1 引言
传统的并网逆变控制策略主要有采用双闭环前馈解耦控制[3]、滞环控制[4]以及无差拍控制[5]等。采用双闭环前馈解耦控制,系统的动、静态性能取决于电流PI调节器,且设计较复杂;虽然采用滞环控制具有良好的动态性能,但其采样频率要求高;无差拍控制虽然具有开关频率固定以及控制简单等优点,但其对系统的参数准确性要求较高。而模型预测控制(MPC)作为一种新型的控制策略,因其具有良好的自适应性和鲁棒性,且不需要内环电流控制和PWM调制,控制方案容易实现等优点,近年来受到越来越多国内外学者关注[6,7,8,9]。模型预测直接电流控制[10,11,12,13](MPDCC)和模型预测直接功率控制[14,15,16](MPDPC)作为模型预测控制的延伸也逐步成为研究的热点。其中针对模型预测直接电流控制,主要集中在对并网电流的静止坐标及旋转坐标下的电流分量进行研究。而对于模型预测直接功率控制,目前还主要集中在两相静止αβ坐标系下的研究,该方法虽然计算量较小,但对系统有功功率和无功功率解耦控制不理想。
本文提出一种基于旋转dq坐标系下用于光伏并网逆变器的模型预测直接功率控制方法,该控制策略通过功率预测模型直接对有功功率P和无功功率Q进行预测,选择最优空间电压矢量,使价值函数最小。最后,采用仿真研究验证了所提出的MPDPC控制策略的可行性。结果表明所提出的基于旋转dq坐标系下的MPDPC控制策略能够快速跟踪给定功率和光照波动变化,实现了对输出有功功率和无功功率的控制,算法简单,易于实现。
2 光伏并网逆变器功率预测数学模型
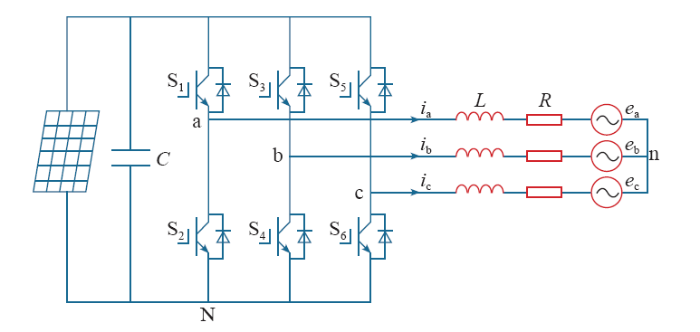
图1为单级式三相光伏并网逆变器,逆变器通过滤波电感L、线路电阻R与电网相连,根据基尔霍夫定律,得到系统在三相静止坐标系下的状态方程为
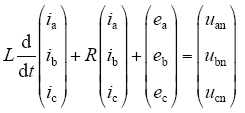
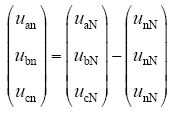
图1
图1
单级式三相光伏并网逆变器
Fig.1
Single-stage three phase grid-connected photovoltaic inverter
式中,ea、eb、ec为电网的三相电压;ia、ib、ic为并网逆变器输出电流;uaN、ubN、ucN为三相并网逆变器输出电压;unN为直流母线与三相电网中性点之间的电压。
对式(1)进行Park变换,得到dq旋转坐标下的状态方程为
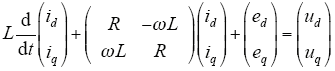
式中,id、iq为并网电流在dq坐标系下的d、q分量;ed、eq为电网电压在dq坐标系下的d、q分量;ud和uq为逆变器输出电压在dq坐标系下的d、q分量。
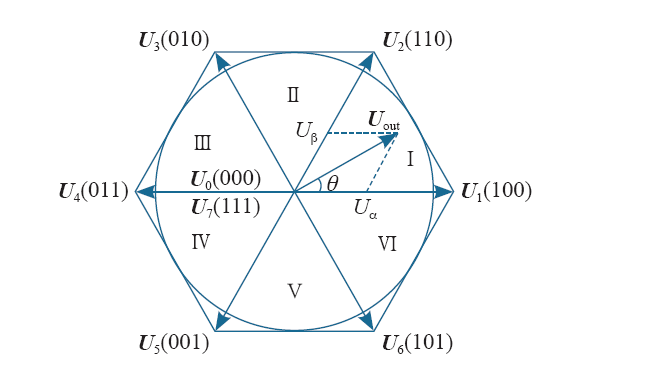
定义三相光伏并网逆变器的开关状态Si(i = a,b,c)为

图2
并网逆变器的输出电压Ui(i = d,q)为
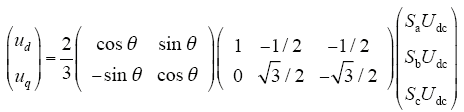
式中,Udc为直流母线电压;θ为电网的空间角度。
由于电阻R较小,故可忽略R的影响,将式(3)整理得
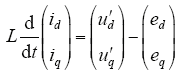
其中
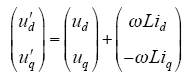
根据瞬时功率理论,在dq坐标系下,三相光伏并网逆变器输出瞬时有功功率P和无功功率Q为
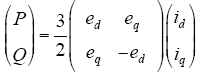
将式(6)离散化得
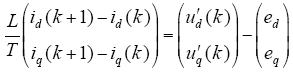
结合式(7),得
