1 引言
本文针对上述问题,从孤岛检测盲区和电流谐波畸变率两种孤岛检测算法有效性评价指标出发,根据算法参数与检测盲区和电流谐波畸变率之间的关系,对主动频率偏移法和Sandia频率偏移法进行了算法的改进,提出一种基于参数自适应的孤岛检测算法,使得当负载发生变化时,能够自动进行参数择优,提高孤岛检测成功率,并减小电流谐波畸变率。
2 主动移频类检测法
2.1 AFD算法基本原理
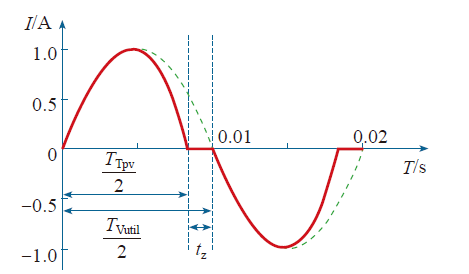
AFD法的基本原理是:基于并网标准前提下,在逆变器输出电流的过零点周期性地引入频率偏移量Δf,使并网电流的给定频率发生偏移最终超过设定的频率阈值范围,检测出发生孤岛效应[15]。
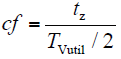
图1
并网运行时,由于主网对公共耦合点的电压产生钳制作用使电压的频率不会发生变化,孤岛效应发生后,耦合点电压摆脱主网的钳制,电压的频率随着被加入扰动信号的电流波形的变化而变化,每个周期都会比前一个周期略微增大。由于每个周期输出电压的波形都跟随畸变的斩波波形,因此电压的频率持续向上偏移,直到超出设定的保护阈值检测出孤岛状态。
AFD法的原理简单,操作方便,检测性能远高于被动检测法,因此在实际工程中被广泛采纳。其缺点是注入的扰动信号使电流波形发生畸变,这对逆变器输出的电能质量有一定的影响,这也是主动检测法固有的缺陷,且在特殊负载条件下存在检测盲区[16]。
2.2 SFS算法基本原理
美国的Sandia实验室为了克服上述AFD法的缺陷提出了一种改进的频率偏移孤岛检测法——Sandia频率偏移法,又称带有正反馈的主动频率偏移法(Active Frequency Drift with Positive Feedback,AFDPF)。
并网运行时,逆变器的输出电流和输出端电压分别为
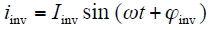
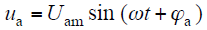
