrical treeing in extruded polypropylene and cross-linked polyethylene cable insulation
[C].
Control and experiment of pulsewidth-modulated modular multilevel converters
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2009.2014236 URL [本文引用: 1]
Impulse breakdown superposed on ac voltage in XLPE cable insulation
[J].
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.011912
URL
PMID:23005457
[本文引用: 1]

Particle-based simulation represents a powerful approach to modeling physical systems in electronics, molecular biology, and chemical physics. Accounting for the interactions occurring among charged particles requires an accurate and efficient solution of Poisson's equation. For a system of discrete charges with inhomogeneous dielectrics, i.e., a system with discontinuities in the permittivity, the boundary element method (BEM) is frequently adopted. It provides the solution of Poisson's equation, accounting for polarization effects due to the discontinuity in the permittivity by computing the induced charges at the dielectric boundaries. In this framework, the total electrostatic potential is then found by superimposing the elemental contributions from both source and induced charges. In this paper, we present a comparison between two BEMs to solve a boundary-integral formulation of Poisson's equation, with emphasis on the BEMs' suitability for particle-based simulations in terms of solution accuracy and computation speed. The two approaches are the collocation and qualocation methods. Collocation is implemented following the induced-charge computation method of D. Boda et al. [J. Chem. Phys. 125, 034901 (2006)]. The qualocation method is described by J. Tausch et al. [IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 20, 1398 (2001)]. These approaches are studied using both flat and curved surface elements to discretize the dielectric boundary, using two challenging test cases: a dielectric sphere embedded in a different dielectric medium and a toy model of an ion channel. Earlier comparisons of the two BEM approaches did not address curved surface elements or semiatomistic models of ion channels. Our results support the earlier findings that for flat-element calculations, qualocation is always significantly more accurate than collocation. On the other hand, when the dielectric boundary is discretized with curved surface elements, the two methods are essentially equivalent; i.e., they have comparable accuracies for the same number of elements. We find that ions in water--charges embedded in a high-dielectric medium--are harder to compute accurately than charges in a low-dielectric medium.
Electrical treeing initiation and breakdown phenomenon in polypropylene under dc and pulse combined voltages
[J].
Moisture and space charge in oil-impregnated pressboard under HVDC
[C].
Effect of space charge on the breakdown strength under polarity reversal
[J].
Numerical simulation on the surface charge accumulation process of epoxy insulator under needle-plane corona discharge in air
[J].
DOI:10.3791/58233
URL
PMID:30417884
[本文引用: 1]

During energy conversion, material production, and metallurgy processes, reactions often have the features of unsteadiness, multistep, and multi-intermediates. Thermogravimetry-mass spectrum (TG-MS) is seen as a powerful tool to study reaction features. However, reaction details and reaction mechanics have not been effectively obtained directly from the ion current of TG-MS. Here, we provide a method of an equivalent characteristic spectrum analysis (ECSA) for analyzing the mass spectrum and giving the mass flow rate of reaction gases as precise as possible. The ECSA can effectively separate overlapping ion peaks and then eliminate the mass discrimination and temperature-dependent effect. Two example experiments are presented: (1) the decomposition of CaCO3 with evolved gas of CO2 and the decomposition of hydromagnesite with evolved gas of CO2 and H2O, to evaluate the ECSA on single-component system measurement and (2) the thermal pyrolysis of Zhundong coal with evolved gases of inorganic gases CO, H2, and CO2, and organic gases C2H4, C2H6, C3H8, C6H14, etc., to evaluate the ECSA on multi-component system measurement. Based on the successful calibration of the characteristic spectrum and relative sensitivity of specific gas and the ECSA on mass spectrum, we demonstrate that the ECSA accurately gives the mass flow rates of each evolved gas, including organic or inorganic gases, for not only single but multi-component reactions, which cannot be implemented by the traditional measurements.
Space charge injected via interfaces and tree initiation in polymers
[J].
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.011912
URL
PMID:23005457
[本文引用: 1]

