1 引言
非线性绝缘材料具有简化绝缘结构设计、减薄绝缘厚度的效果,在高电压复杂绝缘结构设计和制造领域具有广泛的应用前景。事实上,非线性绝缘介质在高电压绝缘领域已得到了较为广泛的应用,如高压电机定子线棒端部防电晕结构中的防电晕带[8,9]、电缆终端用电场应力控制片(或管)等[10,11]。非线性绝缘介质在高压直流电缆主绝缘和附件绝缘结构[12]以及高压复合绝缘子[13,14,15,16,17]中具有潜在应用前景。在世界范围内,高压直流输电技术得到广泛的关注,在我国“十三五”期间也将得到更快发展[18]。高压直流输电技术的迅猛发展对电力设备绝缘技术是一个巨大挑战,因为直流绝缘技术相比交流绝缘技术要复杂,其原因之一就是非线性问题。
2 国内外研究进展
2.1 非线性绝缘直流稳态介电特性
非线性绝缘介质直流稳态介电特性则用电导率与电场强度的函数关系(电流密度与电场强度曲线或伏安特性曲线)来表征[35]。从原理上讲,非线性直流稳态性能测试技术相对比较简单。从技术角度看,非线性绝缘直流稳态介电特性面临三个技术难点:其一是在高电场下测试时如何消除试样因焦耳热引起的温升,已有研究者设计了特殊形式的试样室,通过注入冷却的氮气来排除因焦耳热产生的热量[8];其二是弱电流信号测试时干扰问题,除了选用高稳定度直流电源和提供良好的屏蔽外,同时也可以采用时域数字信号插值滤波技术;其三是消除绝缘介质极化过程吸收电流的影响问题,个别绝缘介质极化建立过程十分缓慢,测试时间达到105s仍未达到真正意义的稳态,具体的方法是采用极化电流与去极化电流求和运算求得。采用极化电流与去极化电流求和运算实现稳态传导电流测试仍存在一定的问题,因为求和运算获取稳态电流技术是建立在极化充分建立和极化与去极化过程是对称这两个基本假设基础上的。在实际测量过程中,这两个假设条件并非真正意义上的满足。
由于非线性直流稳态介电特性表征和测试技术相对成熟,相关机理研究也趋于完善,如空间电荷限制电流理论、热激跳跃电导理论、肖特基效应和普尔-费兰凯尔效应等成功地建立直流稳态电导率与温度和电场强度的非线性函数关系[36]。
本课题组通过大量实验研究,得出LDPE/SiC复合材料的非线性稳态电导影响因素及其规律;结合非线性复合材料的微观结构和经典电介质理论,提出了复合材料的三步输运电导模型;根据所建立的三步输运电导模型,理论推导得出了聚合物基非线性复合材料稳态直流电导率与表观平均电场强度和温度的近似理论[37],即
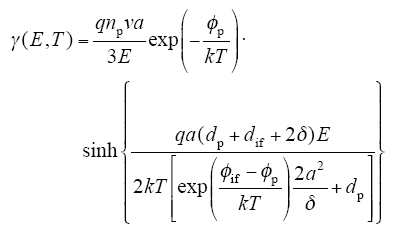
该理论公式包含聚合物基体属性、半导电无机填料属性和界面厚度、界面势垒等微观信息,并定性地解释了复合材料非线性电导与电场强度、温度、填料粒径和填加浓度的关系。
2.2 非线性绝缘交流稳态介电特性
关于非线性绝缘电介质交流稳态介电性能表征问题,国内外从事工程电介质研究的学者普遍借鉴线性绝缘介质交流稳态介电特性表征途径,即用并联等效电路模型表征介于平板电极间的绝缘介质,不同之处在于采用电压控制性电阻和电容。与此对应的表征非线性绝缘交流稳态介电特性参数体系为电场依赖型电导率和相对介电常数。
非线性绝缘交流稳态介电特性测试,同样可沿用线性绝缘介电特性的测试方法,但可能面临一些技术问题。
高压交流电桥法通常用于线性绝缘介质介电常数和损耗因数(或复介电常数)的测量。采用高压交流电桥研究非线性绝缘交流稳态介电特性时,通过不同幅值交流电压的多次测量可以得到介电常数和损耗因数与电场强度的关系(或复介电常数实部和虚部与电场强度的关系)。常用高压交流电桥均为工频高压电桥,只反映工频条件下交流稳态特性,所获的信息局限性很大;更重要的是高压交流电桥平衡条件与频率有关,非线性绝缘电介质在标准正弦交流电压作用下响应电流含有高次谐波,因此电桥不可能实现平衡。
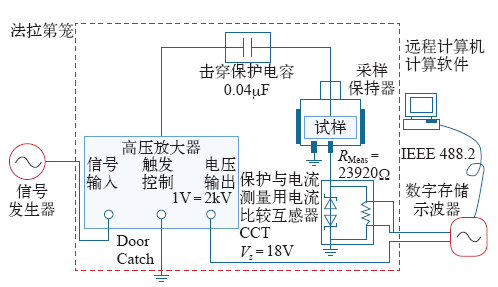
图1
图1