式中,Iinv和Uam分别为电流和电压的幅值;ϕinv和ϕa分别为电流和电压的初始相位。
定义SFS算法中的截断系数cf为
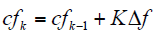
式中,cfk和cfk-1分别为第k个周期和第k-1个周期的截断系数;K为反馈系数;Δf = f - fg是逆变器端输出电压的频率f和电网电压的额定频率fg之间的频率偏差。
由上述截断系数的定义可以看出,Δf越大,cf越大,也就是说逆变器输出端电压的频率偏离电网电压额定频率越多,频率偏移的速度越快,Sandia频率偏移法利用这种正反馈效应使逆变器输出端电压的频率持续偏移超出设定的阈值,从而检测出孤岛状态。
3 算法参数的分析
3.1 参数与检测盲区的关系
理论分析及相关实验表明,几乎任何一种孤岛检测法都有检测失败的可能性,即一定存在检测盲区。本文采用Qf0×Cnorm坐标系来对算法的检测盲区进行描述,该坐标系能够在一个二维平面上体现出基于频率的孤岛检测法的盲区特性,且坐标之间相互独立不会发生耦合现象[17]。
经过理论推导得出AFD法和SFS法的盲区边界的公式分别为
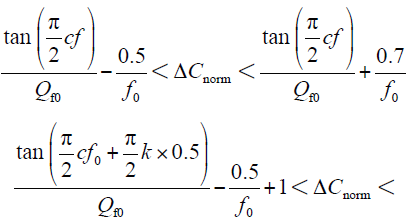

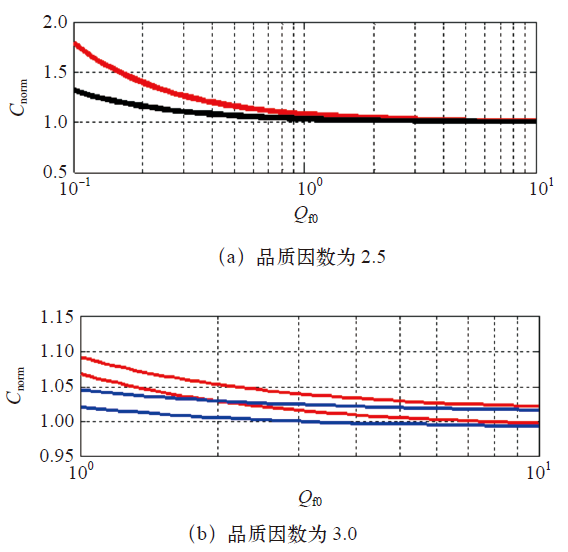
根据式(5),通过Matlab编程得到AFD检测法对应的孤岛检测盲区边界如图2所示。
图2
由图2可以看出,对品质因数不同的负载而言,AFD检测法的检测盲区一定存在,且截断系数cf的变化会导致检测盲区的位置发生变化,而对盲区的大小影响不大。
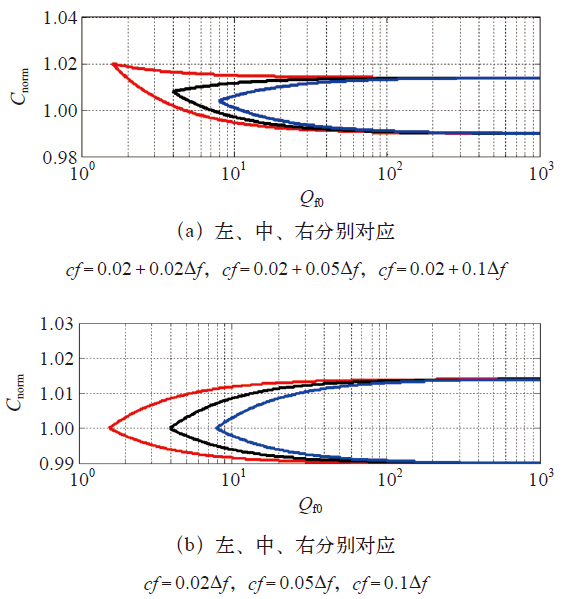
根据式(6),通过Matlab编程得到SFS检测法对应的孤岛检测盲区边界如图3所示。
图3
3.2 参数与电流谐波畸变率的关系
3.2.1 AFD算法参数与电流谐波畸变率的关系
文献[18]分析了电流谐波畸变率和截断系数cf之间的关系,截断系数越大,电流谐波畸变率越大。当系统引入AFD检测算法,不同截断系数条件下的电流谐波畸变率见下表。
表 截断系数对电流谐波畸变率的影响
Tab.