Particle-based simulation represents a powerful approach to modeling physical systems in electronics, molecular biology, and chemical physics. Accounting for the interactions occurring among charged particles requires an accurate and efficient solution of Poisson's equation. For a system of discrete charges with inhomogeneous dielectrics, i.e., a system with discontinuities in the permittivity, the boundary element method (BEM) is frequently adopted. It provides the solution of Poisson's equation, accounting for polarization effects due to the discontinuity in the permittivity by computing the induced charges at the dielectric boundaries. In this framework, the total electrostatic potential is then found by superimposing the elemental contributions from both source and induced charges. In this paper, we present a comparison between two BEMs to solve a boundary-integral formulation of Poisson's equation, with emphasis on the BEMs' suitability for particle-based simulations in terms of solution accuracy and computation speed. The two approaches are the collocation and qualocation methods. Collocation is implemented following the induced-charge computation method of D. Boda et al. [J. Chem. Phys. 125, 034901 (2006)]. The qualocation method is described by J. Tausch et al. [IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 20, 1398 (2001)]. These approaches are studied using both flat and curved surface elements to discretize the dielectric boundary, using two challenging test cases: a dielectric sphere embedded in a different dielectric medium and a toy model of an ion channel. Earlier comparisons of the two BEM approaches did not address curved surface elements or semiatomistic models of ion channels. Our results support the earlier findings that for flat-element calculations, qualocation is always significantly more accurate than collocation. On the other hand, when the dielectric boundary is discretized with curved surface elements, the two methods are essentially equivalent; i.e., they have comparable accuracies for the same number of elements. We find that ions in water--charges embedded in a high-dielectric medium--are harder to compute accurately than charges in a low-dielectric medium.
Observation of space charge accumulation behavior in cross-linked polyethylene at voltage polarity reversal
[C].
Electrical tree initiation in XLPE cable insulation by application of DC and impulse voltage
[J].Electrical tree initiation behavior of XLPE cable insulation was investigated by application of DC voltage, impulse voltage, repetitive DC voltage, and impulse voltage after DC prestressing. Treeing test samples are made of XLPE specimens with a pin-plane electrode system. The needle inserted has a tip radius of 5 mu m and a pinpoint angle of 30 degrees, and the pin-plane distance is 2 mm. No trees appeared when DC voltage up to 70 kV or -60 kV was applied on the samples continuously or repetitively. Impulse voltage with or without DC prestressing could initiate an electrical tree. The tree initiation ratio increased due to higher impulse voltage, increased DC prestress level and shorter rest time between DC prestress and impulse voltage. The measured initial tree length showed a proportional relation with the impulse magnitude, whereas it was almost independent of DC prestress level and the rest time. The observations are explained by the injection, accumulation, dissipation, trapping and detrapping of space charges in the region around the needle tip.
Tree initiation in polyethylene by application of DC and impulse voltage
[C].
The impact of DC bias on electrical tree growth characteristics in epoxy resin samples
[C].
Growth and partial discharge characteristics of electrical tree in XLPE under AC-DC composite voltage
[J].
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.011912
URL
PMID:23005457
[本文引用: 1]

