1 引言
目前,电压暂降检测的常用算法有RMS法、求导法、瞬时无功率法和短时傅里叶变换法等。其中,RMS法通过计算每个周波电压有效值来判断暂降的发生,是一种经典检测法,具有原理简单,计算量小等优势。但该方法对谐波和噪声较为敏感,精度有限,且无法描述暂降后的电压相角变化[4]。求导算法同样具有计算量小、易实现的优势,但其计算精度亦会受到谐波和噪声干扰,且还会受到采样频率的影响[5,6]。瞬时无功功率法在dq坐标或αβ坐标中计算电压暂降参数,精度较高,但在单相或三相不对称系统中应用时存在一定相位延迟,且算法需进行低通滤波,实时性会进一步下降[7,8,9]。短时傅里叶变换法将非平稳信号视为一系列短时平稳信号的叠加,其短时性通过时间窗来获得,在合适的窗函数条件下,所得结果具有较高精度和实时性[10,11]。该算法缺陷在于窗口形状一经确定便无法改变,这相当于使用固定尺度对信号进行分析,故对于具有瞬变特性的电压暂降信号,窗函数选择较为困难[12],具有一定局限性。
为此,本文提出了基于滑窗小波和二点算法的电压暂降检测方法,该方法并不利用高频小波系数检测暂降参数,而是利用滑窗小波对电压信号进行滤波,排除谐波干扰,再通过二点算法计算电压暂降比及相角变化量。仿真结果表明,该方法能够在谐波干扰条件下有效检测电压暂降过程。
2 基于小波变换的电压暂降检测
小波变换可将信号f (t)通过不同尺度分解至尺度空间和小波空间中。此时,信号可用多分辨率公式表示
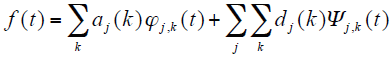
式中,aj(k)为概貌系数;dj(k)为小波系数;ϕj,k(t)为尺度函数;Ψj,k(t)为小波函数;下标j为小波分解层数。
式(1)中,ϕj,k(t)和Ψj,k(t)为尺度空间和小波空间的标准正交基。aj(k)和dj(k)可由如下分解公式求解
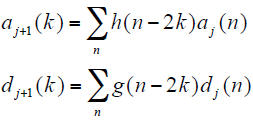
式中,h(n)和g(n)分别为小波变换的低通和高通滤波器系数。
小波分解后,第j层的概貌系数可由第j + 1层的概貌系数和小波系数重构得到
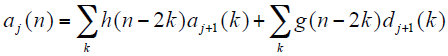
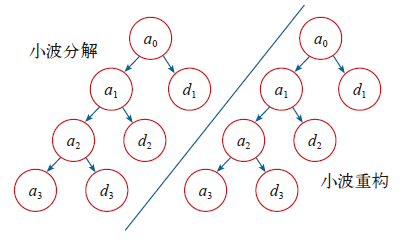
上述小波变换分解及重构过程的示意图如图1所示。
图1
图1
小波分解及重构示意图
Fig.1
Schematic diagram of wavelet decomposition and wavelet reconstruction
经过合理的层数划分和采样频率选取,小波变换的各层小波系数能够有效反映电网电压谐波分量。当电网电压发生暂降时,原始电压信号中等效于叠加了一个高频分量,因此通过检测小波系数的突变情况可以有效定位暂降时刻,从而实现电压暂降检测。
然而,电网电压暂降时刻是随机的,电网谐波分量的频率与相位亦是随机出现的,因此暂降引起的高频分量可能与谐波分量相互干扰,造成小波系数突变点难以识别,进而导致电压暂降检测精度下降,甚至检测失效。此为小波变换电压暂降检测的主要缺陷。