B.R.Varlow实验室非线性绝缘交流稳态介电特性测试系统原理图
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of testing system for the nonlinear insulation steady-state AC dielectric characteristics of B.R. Varlow laboratory
B.R.Varlow等在忽略阻性电流前提下,通过不同工频交流电压幅值下电压等效电容的测量得到电容–电压(介电常数–电场强度)曲线,进而得到了静态和动态介电常数与电场强度的关系。
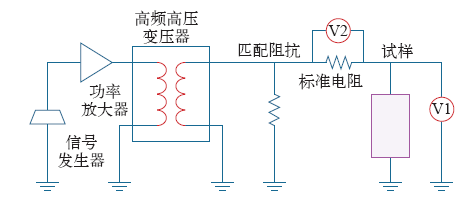
图2
图2
非线性绝缘电介质高频、高压伏安特性测试系统
Fig.2
The testing system for high frequency and high voltage volt-ampere characteristics of nonlinear insulated dielectrics
美国桑迪亚国家实验室测试系统实验能力最强,最高频率为1GHz,最高电压可达20kV,最大电流可达10kA,可实现电容值在1~50nF范围内的非线性电介质试样极化强度与电场强度(P-E)电滞回线的测量,代表着当今非线性绝缘介质交流稳态介电特性测试领域在硬件方面的最高水平。
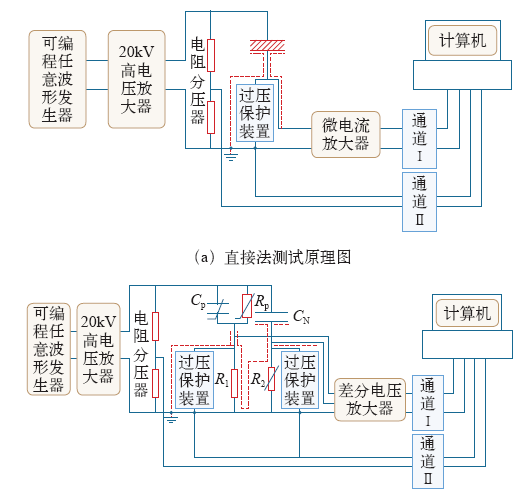
图3
图3
本课题组非线性绝缘交流介电特性测试平台原理图
Fig.3
Schematic diagram of the measuring platform for the AC dielectric properties of non-linear insulation developed by our team
表1 11 非线性绝缘材料及绝缘结构介电特性表征参数体系
Tab.1
| 表征对象 | 基本特性曲线 | 静态参数特性曲线 | 动态参数特性曲线 | 等效参数特性曲线 | 表征行为 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非线性绝缘结构 | 阻性伏安(IR-U)特性 | Gs及Gs-U特性曲线 | Gd及Gd-U特性曲线 | Geff及Geff-U特性曲线 | 阻性 |
| Rs及Rs-U特性曲线 | Rd及Rd-U特性曲线 | Reff及Reff-U特性曲线 | |||
| 电荷–电压(Q-U)特性 | Cs及Cs-U特性曲线 | Cd及Cd-U特性曲线 | Ceff及Ceff-U特性曲线 | 容性 | |
| 静态复阻抗及其与电压 特性曲线 | 动态复阻抗及其与电压 特性曲线 | 等效复阻抗及其与电压 特性曲线 | 综合 | ||
| 非线性绝缘材料 | JR-E特性曲线 | γs及γs-E特性曲线 | γd及γd-E特性曲线 | γeff及γeff-E 特性曲线 | 阻性 |
| ρs及ρs-E特性曲线 | ρd及ρd-E特性曲线 | ρeff及ρeff-E特性曲线 | |||
| D-E特性曲线 | εs及εs-E特性曲线 | εd及εd-E特性曲线 | εeff及εeff-E特性曲线 | 容性 | |
| P-E特性曲线 | χs及χs-E特性曲线 | χd及χd-E特性曲线 | χeff及χeff-E特性曲线 | ||
| 静态复介电常数及其 与电场特性曲线 | 动态复介电常数及其 与电场特性曲线 | 等效复介电常数及其 与电场特性曲线 | 综合 |
综合国内外研究发现,几乎所有研究者均仿照线性绝缘介质的等效电路建立非线性绝缘交流稳态特性非线性并联等效电路,没有将极化过程松弛极化行为和非松弛极化行为分开,导致同一试样不同频率下的测试结果不同[52]。松弛极化行为和非松弛极化行为混在一起,所得表征参数无法反映非线性绝缘介质极化行为的物理本质。由于交流稳态介电参数表征体系没有反映非线性绝缘介质极化行为的物理本质,非线性绝缘交流稳态介电机理研究必然存在相当大的局限性。