| 截断系数cf | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总谐波畸变率(%) | 3.56 | 5.30 | 5.92 | 7.08 |
分析可知,主动频率偏移法由于扰动信号的引入对电能质量造成影响,总谐波畸变率明显增大,证明了AFD检测法会对系统电能的质量产生不利影响,并且依据截断系数的不同,对电能质量的影响程度也有所差别。从上表中数据可知,当截断系数cf增大时,电流谐波畸变率也随之增大。因此能够得出在保证孤岛检测成功的前提下,截断系数cf的取值尽可能小可以减小主动频率偏移检测法对供电电能质量的影响。
3.2.2 SFS算法参数与电流谐波畸变率的关系
相较于AFD检测法而言,SFS检测法的截断系数从固定值变成了带反馈系数的变化值。
(1)选取相同的初始截断系数。若初始截断系数均设为0,反馈系数从K = 0.06变成K = 0.02时,电流谐波畸变率从2.54%变成2.17%,谐波畸变率变化幅度很小,由此证明反馈系数K会对电流的谐波畸变率产生影响,但是影响程度非常小,几乎可以忽略不计。而反馈系数K的增大却能够使孤岛算法的检测盲区有明显的减小,从而也有力地证明了SFS检测法的优越性。
(2)选取相同的反馈系数。当截断系数分别为cf = 0.02 + 0.03Δf,cf = 0.03 + 0.03Δf,cf = 0.05 + 0.03Δf时,逆变器输出电流的谐波畸变率分别为1.10%、4.06%和10.21%,该结果验证了截断系数越大,电流谐波畸变率越大的理论,并且当反馈系数K一定时,初始截断系数cf0越小,电流谐波畸变率就越小,所以通常情况下将初始截断系数cf0设作零。
综上所述,反馈系数K对谐波畸变率的影响较小,但是增大K的值能够减小孤岛检测盲区,而截断系数中的cf0对谐波畸变率的影响较大。因此,在设置算法参数时为了达到减小检测盲区并降低逆变器输出电流的谐波畸变率的目的,应该将初始截断系数cf0的值设置得尽量小,而反馈系数K的值则根据具体情况确定。
4 算法改进与仿真验证
4.1 基于参数自适应的算法改进
从上文对孤岛检测盲区的分析可知,虽然负载品质因数Qf的增大会增加孤岛检测难度,但选取不同的截断系数cf会使得检测盲区的位置不同,因此,可以通过负载的电阻、电容和电感值计算出Qf0和Cnorm的值,并将截断系数设置成检测盲区之外的参数,这种参数自适应的方法大大减小了主动频率偏移法孤岛检测失败的可能性。另外,Sandia频率偏移法中截断系数的选取原则类似,从上文的盲区分析中可知,反馈系数K的大小对孤岛检测盲区的大小有一定的影响,反馈系数K的取值越大,孤岛检测盲区越小。但是从电流谐波畸变率的角度而言,反馈系数K的增大会导致电流谐波畸变率略有增大。参数自适应算法可以将这种矛盾进行折中,它的核心思想就是在负载改变的情况下,进行参数寻优,使孤岛检测方法更加灵活、有效。
4.2 仿真验证