3 基于滑窗小波和二点算法的电压暂降检测
3.1 电压暂降检测二点法原理
为克服小波变换电压暂降检测的不足,首先提出一种暂降检测的二点法,下面推导算法原理。
设单相电压暂降前为理想电压u(t),则有
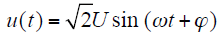
式中,U为电压有效值;ω为角频率;ϕ为初相角。
暂降后电压变为

式中,k为电压暂降的幅值比;φ为电压暂降的相位跳变角。k和φ即为电压暂降特征量。
设相邻两个采样时刻的电网电压信号u1(t)及u2(t)表达式为
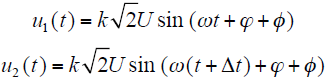
其中
令
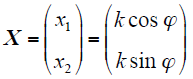
再令
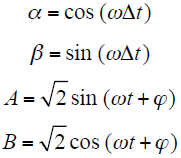
式中,A和B可由锁相环得到。
将u1(t)和u2(t)进行三角变换,得
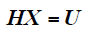
其中
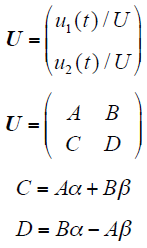
求解式(4),得x1和x2,进而得到k和φ,完成电压暂降特征量的求解。
下面分析一下式(4)的有解条件。若系数矩阵H不满秩,即
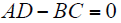
解得:β = 0。
由式(4)可得增广矩阵
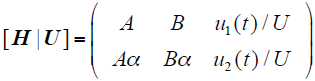
根据α和β的定义,当β = 0时,必有α = 1。那么,当u1(t) = u2(t)时,增广矩阵与系数阵等秩,但不满秩,式(4)有无穷解;当u1(t) ≠ u2(t)时,增广矩阵与系数阵不等秩,式(4)无解。
当且仅当β ≠ 0时,式(5)有唯一解
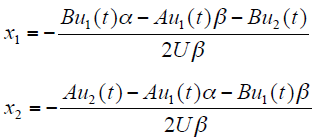
根据式(3),可得电压暂降特征量
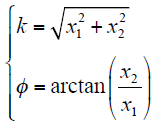
根据β ≠ 0条件,易得
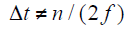
式中,f为电网频率,n = 0,1,2…。可见,只要采样周期满足式(7),即可求得特征量。对于电网工频信号而言,Δt通常远小于f,不构成无穷解条件,而满足唯一解条件。
从算法原理上看,二点法仅需两个采样点即可计算电压暂降特征量,具有良好快速性。但由于算法是基于理想正弦电压推导的,因此电网谐波必然会降低其计算精度。
3.2 滑窗小波变换与二点算法结合的电压暂降检测原理
谐波会对电压暂降检测的小波变换法和二点法的精度造成影响,为此提出一种基于滑窗小波和二点法的电压暂降检测算法。
该算法的思想是利用小波变换的时频域分析能力滤除电压谐波干扰,提取基波信号,再通过二点法对暂降特征量进行检测。由于小波变换需要一个工频周期采样数据参与运算,这意味着电压暂降信号的基波检测将至少延迟一个工频周期,因此可在小波变换中加入滑动时间窗,使之构成滑窗小波[18]。滑窗小波能在时域中对采样信号进行滑动加窗,使每个时刻的电压采样值均与之前采样值构成小波变换初始信号,从而实现电压暂降特征量的检测延迟小于一个工频周期。