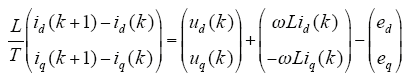
式中,id(k)、iq(k)为kTs时刻电流采样值通过dq变换后得到的d、q分量;ud(k)和uq(k)为逆变器输出电压在kTs时刻dq轴下的d、q分量。
将式(8)离散化得
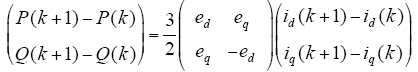
将式(10)代入式(11),整理得
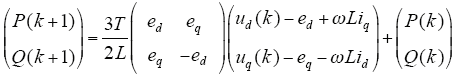
式(12)即为光伏并网逆变器模型预测直接功率控制预测函数。
3 模型预测控制原理
图3
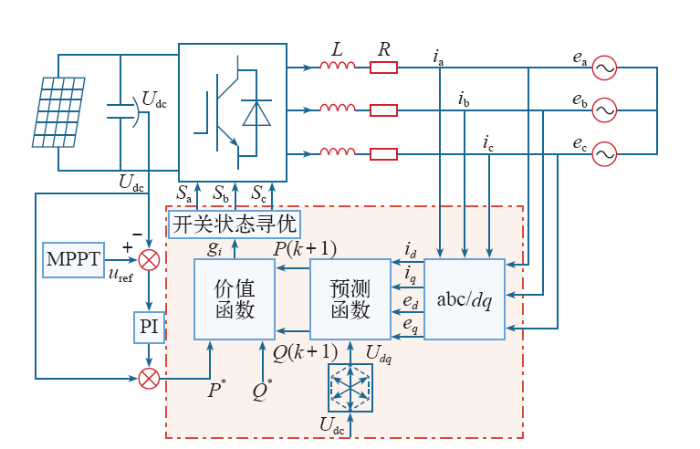
模型预测直接功率控制结构如图4所示。采集的电网电压ea、eb、ec和电流ia、ib、ic经过dq变换,转换成作为预测函数输入的直流量ed、eq和id、iq,电压矢量Udq通过直流电压Udc变换得到,预测函数输出的P(k + 1)、Q(k + 1)作为价值函数的输入,价值函数有功功率参考值P*通过MPPT得到,无功功率参考值Q*为给定值。通过价值函数去评估电压矢量,使价值函数最小的电压矢量将会应用到下一个采样周期,由此在开关状态寻优环节得到该电压矢量对应的开关状态Sa、Sb、Sc,从而控制开关管导通和关断。
图4
图4
模型预测直接功率控制结构图
Fig.4
Structure diagram of model predictive direct power control
根据系统预测模型函数式(12),在tk+1时刻,有功功率P(k + 1)和无功功率Q(k + 1)由tk时刻状态预测得到,为了预测tk+1时刻的瞬时有功功率P(k + 1)和无功功率Q(k + 1),需要知道当前时刻的电网电流id、iq及电网电压ed、eq,采样电压ud(k)、uq(k)以及三相逆变器的开关状态Si及直流母线电压Udc。为了挑选出最佳的电压矢量ud(k)、uq(k),需要建立价值函数g,通过价值函数将预测的所有功率值进行比较,挑选出使价值函数最小的电压矢量应用到下一时刻。选用预测功率与给定功率误差的绝对值之和作为价值函数,即
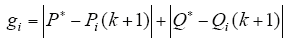
式中,P*为有功功率参考值;Q*为无功功率参考值。
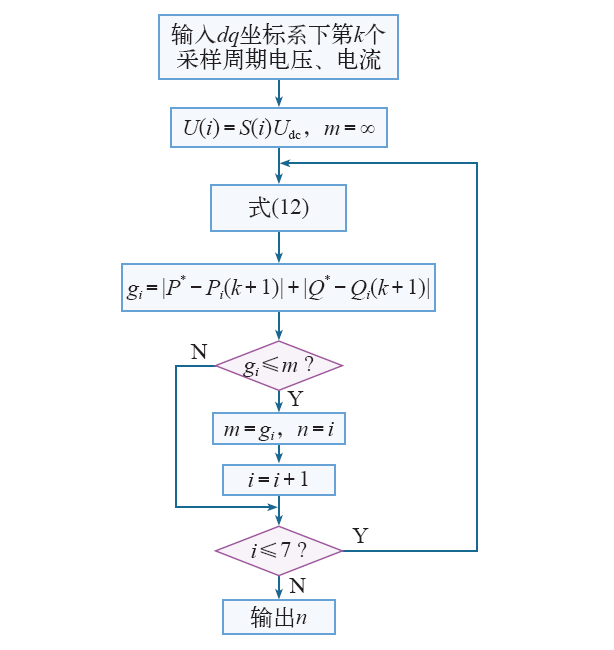
根据三相光伏并网逆变器模型预测直接功率控制算法,其算法流程如图5所示。
图5
图5
模型预测直接功率控制算法流程图
Fig.5
Flow diagram of model predictive direct power control algorithm
4 仿真
为验证所提出的控制策略,利用Matlab进行了仿真,参数见下表。
表 仿真系统参数
Tab.
| 参 数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| 直流母线电压Udc/V | 380 |
| 光伏电池板开路电压Ud/V | 468 |
| 网侧滤波电感L/mH | 15 |
| 电网相电压e/V | 150 |
| 电网频率f/Hz | 50 |
| 直流母线电容C/µF | 3 000 |
| 采样频率fs/kHz | 20 |
图6
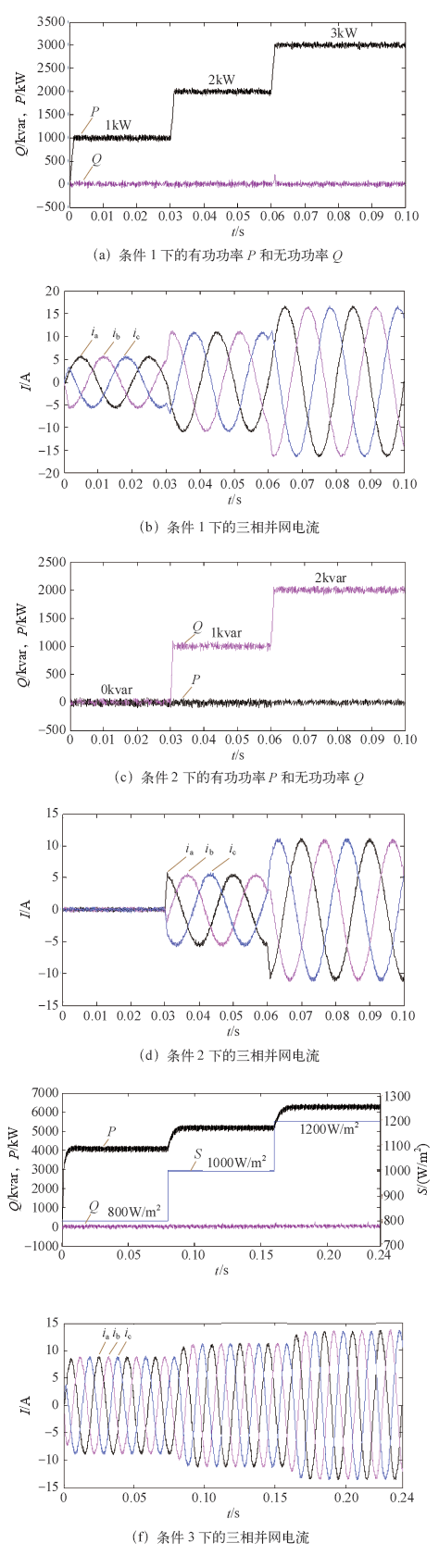