4.2.1 改进的AFD法仿真验证
设置负载参数为Qf0 = 2.5,Cnorm = 1.00。
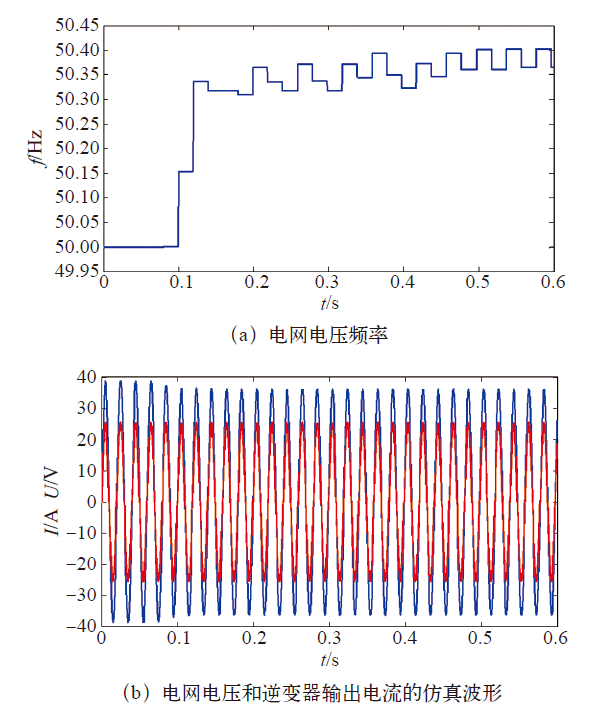
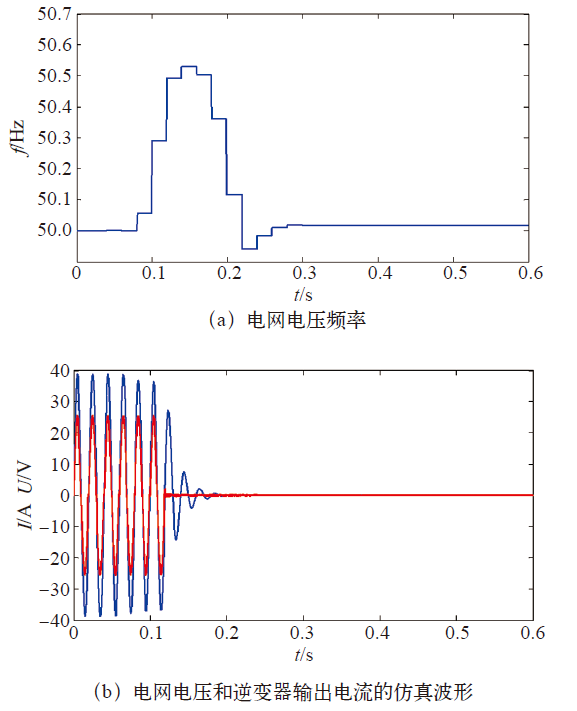
(1)当cf = 0.03时,电流的频率没有超过设定的阈值50.5Hz,孤岛检测失败。结果如图4所示。
图4
图4
未采用参数自适应算法的仿真结果
Fig.4
The simulation results of algorithm without parameter adaptive
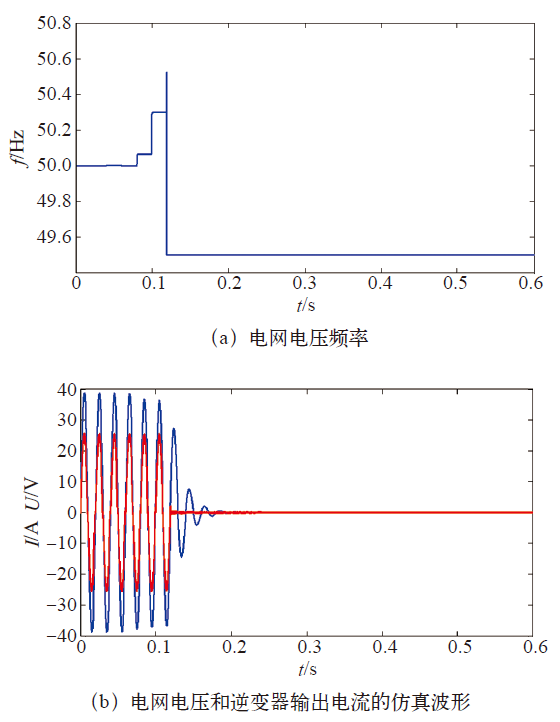
(2)采用自适应算法后,算法在经验区域内选择最适合的截断系数,使得孤岛检测成功。结果如图5所示。
图5
图5
采用参数自适应算法的仿真结果
Fig.5
The simulation results of parameter adaptive algorithm
利用参数自适应算法改变截断系数cf的值来改变检测盲区边界的位置,使得相应的负载远离检测盲区,这样使原本处于检测盲区之内的负载条件也能够成功地检测出孤岛,使孤岛检测的成功率得到提高。
4.2.2 改进的SFS法仿真验证
在SFS检测法中,当截断系数cf为变量时,若cf0的取值较大,则引入的谐波也比较大,因此在两个cf0都能检测成功时,应自动选取较小的cf0减小引入的谐波电流,提高供电电能质量。本文采用在SFS检测算法下,通过负载参数计算出Qf0和Cnorm的值,并利用查表法给出最佳的反馈系数K的值,使得负载发生变化时,能够自适应调节反馈系数K成功检测出孤岛,并使电流的谐波畸变率最小。该算法相较于传统的Sandia频率偏移法的优势是检测盲区小,电流的谐波畸变率大大减小并且运行灵活性强。
负载参数为Qf0 = 2.5,Cnorm = 1.00,当cf = 0.06 + 0.06Δf和cf = 0.06Δf时,都能够检测出孤岛,但是cf0的取值会对电流谐波畸变率产生较大的影响,因此在保证孤岛检测成功的前提下,算法应该能够选择谐波畸变率较小的参数。
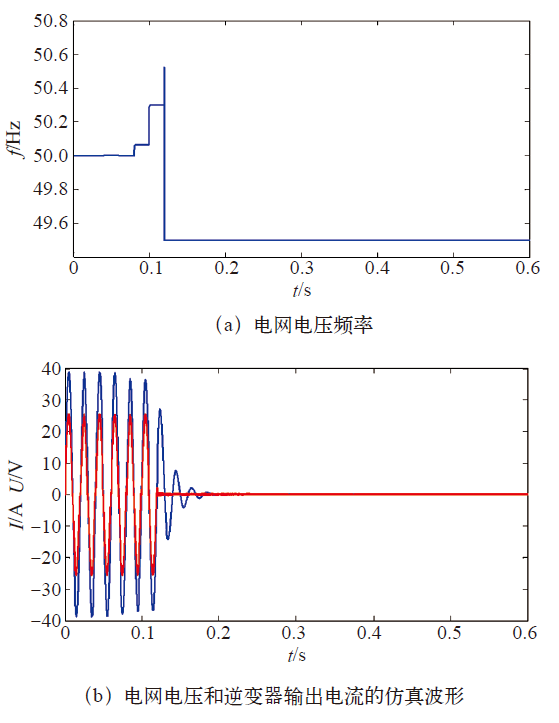
(1)未采用参数自适应算法的情况下,当参数为Qf0 = 2.5,Cnorm = 1.00,cf = 0.06 + 0.06Δf时,孤岛检测成功,其电流谐波畸变率为12.43%。仿真结果如图6所示。
图6
图6
未采用参数自适应算法的仿真结果
Fig.6
The simulation results of algorithm without parameter adaptive
(2)使用参数自适应算法,在相同的负载条件下,选择最优的参数。仿真波形如图7所示。
图7
图7
采用参数自适应算法的仿真结果
Fig.7