2.3 非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性
非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性是指非线性绝缘介质在脉冲、阶跃以及直流叠加脉冲等非周期瞬变电场下表现出的宏观介电响应特性。
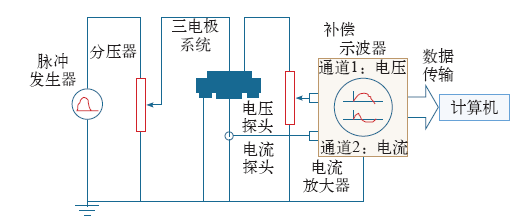
图4
图4
Boggs实验室冲击电压下非线性电介质暂态介电性能测试系统
Fig.4
The measurement system for transient dielectric Properties of nonlinear dielectrics under impulse voltage in Boggs laboratory
图5
图5
Boggs非线性绝缘暂态等效电路
Fig.5
Boggs transient equivalent circuit for nonlinear insulation
3 关于非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性表征和测试技术的思考
3.1 关于暂态介电特性的表征的思考
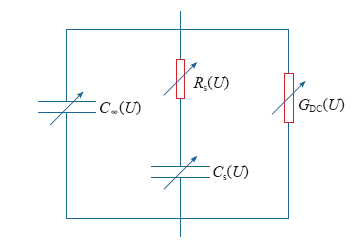
为了克服现有非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性等效电路模型在表征非线性松弛极化行为的不足,参照线性绝缘暂态特性等效电路模型,可采用图6所示的非线性绝缘暂态介电特性等效电路模型。
图6
图6
非线性绝缘暂态介电特性等效电路模型
Fig.6
Equivalent circuit model for transient dielectric characteristics of nonlinear insulation
该等效电路模型中,GDC(U)表征非线性直流稳态电导特性;C∞(U)表征高频非松弛极化非线性极化特性;CS(U)和RS(U)串联支路表征非线性绝缘松弛极化特性,非线性松弛时间用τ(U) = CS(U)RS(U)来表征,其中,CS(U)表征非线性绝缘松弛极化对直流静态电容的增量。表征松弛极化特性的支路可以有多个支路的并联,支路个数取决于松弛极化机制的个数。模型中除RS(U)外,GDC(U)、C∞(U)和CS(U)均具有明确的物理意义,但RS(U)与CS(U)共同表征松弛极化的松弛特性。暂态激励电压U是时间的函数,所以上述所有参数均是时间的函数。
在平板均匀电场条件下,消除试样几何尺寸因素后可得到表征非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性参数 χ∞(E)、χs(E)、γDC(E)和τ(E)。由于暂态过程松弛极化行为是出于动态随时间变化的,故用极化率 和τ(E)来表征,而不是εs(E)和τ(E)。各参数与电场强度的函数形式可采用多项式,由此可定义类似非线性光学中的高阶电导率和极化率。
非线性绝缘暂态介电特性参数体系全面反映其介电属性和物理本质,换言之,通过暂态介电参数进行理论计算可得到任意激励电压形式的稳态及暂态介电响应特性。
3.2 关于非线性绝缘暂态介电特性测试技术的思考
非线性暂态介电特性的表征涉及多个物理量与电场强度的函数关系,测试技术就是通过实验的途径获取这些参数及其函数形式。对测试技术而言,可测得不同形式波形和幅值暂态电压(电场)时域波形和对应响应电流时域波形。