条件3:直流侧连接PV电池板,电池板选用SNM-P200型,连接方式为13串2并,额定功率为5kW。给定光照在0~0.08s时间内为800W/m2,0.08~0.16s时间内为1 000W/m2,0.16~0.24s时间内为1 200W/m2。根据图4所示的最大功率跟踪算法,有功功率参考值P*会跟随光照变化,为使逆变器工作在单位功率因数状态下,使无功功率参考值Q* = 0。其他参数保持不变,仿真结果如图6e、图6f所示,其中图6e为光照强度S变化和输出的有功功率P随光照变化的曲线及无功功率Q的波形,图6f为三相并网电流波形。图6e表明当光照强度发生突变时,实际的有功功率经过大约1.1ms实现最大有功功率输出。同时三相并网电流在光照强度发生突变时,也可以在给定功率跳变时刻快速跟随功率的变化。
仿真结果表明,当改变功率给定值时,输出功率快速调整至功率给定值;当改变有功功率时,无功功率可以保持不变;当改变无功功率时,有功功率也可以保持不变。说明有功功率和无功功率实现了解耦控制。且并网电流可以很好地跟踪功率的变化,系统具有较好的动、静态性能。
5 结束语
本文针对旋转dq坐标系下三相光伏并网逆变器的MPDPC控制策略进行了研究,对MPC原理进行了分析,建立了系统的数学模型,通过对系统的仿真研究得到以下结论:
(1)模型预测直接功率控制具有良好的动态性能。
(2)模型预测直接功率控制结构简单,便于算法实现,通过改变给定的无功功率值,可以实现对电网的无功补偿。
(3)该控制方法能够实现对功率因数任意调节,且有功功率P和无功功率Q实现了解耦控制。
模型预测控制良好的动态性能必将使其在太阳能、风能等新能源领域有着广阔的应用前景。
参考文献
Evalua- tion of current controllers for distributed power generation systems
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2009.2012527 URL [本文引用: 1]
Voltage source converter-based topologies to further integrate renewable energy sources in distribution systems
[J].
DOI:10.1049/iet-rpg.2011.0246
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This study presents and thoroughly compares different alternatives to create DC links in distribution networks by means of voltage source converters (VSC). Such links give rise to fully controllable loops in nowadays radially operated systems, allowing higher levels of distributed generation penetration. Suitable VSC-based devices are reviewed and compared from several points of view, including topologies, degrees of freedom, operating ranges and performance. Several case studies, involving actual urban and rural distribution networks, are worked out to show the potential benefits provided by the use of the proposed smart links.
An advanced SVPWM-based predictive current controller for three-phase inverters in distributed generation systems
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2007.907674 URL [本文引用: 1]
A hysteresis current controller for single-phase three-level voltage source inverters
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2011.2181419
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Conventional hysteresis current controllers have the disadvantage of a variable switching frequency. This paper presents a novel hysteresis current control method which uses the adjacent current error zero-crossing time to calculate the upper/lower hysteresis bandwidth after the measured half current error period. This strategy makes the algorithm independent of load parameters and thus it can achieve a stable switching frequency. An improved switching scheme has been successfully applied to a single-phase three-level H-bridge voltage source inverter driving a vibration test bench based on the novel hysteresis current. It can select appropriate switching states to overcome dead-time effects without dead-time compensation according to the relation of the current switching state, the current error, and the upper/lower hysteresis bandwidth. Field-programmable gate array has enough computational power to allow multiple sampling within a current error period and logic control power to implement state machine transitions. The simulation and experimental results are given to demonstrate the validity and features of the novel hysteresis current controller with the improved switching scheme.