The simulation results of parameter adaptive algorithm
由以上分析可知,截断系数cf = 0.06 + 0.06Δf和cf = 0.06Δf均可以成功检测出孤岛,从图中可以看出,当cf = 0.06Δf时,电流的谐波畸变率为2.54%。对比可知,通过参数自适应的算法可以自动选择最优参数,在孤岛检测成功的前提下使得电流的总谐波畸变率更小。
5 结论
本文提出了一种基于参数自适应算法的孤岛改进算法,该算法能够根据参数与检测盲区和电流谐波畸变率之间的关系,在负载发生变化时,能够在经验区域内自适应选择最优的参数,提高孤岛检测成功率,降低电流谐波畸变率。但是该算法中还存在一些不足之处,在今后的研究中,可以进一步优化,使孤岛检测达到最佳效果。
参考文献
单相逆变器并网控制技术研究
[J].设计了一种具有零稳态误差的并网逆变器系统,系统控制器由比例调节器P和谐振调节器R组成。与传统的PI控制器比较,该比例谐振控制器(PR)在基波频率处增益无穷大,因此可以完全消除稳态误差。通过理论分析,系统中采用了一种更易实现的准谐振控制器,并给出控制器参数具体的设计方法。此外,为了消除电网电压畸变或扰动对逆变器输出电流的影响,系统中引入了电网电压前馈解耦控制,改善了系统输出电流的质量。理论分析和实验结果验证了系统具有较好的稳态性能和抗扰性能。
Research on control strategy for single-phase grid-connected inverter
[J].设计了一种具有零稳态误差的并网逆变器系统,系统控制器由比例调节器P和谐振调节器R组成。与传统的PI控制器比较,该比例谐振控制器(PR)在基波频率处增益无穷大,因此可以完全消除稳态误差。通过理论分析,系统中采用了一种更易实现的准谐振控制器,并给出控制器参数具体的设计方法。此外,为了消除电网电压畸变或扰动对逆变器输出电流的影响,系统中引入了电网电压前馈解耦控制,改善了系统输出电流的质量。理论分析和实验结果验证了系统具有较好的稳态性能和抗扰性能。
分布式发电系统的孤岛检测方法研究
[J].DOI:10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2011.01.027 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research on islanding detection of distributed power generation systems
[J].DOI:10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2011.01.027 URL [本文引用: 1]
Islanding detection of inverter-based distributed generation
[J].