Particle-based simulation represents a powerful approach to modeling physical systems in electronics, molecular biology, and chemical physics. Accounting for the interactions occurring among charged particles requires an accurate and efficient solution of Poisson's equation. For a system of discrete charges with inhomogeneous dielectrics, i.e., a system with discontinuities in the permittivity, the boundary element method (BEM) is frequently adopted. It provides the solution of Poisson's equation, accounting for polarization effects due to the discontinuity in the permittivity by computing the induced charges at the dielectric boundaries. In this framework, the total electrostatic potential is then found by superimposing the elemental contributions from both source and induced charges. In this paper, we present a comparison between two BEMs to solve a boundary-integral formulation of Poisson's equation, with emphasis on the BEMs' suitability for particle-based simulations in terms of solution accuracy and computation speed. The two approaches are the collocation and qualocation methods. Collocation is implemented following the induced-charge computation method of D. Boda et al. [J. Chem. Phys. 125, 034901 (2006)]. The qualocation method is described by J. Tausch et al. [IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 20, 1398 (2001)]. These approaches are studied using both flat and curved surface elements to discretize the dielectric boundary, using two challenging test cases: a dielectric sphere embedded in a different dielectric medium and a toy model of an ion channel. Earlier comparisons of the two BEM approaches did not address curved surface elements or semiatomistic models of ion channels. Our results support the earlier findings that for flat-element calculations, qualocation is always significantly more accurate than collocation. On the other hand, when the dielectric boundary is discretized with curved surface elements, the two methods are essentially equivalent; i.e., they have comparable accuracies for the same number of elements. We find that ions in water--charges embedded in a high-dielectric medium--are harder to compute accurately than charges in a low-dielectric medium.
Effect of ambient temperature on electrical treeing and breakdown phenomenon of polypropylene with repetitive pulse voltage
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2017.006229 URL [本文引用: 7]
Solid insulation and its deterioration
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acsnano.9b07042
URL
PMID:31697468
[本文引用: 1]

The issue of material dissolution is common in aqueous batteries, leading to serious performance deterioration. However, it is difficult to be solved so far. In this study, a single component cathode solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer (CaSO4·2H2O) is observed via in situ electrochemically charging process, as demonstrated in a Ca2MnO4 cathode for an aqueous zinc-ion battery. Density functional theory calculation confirms its electronic insulation and ionic conductor properties, indicating that it is an appropriate SEI film. The material dissolution seems to be effectively suppressed by the presence of the SEI layer on the cathode side. Meanwhile, this in situ formed interface layer is advantageous for lowering impedance, ameliorating interface, and reducing activation energy. As a result, significantly superior rate performance and cycle stability are exhibited. The observation of a protective SEI layer in an aqueous system may provide an insight into the development of high stability aqueous batteries.
DC treeing breakdown associated with space charge formation in polyethylene
[J].DOI:10.1109/TEI.1977.298002 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effect of temperature on space charge detrapping and periodic grounded DC tree in cross-linked polyethylene
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2016.005986 URL [本文引用: 1]
Temperature dependence of DC electrical tree initiation in silicone rubber considering defect type and polarity
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2017.006093 URL [本文引用: 1]
聚合物纳米复合电介质的界面性能研究进展
[J].
Research progress on interface properties of polymer nanodielectrics
[J].
Space charge behaviors of PP/POE/ZnO nanocomposites for HVDC cables
[J].
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.011912
URL
PMID:23005457
[本文引用: 1]