如何以测试得到的激励电压和响应电流时域信号为基础数据获得非线性绝缘电介质介电特性表征参数是非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性测试技术的关键。这一过程和自动控制领域的非线性模式在原理上是相同的,非线性参数数量越多,自由度越高,模式识别难度越大,或鲁棒性越差。
为了克服非线性模式识别因自由度高、鲁棒性差的问题,从理论上讲需要适当增加约束条件。每一种测试条件下测得一组激励电压和响应电流时域信号数据为一个约束条件,这就要求进行多种激励电压波形的组合测试。电压波形组合的合理优化,可有效减少测试次数和提高非线性绝缘介质介电参数的测试精度和准确性。要实现这一目标需要开展大量基础理论研究和实验研究。
非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性参数测量的基础是如何准确测得激励电压和响应电流时域信号。这就要求测试系统能提供各种可能的暂态激励电压,同时满足响应电流信号的宽频段、宽量限精准测量。往往仅靠硬件电路的优化设计很难满足宽频段、宽量限精准测量,需要通过软件进行测试系统的校验和响应电流信号时域波形的重构。
3.3 关于非线性绝缘暂态介电特性表征和测试技术后续需要开展的研究
非线性绝缘介质的暂态介电特性表征和测试技术研究现状十分落后,甚至处于空白状态。测试技术是支撑相关基础理论研究和工程应用技术研究的手段。综合分析非线性绝缘介质暂态介电行为,建议开展以下几方面的研究工作:
(1)非线性绝缘暂态介电特性表征参数体系的建立。可借鉴非线性光学的表征途径,建立高阶电导、高阶极化率和极化松弛特性形状函数等参数体系。表征参数体系中,非线性松弛极化的形状函数的确定难度最大,需要通过大量实验规律的总结和理论分析来确定。
(2)非线性绝缘暂态介电特性等效电路的建立。等效电路的作用是建立非线性绝缘介质介电参数体系和激励电压、响应电流时域信号关联的桥梁,即首先通过激励电压和响应电流信号作为基础数据,通过适当的算法求取非线性等效电路非线性器件参数函数,而后消除试样几何尺寸因素得到介质表征参数。需要通过理论和实验综合研究确定等效电路的形式,以确保等效电路的有效性。有效性的评价应通过验证性实验进行验证。
(3)非线性等效电路非线性器件表征函数和参数的求取。即以激励电压和响应电流信号作为基础数据,通过适当的算法确定非线性等效电路非线性器件参数函数和求取函数中的具体参数。该过程可借鉴非线性模式识别技术得以实现。
(4)激励电压波形组合的优化。每一种激励电压与响应电流时域测试数据视为一个约束条件,至少需要多少组测试数据可保证非线性模式识别的鲁棒性是值得深入研究的问题。
(5)非线性绝缘暂态介电特性测试平台的建立。搭建测试平台的硬件系统和开发软件系统。硬件系统主要由电源与激励电压和响应电流测试系统组成。电源系统可采用可编程信号发生器和高精度线性高压放大器组合构成。激励电压和响应电流测试系统应满足宽频段、宽量限精准测量的要求,可通过硬件设计和软件修正两个环节得以实现。
4 结论
非线性绝缘暂态介电行为十分复杂,涵盖直流稳态和交流稳态及极化动态松弛行为。非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性表征参数体系将是反映材料介电属性最完备的参数体系。采用暂态介电表征参数体系开展相关基础理论研究和应用技术研究可实现研究过程的全面性、系统性和彻底性。然而,因非线性和暂态双重因素,非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性表征和测试技术面临极大的挑战。非线性绝缘介质暂态介电特性测试技术研究不仅为非线性绝缘电介质理论研究和工程应用研究奠定基础,同时可促进包括铁电体在内的非线性功能电介质介电特性研究。
参考文献
Nonlinear fillers in electrical insulation
[J].