一种使用的组合式光伏并网系统孤岛效应检测方法
[J].On the basis of traditional active frequency drift(AFD) method, an improved islanding detection method is presented adopting the pulse current amplitude disturbance. The method to inject the current amplitude disturbance is introduced, especially the method to choose disturbance time. The islanding detection is simulated in combination with over-voltage protection /under-voltage protection(OVP/UVP) and over-frequency protection /under-frequency protection(OFP/UFP). The results show that the combined method overcomes the problems associated with AFD or the current disturbing method. Islanding occurrence can be detected effectively with the presented method, and the photovoltaic system can be disconnected from the system before high-speed auto-reclosing, with limited harmonics and reduced non-detection zone.
A practical hybrid islanding detection method for grid-connected photovoltaic system
[J].On the basis of traditional active frequency drift(AFD) method, an improved islanding detection method is presented adopting the pulse current amplitude disturbance. The method to inject the current amplitude disturbance is introduced, especially the method to choose disturbance time. The islanding detection is simulated in combination with over-voltage protection /under-voltage protection(OVP/UVP) and over-frequency protection /under-frequency protection(OFP/UFP). The results show that the combined method overcomes the problems associated with AFD or the current disturbing method. Islanding occurrence can be detected effectively with the presented method, and the photovoltaic system can be disconnected from the system before high-speed auto-reclosing, with limited harmonics and reduced non-detection zone.
带正反馈的主动移频孤岛检测法的参数优化
[J].
Parameter optimization for active frequency drift with positive feedback islanding detection strategy
[J].
光伏并网发电系统孤岛检测
[J].
Islanding detection method for photovoltaic grid -connected power system
[J].
Overview of anti-islanding algorithms for PV systems: Part I passive methods
[C].
改进的主动频率偏移孤岛检测算法
[J].Since passive islanding detection methods have non-detection zone and traditional active frequency drift(AFD) methods may cause active current fluctuation, an improved AFD islanding detection algorithm is proposed. The algorithm realizes current frequency drift by controlling reactive current, so as to achieve positive feedback of voltage frequency at the point of common coupling(PCC) in islanding state and realize anti-islanding function. To reduce reactive current injection to the power system, the improved AFD algorithm should be combined with traditional passive islanding detection algorithm. Simulation and experiment results show that the improved algorithm can not only eliminate the non-detection zone of passive islanding detection algorithms when the loads power and the inverter power match, but also overcome the active current fluctuation of traditional AFD algorithms and improve the stability of DC bus voltage.
Improved active frequency drift anti-islanding algorithm
[J].Since passive islanding detection methods have non-detection zone and traditional active frequency drift(AFD) methods may cause active current fluctuation, an improved AFD islanding detection algorithm is proposed. The algorithm realizes current frequency drift by controlling reactive current, so as to achieve positive feedback of voltage frequency at the point of common coupling(PCC) in islanding state and realize anti-islanding function. To reduce reactive current injection to the power system, the improved AFD algorithm should be combined with traditional passive islanding detection algorithm. Simulation and experiment results show that the improved algorithm can not only eliminate the non-detection zone of passive islanding detection algorithms when the loads power and the inverter power match, but also overcome the active current fluctuation of traditional AFD algorithms and improve the stability of DC bus voltage.