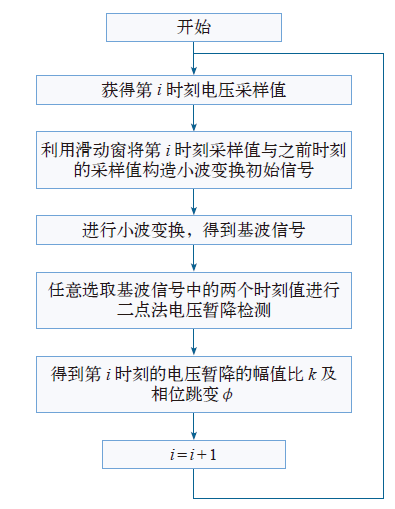
基于滑窗小波和二点法的电压暂降检测实现流程如图2所示。
图2
图2
基于滑窗小波和二点法的电压暂降检测实现流程
Fig.2
Implementation procedure for voltage sag detection based on sliding window wavelet and two points method
4 实例仿真与结果分析
4.1 仿真信号
设一组带有谐波的电压暂降仿真信号如下
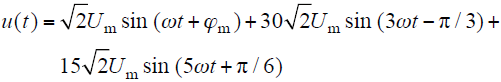
式中,Um为基波电压幅值,ϕm为基波电压相角,ω为角频率。若电压暂降发生时刻为td,电压恢复时刻为tr,Um初始值为220V,ϕm初始值为-π/3 rad,电压暂降幅值比k为0.5,暂降相位跳变角φ为 -π/6 rad,则暂降发生前后的电压幅值及相位可表示如下
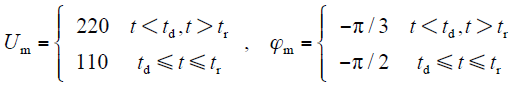
4.2 小波变换电压暂降检测的仿真分析
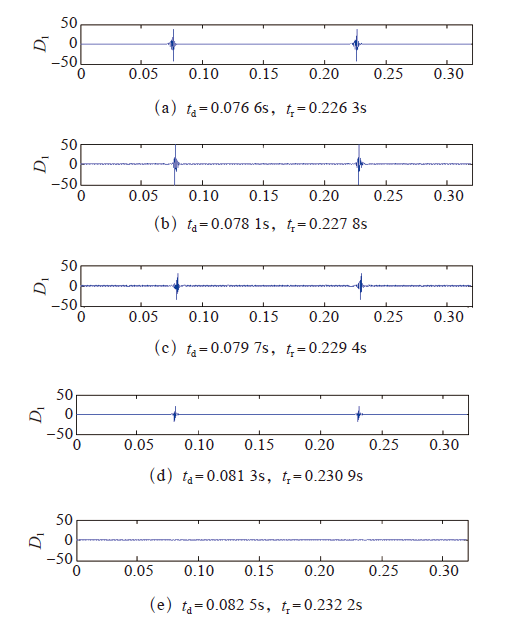
首先利用式(8)所示的仿真信号验证小波变换电压暂降检测的不足。为使谐波和电压暂降对仿真信号的时频特性造成影响,仿真在如表1所示的不同td和tr条件下进行。仿真时,采样频率为3.2kHz。
表1 电压暂降和恢复时刻的取值
Tab.1
| 序号 | 暂降时刻td/s | 恢复时刻tr/s |
|---|---|---|
| Case1 | 0.0766 | 0.2263 |
| Case2 | 0.0781 | 0.2278 |
| Case3 | 0.0797 | 0.2294 |
| Case 4 | 0.0813 | 0.2309 |
| Case 5 | 0.0825 | 0.2322 |
图3
图3
不同td和tr条件下的小波变换电压暂降检测结果
Fig.3
The results of voltage sag detection based on wavelet transform with the various td and tr
4.3 二点法电压暂降检测的仿真分析
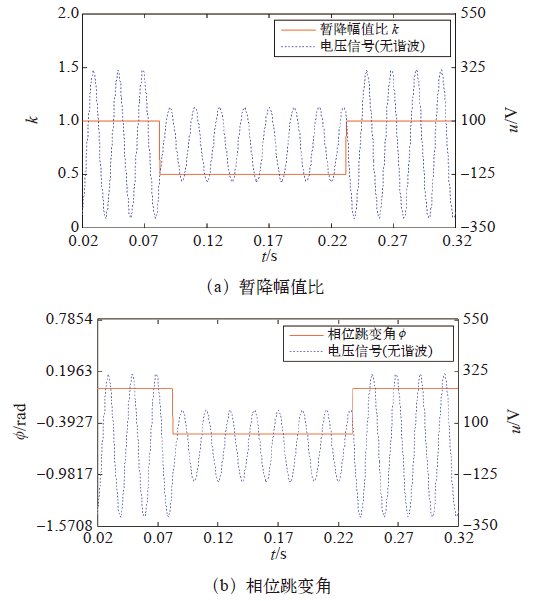
再对电压暂降检测二点法的特点进行仿真分析。首先去除暂降仿真信号中的谐波干扰,在无谐波条件下分析算法优势。图4中的仿真结果表明当电压发生暂降和恢复时,二点法所得暂降幅值比及相位跳变角检测相对误差分别仅为0.28%和0.35%,且几乎无延迟。这验证了算法在电网无谐波时的快速性和精度优势。
图4
图4
无谐波干扰条件下的二点法电压暂降检测结果
Fig.4
The results of voltage sag detection based on two points method without the harmonic interference