Particle-based simulation represents a powerful approach to modeling physical systems in electronics, molecular biology, and chemical physics. Accounting for the interactions occurring among charged particles requires an accurate and efficient solution of Poisson's equation. For a system of discrete charges with inhomogeneous dielectrics, i.e., a system with discontinuities in the permittivity, the boundary element method (BEM) is frequently adopted. It provides the solution of Poisson's equation, accounting for polarization effects due to the discontinuity in the permittivity by computing the induced charges at the dielectric boundaries. In this framework, the total electrostatic potential is then found by superimposing the elemental contributions from both source and induced charges. In this paper, we present a comparison between two BEMs to solve a boundary-integral formulation of Poisson's equation, with emphasis on the BEMs' suitability for particle-based simulations in terms of solution accuracy and computation speed. The two approaches are the collocation and qualocation methods. Collocation is implemented following the induced-charge computation method of D. Boda et al. [J. Chem. Phys. 125, 034901 (2006)]. The qualocation method is described by J. Tausch et al. [IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 20, 1398 (2001)]. These approaches are studied using both flat and curved surface elements to discretize the dielectric boundary, using two challenging test cases: a dielectric sphere embedded in a different dielectric medium and a toy model of an ion channel. Earlier comparisons of the two BEM approaches did not address curved surface elements or semiatomistic models of ion channels. Our results support the earlier findings that for flat-element calculations, qualocation is always significantly more accurate than collocation. On the other hand, when the dielectric boundary is discretized with curved surface elements, the two methods are essentially equivalent; i.e., they have comparable accuracies for the same number of elements. We find that ions in water--charges embedded in a high-dielectric medium--are harder to compute accurately than charges in a low-dielectric medium.
Investigating charge trapping behaviour of nanocomposite isotactic and syndiotactic polypropylene matrix
[C].
低密度聚乙烯-蒙脱土纳米复合材料的电树枝生长特性
[J].绝缘材料的电树枝生长特性分析是评估其绝缘性能的重要方法之一。采用熔融插层复合法制备了一种低密度聚乙烯–蒙脱土纳米复合材料,设计制作了纳米复合材料的电树枝生长试样及实验系统,在实验中观测了恒定电压下试样中电树枝生长过程及电树枝形态,测量了试样中电树枝的生长速度与扩散系数,分析了电树枝的局部放电统计特性。通过分析低密度聚乙烯–蒙脱土纳米复合材料的结晶行为,说明了纳米蒙脱土对该纳米复合材料中电树枝的抑制机制。实验与分析结果表明:纳米蒙脱土粒子有效提高了低密度聚乙烯的结晶度并减小了晶粒尺寸。同时,纳米蒙脱土粒子有利于降低纳米复合材料电树枝局部放电量与放电重复率,延缓了电树枝的引发与生长。
Growth properties of the electrical trees in LDPE-MMT nano-composites
[J].绝缘材料的电树枝生长特性分析是评估其绝缘性能的重要方法之一。采用熔融插层复合法制备了一种低密度聚乙烯–蒙脱土纳米复合材料,设计制作了纳米复合材料的电树枝生长试样及实验系统,在实验中观测了恒定电压下试样中电树枝生长过程及电树枝形态,测量了试样中电树枝的生长速度与扩散系数,分析了电树枝的局部放电统计特性。通过分析低密度聚乙烯–蒙脱土纳米复合材料的结晶行为,说明了纳米蒙脱土对该纳米复合材料中电树枝的抑制机制。实验与分析结果表明:纳米蒙脱土粒子有效提高了低密度聚乙烯的结晶度并减小了晶粒尺寸。同时,纳米蒙脱土粒子有利于降低纳米复合材料电树枝局部放电量与放电重复率,延缓了电树枝的引发与生长。
Quantum mechanical criteria for choosing appropriate voltage stabilization additives for polyethylene
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113801
URL
PMID:31891908
[本文引用: 1]

Via the thermal sintering, a nanocrystalline IrO2 coating was formed on the Ti substrate to successfully prepare a Ti/IrO2 electrode. Based on the electrochemical analysis, the prepared Ti/IrO2 electrode was found to have powerful oxidation effect on the organics in the TNT red water, where the nitro compound was oxidized through an irreversible electrochemical process at 0.6 V vs. SCE. According to the analysis of the nitro compound content, the UV-vis spectra, and the FTIR spectra of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) red water with electrolytic periods, the degradation mechanism of the dinitrotoluene sulfonate (DNTS) was developed. And the intermediates were characterized by UPLC-HRMS. The DNTS mainly occurred one electron transfer reaction on the Ti/IrO2 electrode. At the early stage of the electrolysis, the polymerization of DNTS was mainly dominated. The generated polymer did not form a polymer film on the electrode surface, but instead it promoted a further reduction. After electrolyzing for 30 h, all NO2 function group in the TNT red water was degraded completely.
Tailored side-chain architecture of benzil voltage stabilizers for enhanced dielectric strength of cross-linked polyethylene
[J].DOI:10.1002/polb.v52.16 URL [本文引用: 1]
Laboratory studies of treeing in solid dielectrics and voltage stabilization of polyethylene
[C].
Degradation mechanism at XLPE/semicon interface subjected to high electrical stress
[J].DOI:10.1109/14.78329 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effects of phenolic and sulfur type antioxidants on polymeric dielectrics
[C].
DC tree and grounded DC tree in XLPE
[C].