DOI:10.3390/molecules23123153
URL
PMID:30513654
[本文引用: 1]

Recently, composite materials with nonlinear dielectric or resistive properties performed well in electric field homogenization and space charge suppression in a high voltage transmission and distribution system. For the purpose of obtaining insulation materials with desirable dielectric and electrical resistance properties, we investigated several fillers with nonlinear electrical properties doped in silicon rubber composites, and their dependency on the temperature and field. The samples of silicone rubber composites with different components were prepared using barium strontium titanate (BST) and zinc oxide (ZnO) as the filler, and high temperature vulcanized silicone rubber (SiR) as the matrix. The investigations revealed that the BST-doped samples showed different dielectric properties compared to ZnO-doped composites, with an increase in the electric field, which was nonlinear. The resistivity of both doped samples was similar. Results demonstrated that it was possible to achieve higher values of permittivity, and lower values of tanδ and resistivity, with respect to unfilled silicone rubber composites over a wide electrical field and temperature range. Discussion of the results attributes these important functional behaviours to the spontaneous polarization of nonlinear nanoparticles and the interaction between the SiR chains and the nonlinear nanoparticles at the interfacial area.
Engineering with nonlinear dielectrics
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b02844
URL
PMID:31405278
[本文引用: 3]

Nonlinear wavefront control is a crucial requirement in realizing nonlinear optical applications with metasurfaces. Numerous aspects of nonlinear frequency conversion and wavefront control have been demonstrated for plasmonic metasurfaces. However, several disadvantages limit their applicability in nonlinear nanophotonics, including high dissipative loss and low optical damage threshold. In contrast, it has been shown that metasurfaces made of high-index dielectrics can provide strong nonlinear responses. Regardless of the recent progress in nonlinear optical processes using all-dielectric nanostructures and metasurfaces, much less advancement has been made in realizing a full wavefront control directly with the generation process. Here, we demonstrate the nonlinear wavefront control for the third-harmonic generation with a silicon metasurface. We use a Pancharatnam-Berry phase approach to encode phase gradients and holographic images on nanostructured silicon metasurfaces. We experimentally demonstrate the polarization-dependent wavefront control and the reconstruction of an encoded hologram at the third-harmonic wavelength with high fidelity. Further, we show that holographic multiplexing is possible by utilizing the polarization states of the third harmonic generation. Our approach eases design and fabrication processes and paves the way to an easy to use toolbox for nonlinear optical wavefront control with all-dielectric metasurfaces.
Mechanism for omposite materials with dielectric constant which increases with electric field
[J].
DOI:10.1073/pnas.1604145113
URL
PMID:27078108
[本文引用: 2]

Superconductivity of n-doped SrTiO3, which remained enigmatic for half a century, is treated as a particular case of nonadiabatic phonon pairing. Motivated by experiment, we suggest the existence of the mobility edge at some dopant concentration. The itinerant part of the spectrum consists of three conduction bands filling by electrons successively. Each subband contributes to the superconducting instability and exhibits a gap in its energy spectrum at low temperatures. We argue that superconductivity of n-doped SrTiO3 results from the interaction of electrons with several longitudinal (LO) optical phonons with frequencies much larger than the Fermi energy. Immobile charges under the mobility edge threshold increase the "optical" dielectric constant far above that in clean SrTiO3 placing control on the electron-LO phonon interaction. TC initially grows as density of states at the Fermi surface increases with doping, but the accumulating charges reduce the electrons-polar-phonon interaction by screening the longitudinal electric fields. The theory predicts maxima in the TC-concentration dependence indeed observed experimentally. Having reached a maximum in the third band, the transition temperature finally decreases, rounding out the TC (n) dome, the three maxima with accompanying superconducting gaps emerging consecutively as electrons fill successive bands. This arises from attributes of the LO optical phonon pairing of electrons. The mechanism of LO phonons opens the path to increasing superconducting transition temperature in bulk transition-metal oxides and other polar crystals, and in charged 2D layers at the LaAaO3/SrTiO3 interfaces and on the SrTiO3 substrates.
改善不均匀电场的非线性复合材料研究进展
[J].
Progress of nonlinear polymer composites for improving nonuniform electrical fields
[J].
Inprovement in electrical by nonlinear fillers
[J].
Nonlinear resistive electric field grading part 2: materials and applications
[J].DOI:10.1109/MEI.2011.5739419 URL [本文引用: 1]
Comprehensive electrical and thermal analysis of the stress grading system of a large hydro generator
[J].DOI:10.1109/MEI.2018.8246120 URL [本文引用: 1]
Stress control methods on a high voltage insulator: a review
[C].
Temperature and electric field dependence of stress grading on form-wound motor coils
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2010.5412026 URL [本文引用: 1]
非线性电导材料应力锥改善电缆终端电场强度分布
[J].
Improving the electric field strength distribution of cable terminals by stress cone of nonlinear conductivity material
[J].