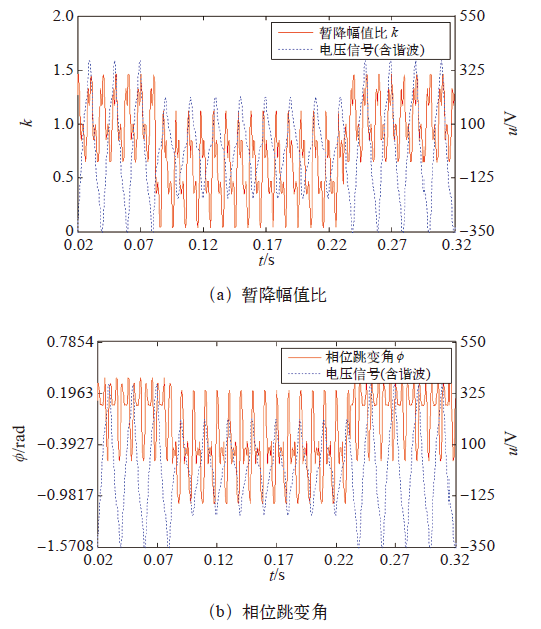
加入谐波干扰后的二点法暂降特征量检测结果如图5所示。可见,在暂降信号含有谐波条件下,暂降幅值比及相位跳变角检测结果存在严重误差,最大误差分别可达42.25%和83.71%。这表明二点法在谐波干扰环境下不应单独使用。
图5
图5
有谐波干扰条件下的二点法电压暂降检测结果
Fig.5
The results of voltage sag detection based on two points method with the harmonic interference
4.4 滑窗小波与二点法电压暂降检测的仿真分析
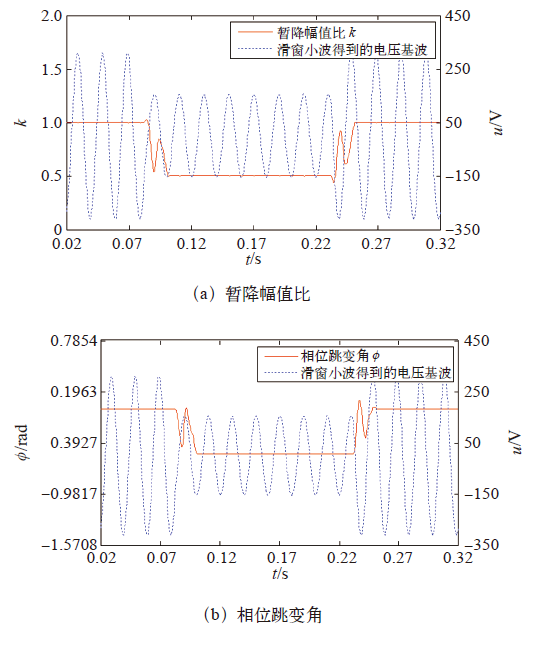
图6
图6
基于滑窗小波与二点法的电压暂降检测结果
Fig.6
The results of voltage sag detection based on sliding window wavelet and two points method
表2给出了不同td和tr条件下,基于滑窗小波与二点法计算得到的电压暂降特征量平均相对误差。分析可见,本文所提算法在td和tr不同取值情况下,均能得到高精度检测结果,不存在因小波系数最大模难以辨识而导致的暂降特征量无法计算问题,相对传统小波变换方法而言,可靠性优势明显。
表2 不同td和tr条件下,基于滑窗小波与二点法的电压暂降检测误差
Tab.2
| 序号 | 暂降时刻td/s | 恢复时刻tr/s | k误差(%) | φ误差(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 0.0766 | 0.2263 | 0.18 | 0.12 |
| Case 2 | 0.0781 | 0.2278 | 0.24 | 0.14 |
| Case 3 | 0.0797 | 0.2294 | 0.16 | 0.23 |
| Case 4 | 0.0813 | 0.2309 | 0.27 | 0.12 |
| Case 5 | 0.0825 | 0.2322 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
5 结论
针对小波变换电压暂降检测算法的不足,提出了一种基于滑窗小波和二点法的电压暂降算法。实例仿真表明,所提算法不存在因小波系数最大模难以辨识而导致的暂降特征量无法计算问题,能够在谐波干扰条件下准确地计算电压暂降幅值比及相位跳变角,检测结果延迟小于一个工频周期,满足实际工程需要。
参考文献
敏感负荷电压凹陷敏感度的随机估计方法
[J].
A method to stochastically estimate voltage sag sensitivity of sensitive equipments
[J].
电压暂降对配电系统可靠性影响及评估指标的研究
[J].