A robust predictive current control for three-phase grid-connected inverters
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.41 URL [本文引用: 1]
Delay compensation in model predictive current control of a three-phase inverter
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TIE.2011.2157284
URL
[本文引用: 1]

When control schemes based on finite control set model predictive control are experimentally implemented, a large amount of calculations is required, introducing a considerable time delay in the actuation. This delay can deteriorate the performance of the system if not considered in the design of the controller. In this paper, the problem is described, and the solution to this issue is clearly explained using a three-phase inverter as an example. Experimental results to validate this solution are shown.
Model predictive control of inverters for both islanded and grid-connected operations in renewable power generations
[J].
DOI:10.1049/iet-rpg.2013.0078
URL
[本文引用: 1]

As the penetration of renewable power generation units connected to the grid increases, high power quality and flexible power regulation have raised much concern. This study proposes a competitive model predictive control strategy for inverters in renewable power generation applications. The controller uses the system model to predict the system behaviour in each sampling interval for each voltage vector, and the most appropriate vector is then chosen according to an optimisation criterion. In islanded mode, the control objectives of the cost function are the alpha and beta components of the voltage so that stable voltage for the local loads can be established. In addition, a fast re-synchronisation scheme is introduced to achieve smooth grid connection. After connected to the grid, a new prediction scheme is developed to fulfill flexible active and reactive power regulation. Furthermore, a switching frequency reduction scheme is presented to reduce switching losses, which are especially significant when considering efficiency for renewable power generations. The effectiveness of the proposed control strategy was tested by simulation using MATLAB/Simulink and experimentally validated on a laboratory prototype.
State of the art of finite control set model predictive control in power electronics
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TII.2012.2221469
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper addresses to some of the latest contributions on the application of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control (FCS-MPC) in Power Electronics. In FCS-MPC, the switching states are directly applied to the power converter, without the need of an additional modulation stage. The paper shows how the use of FCS-MPC provides a simple and efficient computational realization for different control objectives in Power Electronics. Some applications of this technology in drives, active filters, power conditioning, distributed generation and renewable energy are covered. Finally, attention is paid to the discussion of new trends in this technology and to the identification of open questions and future research topics.
Predictive current control of a voltage source inverter
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.isatra.2015.10.007
URL
PMID:26549566
[本文引用: 1]

Due to its fault tolerance, a multiphase brushless direct current (BLDC) motor can meet high reliability demand for application in electric vehicles. The voltage-source inverter (VSI) supplying the motor is subjected to open circuit faults. Therefore, it is necessary to design a fault-tolerant (FT) control algorithm with an embedded fault diagnosis (FD) block. In this paper, finite control set-model predictive control (FCS-MPC) is developed to implement the fault-tolerant control algorithm of a five-phase BLDC motor. The developed control method is fast, simple, and flexible. A FD method based on available information from the control block is proposed; this method is simple, robust to common transients in motor and able to localize multiple open circuit faults. The proposed FD and FT control algorithm are embedded in a five-phase BLDC motor drive. In order to validate the theory presented, simulation and experimental results are conducted on a five-phase two-level VSI supplying a five-phase BLDC motor.
Direct model predictive current control strategy of dc-dc Boost converters
[J].DOI:10.1109/JESTPE.2013.2279855 URL [本文引用: 1]
Model predictive direct current control of modular multilevel converters: modeling, analysis, and experimental evaluation
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2014.2301438 URL [本文引用: 1]
三相电压型逆变器模型预测控制
[J].
Model predictive control of three-phase voltage source inverter
[J].