超导电缆终端用非线性复合材料研究进展
[J].
Research progress in nonlinear polymer composites for superconducting cable terminal
[J].
Effect of insulation properties on the field grading of solid dielectric DC cable
[J].DOI:10.1109/61.956720 URL [本文引用: 1]
The design of dielectric barriers for HVDC bushings
[C].
Electric stress grading of composite bushings using high dielectric constant silicone compositions
[C].
Design optimization of high voltage bushing using electric field computations
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2006.258193 URL [本文引用: 1]
Electrical properties of field grading materials influenced by the silicon carbide grain size
Making old new again: HVDC and FACTS in the northeastern united states and canada
[J].DOI:10.1109/MPE.2015.2501198 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effect of insulation properties on the field grading of solid dielectric DC cable
[J].DOI:10.1109/61.956720 URL [本文引用: 1]
电导及介电自适应调控的复合绝缘材料及其应用
[J].
Composite insulating material with self-adaptively adjusted conductivity/permittivity and its applications
[J].
Nonlinear effective permittivity of field grading composite dielectrics
[J].
Grading electric field in high voltage insulation using composite materials
[J].DOI:10.1109/MEI.2018.8246118 URL [本文引用: 1]
Nonlinear conduction and surface potential decay of epoxy/SiC nanocomposites
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2017.006454 URL [本文引用: 1]
Effects of surface-modification on properties of Graphene/Epoxy composites
[C].
AngEffects of non-linear conductivity on charge trapping and de-trapping behaviours in epoxy/SiC composites under DC stress
[J].
高压直流交联聚乙烯电缆应用与研究进展
[J].
Application and research progress of HVDC XLPE cables
[J].
Novel evaluation methods of end-turn stress grading materials for converter-fed high voltage rotating machines
[C].
HVDC电缆电场分布影响因素的仿真研究
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2016.09.031
URL
[本文引用: 1]

电场分布是决定电缆绝缘短时耐压能力和长期运行可靠性的关键因素。HVDC电缆稳定运行时,绝缘材料的电导率决定电场分布,在较高温度梯度分布下有可能出现电场分布翻转现象。由于电缆绝缘材料的非线性电导率是温度及电场的函数,在投入运行和电压极性反转时HVDC电缆暂态电场分布更为复杂。为此,采用多物理场耦合软件仿真研究了绝缘材料非线性电导属性对不同温度梯度、不同施压方式下电缆绝缘稳态和暂态电场的影响规律。仿真结果发现:当绝缘材料非线性属性确定,绝缘内温度梯度越高,稳态时电场分布翻转现象越严重;电压反转过程暂态电场最大值与电压极性反转时间密切相关,反转时间越短暂态最大电场越高,且暂态最大电场的位置越靠近导体屏蔽。仿真结果同时表明:降低材料电导活化能和提高材料电导率对电场依赖性有利于在温度梯度下对电缆绝缘稳态和暂态电场分布的控制。根据仿真研究结果,建议在HVDC电缆料研发时应采取有效的调控手段降低材料电导活化能和提高场致增强型电导的场强依赖系数;而在HVDC电缆设计时,要特别关注温度梯度效应和极性反转过程中的暂态电场分布问题。
Simulation on the influence factors of electric field distribution in HVDC cable
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2016.09.031
URL
[本文引用: 1]

电场分布是决定电缆绝缘短时耐压能力和长期运行可靠性的关键因素。HVDC电缆稳定运行时,绝缘材料的电导率决定电场分布,在较高温度梯度分布下有可能出现电场分布翻转现象。由于电缆绝缘材料的非线性电导率是温度及电场的函数,在投入运行和电压极性反转时HVDC电缆暂态电场分布更为复杂。为此,采用多物理场耦合软件仿真研究了绝缘材料非线性电导属性对不同温度梯度、不同施压方式下电缆绝缘稳态和暂态电场的影响规律。仿真结果发现:当绝缘材料非线性属性确定,绝缘内温度梯度越高,稳态时电场分布翻转现象越严重;电压反转过程暂态电场最大值与电压极性反转时间密切相关,反转时间越短暂态最大电场越高,且暂态最大电场的位置越靠近导体屏蔽。仿真结果同时表明:降低材料电导活化能和提高材料电导率对电场依赖性有利于在温度梯度下对电缆绝缘稳态和暂态电场分布的控制。根据仿真研究结果,建议在HVDC电缆料研发时应采取有效的调控手段降低材料电导活化能和提高场致增强型电导的场强依赖系数;而在HVDC电缆设计时,要特别关注温度梯度效应和极性反转过程中的暂态电场分布问题。
直流叠加冲击电压下HVDC电缆暂态电场分布特性研究
[J].