Study on distribution reliability considering voltage sag and acceptable indices
[J].
一种改进的电压暂降检测方法
[J].
An improved detection method of voltage sag
[J].
单相电压骤降特征量的求导检测算法
[J].
A derivation algorithm to detect characteristic quantity of single-phase voltage sag
[J].
基于dq变换的动态电压恢复器综合求导检测算法
[J].
A novel integrated derivation detection algorithm based on dq transformation for the dynamic voltage restorer
[J].
System and customer impact: considerations for series custom power devices
[J].DOI:10.1109/61.660890 URL [本文引用: 1]
一种无延时的改进d-q变换在动态电压扰动识别中的应用
[J].
Application of improved d-q transform without time delay in dynamic voltage disturbance identification
[J].
基于短时傅里叶变换的电压暂降扰动检测
[J].用短时傅里叶变换作为时频信号分析工具,研究在电压暂降扰动下暂降电压幅值检测、扰动时间定位和扰动源识别问题。提出利用暂降后电压信号的基频幅值曲线检测暂降电压幅值,利用暂降发生和结束时产生的高频信号对电压暂降扰动时间定位的方法,并提出根据基频幅值和扰动点个数来识别电压暂降扰动源的方法,该方法可以有效区分由短路故障引起的电压暂降和由感应电机启动引起的电压暂降。仿真试验结果表明该方法对电压暂降扰动检测精度高,同时比以往基于小波变换的方法在抵御谐波和噪声干扰方面更具有优越性。
Voltage sag disturbance detection based on short time fourier transform
[J].用短时傅里叶变换作为时频信号分析工具,研究在电压暂降扰动下暂降电压幅值检测、扰动时间定位和扰动源识别问题。提出利用暂降后电压信号的基频幅值曲线检测暂降电压幅值,利用暂降发生和结束时产生的高频信号对电压暂降扰动时间定位的方法,并提出根据基频幅值和扰动点个数来识别电压暂降扰动源的方法,该方法可以有效区分由短路故障引起的电压暂降和由感应电机启动引起的电压暂降。仿真试验结果表明该方法对电压暂降扰动检测精度高,同时比以往基于小波变换的方法在抵御谐波和噪声干扰方面更具有优越性。
Time-frequency and time-scale domain analysis of voltage disturbances
[J].DOI:10.1109/61.891515 URL [本文引用: 1]
电压暂降分析方法研究
[J].