用于单相分布式发电系统孤岛检测的新型电流扰动方法
[J].当分布式发电系统提供的功率与本地负载所需功率匹配, 且负载角和扰动角度相等时, 即使发生孤岛现象, 公共耦合点电压也一直处于非检测区内, 从而导致主动频率偏移法无法识别孤岛效应的问题。针对上述问题, 本文提出了一种新颖的2N电压周期电流扰动方法, 即第2N电压周期采用主动频率偏移方法, 第2N+1电压周期的电流与电压同步。根据公共耦合点相邻周期间的电压频率差是否正负连续交替变化来识别孤岛现象。仿真和实验结果证明该方法很大程度上解决了非检测区的问题, 而且适用于多台逆变器的并网运行情况。
A novel current-disturbing method for islanding detection in single-phase distributed power generation systems
[J].当分布式发电系统提供的功率与本地负载所需功率匹配, 且负载角和扰动角度相等时, 即使发生孤岛现象, 公共耦合点电压也一直处于非检测区内, 从而导致主动频率偏移法无法识别孤岛效应的问题。针对上述问题, 本文提出了一种新颖的2N电压周期电流扰动方法, 即第2N电压周期采用主动频率偏移方法, 第2N+1电压周期的电流与电压同步。根据公共耦合点相邻周期间的电压频率差是否正负连续交替变化来识别孤岛现象。仿真和实验结果证明该方法很大程度上解决了非检测区的问题, 而且适用于多台逆变器的并网运行情况。
主动移频法在光伏并网逆变器并联运行下的孤岛检测机理研究
[J].孤岛检测是光伏并网逆变器所必备的功能。在各种孤岛检测技术中,主动移频法及改进后的带正反馈主动移频法被广泛采用。该类方法通过对逆变器输出电流的频率进行扰动来实现孤岛检测。目前针对该类方法的研究主要集中在单台逆变器。该文采用相位原理和基于负载品质因数与谐振频率坐标系的盲区空间理论,对多机并联工作方式下主动移频法及带正反馈的主动移频法之间的相互影响及孤岛检测有效性进行深入理论分析,揭示了多机并联下孤岛检测可靠性与工作条件的关系,仿真与实验验证了理论分析的正确性。
Islanding detection evaluation for active frequency drifting methods in multiple photovoltaic grid-connected converter
[J].孤岛检测是光伏并网逆变器所必备的功能。在各种孤岛检测技术中,主动移频法及改进后的带正反馈主动移频法被广泛采用。该类方法通过对逆变器输出电流的频率进行扰动来实现孤岛检测。目前针对该类方法的研究主要集中在单台逆变器。该文采用相位原理和基于负载品质因数与谐振频率坐标系的盲区空间理论,对多机并联工作方式下主动移频法及带正反馈的主动移频法之间的相互影响及孤岛检测有效性进行深入理论分析,揭示了多机并联下孤岛检测可靠性与工作条件的关系,仿真与实验验证了理论分析的正确性。
基于置信区间法的分布式发电日出力曲线研究
[J].
Improved active frequency drift anti-islanding detection method for grid connected photovoltaic system
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2011.2171997
URL
[本文引用: 1]

As more distributed generators join the utility grid, the concern of possible undetected islanding operation increases. This concern is due to the safety hazards this phenomenon imposes on the personnel and equipment. Passive anti-islanding detection methods monitor grid parameters to detect islanding, whereas active methods inject a perturbation into the current waveform to drive these parameters out of limit when islanding occurs. The performance of active methods, such as conventional active frequency drift (AFD), is limited by the amount of total harmonic distortion (THD) they inject into the grid, which defines its nondetection zone. In this paper, an improved AFD anti-islanding method is presented based on a different current distortion injection waveform. The proposed method generates 30% less THD compared to classic AFD, resulting in faster island detection and improved nondetection zone. The performance of the proposed method is derived analytically, simulated using Matlab and verified experimentally using a prototype setup. A single-phase grid-tied photovoltaic distributed generation system is used for the simulation and experimental setup, and considered as potential application.