Research on the transient electric field distribution in HVDC cable under DC voltage superimposed impulse voltages
[J].
Applications of nonlinear analysis in power engineering
[C].
On the estimation of AC behavior of field grrading composite
[C].
Measurement of non-linear dielectric properties-theoretical analysis
[C].
Stress dependent conductivity of field grading materials under time varying electrical fields
[C].
Nonlinear resistive electric field grading part 1: theory and simulation
[J].
ZnO microvaristors doped polymer composites with electrical field dependent nonlinear conductive and dielectric characteristics
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.matlet.2016.02.016 URL [本文引用: 1]
High-voltage low-frequency dielectric-spectroscopy used for characterization of nonlinear insulation materials
[C].
Measurement of nonlinear dielectricity in ferroelectric polymers
[J].
压敏陶瓷-硅橡胶复合材料的非线性压敏介电特性
[J].
Nonlinear dielectric and conductivity properties of ZnO varistor/silicone rubber polymer composites
[J].
Insulation characterization with nonlinear impedance spec-troscopy
Non-linear AC properties of a ceramic/resin composite
[C].
Non-linear DC and AC conductivity in electrically insulating composites
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2003.1219645 URL [本文引用: 1]
A comparison between the dynamic and static AC conductivity characteristics of barium titanate filled acrylic resin
[C].
Non-linear ferroelectric composite dielectric materials
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2005.1511103 URL [本文引用: 1]
Non-linear dielectric testing at high AC voltages using waveforms and harmonics
[C].
Impedance and nonlinear dielectric testing at high AC voltages using waveforms
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIM.2005.851414 URL [本文引用: 1]
AC modeling and anisotropic dielectric properties of stress grading of form-wound motor coils
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2010.5492240 URL [本文引用: 1]
A testbed for high voltage, high bandwidth characterization of nonlinear dielectrics
[C].
非线性绝缘电介质AC介电特性参数及其测量
[J].为调控电场分布避免电场集中,由聚合物与无机半导体填料制备的非线性绝缘电介质在许多高压设备中得到应用。非线性绝缘电介质介电特性的测试是其理论与应用技术研究的重要基础。研发了一套基于虚拟仪器技术的非线性绝缘介质交流介电特性测试装置,实现交流激励电压和响应电流瞬时波形的测试。参照激励电压通过确定的算法将响应电流分解成阻性电流和容性电流。通过对电压与电流波形的分
AC dielectric characterization parameters of nonlinear insulating dielectrics and their measurement
[J].为调控电场分布避免电场集中,由聚合物与无机半导体填料制备的非线性绝缘电介质在许多高压设备中得到应用。非线性绝缘电介质介电特性的测试是其理论与应用技术研究的重要基础。研发了一套基于虚拟仪器技术的非线性绝缘介质交流介电特性测试装置,实现交流激励电压和响应电流瞬时波形的测试。参照激励电压通过确定的算法将响应电流分解成阻性电流和容性电流。通过对电压与电流波形的分
A decomposition method for the total leakage current of MOA based on multipleLinear regression
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.61 URL [本文引用: 1]
Circuit to cancel ac displacement current to reveal dissipative and nonlinear conduction phenomena
[J].DOI:10.1063/1.1149987 URL [本文引用: 1]
Dielectric property measurement of nonlinear grading materials
Measurement of nonlinear dielectric properties effect of dielectric dispersion
[C].
Mechanism for composite materials with dielectric constant which increases with electric field
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2015.7116369 URL [本文引用: 1]
Considerations on evaluation methods for reliable stress grading systems of converter-fed high voltage rotating electrical machines
[C].
Measurement of stress grading conductivity to 1.6MV/m and 155℃ computation of grading power density and temperature rise for PWM waveforms
[C].
Rotating machine end turn grading during PWM transitions
[C].
Analytical approximations for the rotating machine end-turn field distribution
[J].DOI:10.1109/TDEI.2015.005240 URL [本文引用: 1]
End-turn grading for PWM-driven machines
[C].
Impulse and step voltage measurements on materials with non-linear V-I characteristic
[C].