Study of the voltage sag analysis methods
[J].
Wavelet based on-line disturbance detection for power quality applications
[J].DOI:10.1109/61.891505 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于小波变换模极大值原理和能量分布曲线的电力系统短期扰动分析
[J].
Analysis of short-term power system disturbance based-on module maximum principle and energy distribution curve
[J].
结合小波变换和能量算子的电压暂降检测方法
[J].This paper proposes a novel hybrid wavelet-energy operator method for accurate voltage sag detection and measurement. In the proposed method, the voltage sag is decomposed into two signal parts by wavelet transform: one is a detail signal, the other is an approximation signal. And in the detail signal, the start time and the end time of the sag signal can be detected. By applying an energy operator to the approximation signal, the temporary sag decline in value can be measured accurately and quickly. At the same time, the wavelet transform (WT) in this method acts like a filter. WT can weaken or remove the high frequency disturbance from voltage sag to enhance the noise immunity and accuracy of the energy operator. Simulation and experimental results verify the effectiveness of the algorithm.
Huang wenqing. Hybrid wavelet-energy operator method for voltage sag detection
[J].This paper proposes a novel hybrid wavelet-energy operator method for accurate voltage sag detection and measurement. In the proposed method, the voltage sag is decomposed into two signal parts by wavelet transform: one is a detail signal, the other is an approximation signal. And in the detail signal, the start time and the end time of the sag signal can be detected. By applying an energy operator to the approximation signal, the temporary sag decline in value can be measured accurately and quickly. At the same time, the wavelet transform (WT) in this method acts like a filter. WT can weaken or remove the high frequency disturbance from voltage sag to enhance the noise immunity and accuracy of the energy operator. Simulation and experimental results verify the effectiveness of the algorithm.
基于小波变换的电压暂降实时检测方法
[J].Voltage sag has become one of the most serious problems of power quality. For voltage sag compensation, it is critical to estimate voltage sag parameters fast and exactly. A wavelet based method for sag detection is presented in this paper. Zero-crossing point of voltage wave is detected, and 1/4 cycle of voltage signal is sampled from the zero-crossing point. The signal samples are preprocessed, and its detailed coefficients are obtained by discrete wavelet transform. It reconstructs the detailed coefficient vector and then gets the high-frequency coefficient vector (d1) with the same length of the sampling signal. The voltage sag parameters can be determined; the appearing instant of modulus maximum value of d1 is the starting point of the sag, and the modulus maximum value reflects the sag amplitude. This method is simple and easy to implement, moreover, the sag delay is less than 2.5 ms, which meets the real-time requirement of dynamic voltage restorer.
Voltage sag real-time detecting method based on wavelet transform
[J].Voltage sag has become one of the most serious problems of power quality. For voltage sag compensation, it is critical to estimate voltage sag parameters fast and exactly. A wavelet based method for sag detection is presented in this paper. Zero-crossing point of voltage wave is detected, and 1/4 cycle of voltage signal is sampled from the zero-crossing point. The signal samples are preprocessed, and its detailed coefficients are obtained by discrete wavelet transform. It reconstructs the detailed coefficient vector and then gets the high-frequency coefficient vector (d1) with the same length of the sampling signal. The voltage sag parameters can be determined; the appearing instant of modulus maximum value of d1 is the starting point of the sag, and the modulus maximum value reflects the sag amplitude. This method is simple and easy to implement, moreover, the sag delay is less than 2.5 ms, which meets the real-time requirement of dynamic voltage restorer.
基于蒙特卡洛的电网节点电压暂降风险分析
[J].
Mallat小波快速变换与IDRNN 在卫星实时故障检测与识别中的应用
[J].
Application of mallat wavelet fast transforms and IDRNN in real-time fault detection and identification for satellites
[J].