微电网非破坏性无盲区孤岛检测技术
[J].传统无源孤岛检测方法存在检测盲区,有源孤岛检测方法可减小或消除检测盲区,但其机制是将系统电压幅值或频率偏离至故障运行范围,从而判断孤岛发生,其本质属于破坏性孤岛检测方法。然而,微电网应用场合需要无盲区且非破坏性孤岛检测方法。为了解决该问题,提出一种基于负序电压正反馈(negative-sequence voltage positive feedback,NSVPF)的孤岛检测方法,并根据IEEE Std.1547测试标准对提出的方法进行理论分析及仿真研究。结果表明,在IEEE Std.1547规定的最差情况下,提出的NSVPF孤岛检测方法在电压处于正常运行范围的情况下仍可快速有效地检测到孤岛的发生,从而实现了非破坏性无盲区孤岛检测。此外,该文提出的孤岛检测方法在电网单相和两相断路情况下仍然有效,最后探讨了如何防止伪孤岛的问题。
Non-devastating islanding detection for micro-grids without non detection zone
[J].传统无源孤岛检测方法存在检测盲区,有源孤岛检测方法可减小或消除检测盲区,但其机制是将系统电压幅值或频率偏离至故障运行范围,从而判断孤岛发生,其本质属于破坏性孤岛检测方法。然而,微电网应用场合需要无盲区且非破坏性孤岛检测方法。为了解决该问题,提出一种基于负序电压正反馈(negative-sequence voltage positive feedback,NSVPF)的孤岛检测方法,并根据IEEE Std.1547测试标准对提出的方法进行理论分析及仿真研究。结果表明,在IEEE Std.1547规定的最差情况下,提出的NSVPF孤岛检测方法在电压处于正常运行范围的情况下仍可快速有效地检测到孤岛的发生,从而实现了非破坏性无盲区孤岛检测。此外,该文提出的孤岛检测方法在电网单相和两相断路情况下仍然有效,最后探讨了如何防止伪孤岛的问题。
用于分布式发电系统孤岛检测的偶次谐波电流扰动法
[J].Islanding protection is necessary for the distributed generation (DG) systems, but it is difficult for some traditional methods such as frequency or phase variation methods to detect the islanding effect when the power generated by the DG systems matches with the demand power of the local load. The islanding detection capabilities about different disturbing signals are analyzed and even harmonic current disturbing signal suiting to multi-inverter DG system is available in this paper. Combining with a zero-crossing frequency detector, the positive feedback loop with even harmonic current disturbance is introduced to detect the islanding phenomenon. Output current reference in the grid-connected inverter is affected by a minute disturbance signal in general. Once the islanding occurs, the positive feedback of disturbance current makes the voltage frequency at the point of common coupling go beyond a preset threshold value. It is easy to design the software program, less to inject the current harmonics into the grid, quick to detect the islanding effect, equal to form the multi-inverter system. Simulation and experimental results verify that the method is effective and reliable.
Even harmonic current disturbing method for islanding detection in the distributed power generation systems
[J].Islanding protection is necessary for the distributed generation (DG) systems, but it is difficult for some traditional methods such as frequency or phase variation methods to detect the islanding effect when the power generated by the DG systems matches with the demand power of the local load. The islanding detection capabilities about different disturbing signals are analyzed and even harmonic current disturbing signal suiting to multi-inverter DG system is available in this paper. Combining with a zero-crossing frequency detector, the positive feedback loop with even harmonic current disturbance is introduced to detect the islanding phenomenon. Output current reference in the grid-connected inverter is affected by a minute disturbance signal in general. Once the islanding occurs, the positive feedback of disturbance current makes the voltage frequency at the point of common coupling go beyond a preset threshold value. It is easy to design the software program, less to inject the current harmonics into the grid, quick to detect the islanding effect, equal to form the multi-inverter system. Simulation and experimental results verify that the method is effective and reliable.
An active anti-islanding method based on Phase-PLL perturbation
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2010.2089643
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper presents a new active anti-islanding detection method for distributed power generation systems. This method is based on introducing a disturbance at the inverter output and observing the behavior of the voltage at the point of common coupling (PCC), which depends on the impedance connected to the PCC in an islanding situation. The islanding detection is based on the Goertzel algorithm.
一种有效的孤岛检测盲区描述方法
[J].
A novel method for mapping non-detection zone
[J].
Evaluation of inverter resident passive islanding detection method for grid connected PV system under constant power mode
[C].