三相并网逆变器模型电流预测控制技术
[J].针对三相并网逆变器的特点, 在dq旋转坐标系下, 提出了一种模型电流预测控制方法。在每一个采样周期, 根据预测模型, 对三相并网逆变器的8个电压矢量进行在线评估, 使价值函数最小的电压矢量在下一个采样周期应用, 实现了对d轴和q轴给定电流的快速跟踪。同时采用电网电压定向的矢量控制策略, 实现d轴电流和q轴电流解耦控制, 使d轴电流控制并网逆变器的有功功率, q轴电流控制并网逆变器的无功功率。实验结果表明:采用模型电流预测控制的三相并网逆变器有很好的静、动态特性。从而验证了该方案的可行性和正确性。
Model current predictive control for three-phase grid-connected inverters
[J].针对三相并网逆变器的特点, 在dq旋转坐标系下, 提出了一种模型电流预测控制方法。在每一个采样周期, 根据预测模型, 对三相并网逆变器的8个电压矢量进行在线评估, 使价值函数最小的电压矢量在下一个采样周期应用, 实现了对d轴和q轴给定电流的快速跟踪。同时采用电网电压定向的矢量控制策略, 实现d轴电流和q轴电流解耦控制, 使d轴电流控制并网逆变器的有功功率, q轴电流控制并网逆变器的无功功率。实验结果表明:采用模型电流预测控制的三相并网逆变器有很好的静、动态特性。从而验证了该方案的可行性和正确性。
Model-predictive direct power control of doubly-fed induction generators under unbalanced grid voltage conditions in wind energy applications
[J].
DOI:10.1049/iet-rpg.2013.0312
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Unbalanced grid voltage conditions in wind farms degrade the performance of the wind turbines and inject severely distorted current into the power system. This study proposes a new model-predictive direct power control strategy for a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) under unbalanced grid voltage conditions. An optimised cost function is derived in order to select an appropriate voltage vector. This directly regulates the instantaneous active and reactive powers in the stationary stator reference frame without the requirement for coordinate transformation, proportional-integral regulators, switching table or pulse-width modulation modulators. After that, the behaviour of the DFIGs under unbalanced grid voltage is investigated. A power compensation scheme is developed, which does not require the extraction of the negative stator current sequence. This can achieve several different control objectives; that is, obtaining sinusoidal and symmetrical stator currents, and the cancellation of electromagnetic torque oscillations. The effectiveness of the proposed control strategy is validated experimentally on a 20 kW laboratory DFIG prototype.
Model-predictive control of grid-tied four-level diode-clamped inverters for high-power wind energy conversion systems
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2013.2276120
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, a model-predictive control of medium voltage, grid-tied four-level diode-clamped inverter for use in high-power wind energy conversion systems is presented. The control objectives such as regulation of net dc-link voltage, reactive power generation to meet the grid operator request, dc-link capacitor voltages balancing, and switching frequency minimization are included in the cost function. The latter objective is an important requirement for high-power converters, and this has been achieved without any modifications to the software or hardware configuration. The future behavior of the grid currents and dc-link voltages is predicted for all the possible switching states using the discrete-time model of the inverter, dc-link, inductive filter, and grid. The switching state that minimizes the cost function has been chosen and applied to the inverter directly. During different operating conditions, the switching frequency is regulated between 750 and 850 Hz with the help of a lookup-table-based weighting factor, and thus, the proposed methodology appears as a promising tool to control the high-power grid-tied inverters. The results obtained through the MATLAB simulations on 4 MVA/4000 V system and dSPACE DS1103-based experiments on 5 kW/208 V prototype are in a close relationship and thus validate the proposed control strategy.
单相并网变换器预测直接功率控制策略研究
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.30.002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

针对单相并网变换器,通过二阶广义积分构造与电网电压、并网电流正交的虚拟电压、电流分量来形成αβ坐标系下的两相系统。将αβ坐标系下的两相系统变换到按电网电压定向的dq旋转坐标系下。推导两相系统在αβ坐标系和dq旋转坐标系下的数学模型,在此基础上简要分析单相并网变换器的矢量控制原理。根据瞬时功率理论和预测方法推导两相系统在dq旋转坐标系下的功率预测模型,根据此模型提出一种预测直接功率控制策略。搭建1kW的样机,对矢量控制和预测直接功率控制进行研究。实验表明预测控制方案的可行性和正确性,与矢量控制相比,预测直接功率控制具有更快的功率响应。
A predictivedirect power control scheme for single-phase grid-connected converters
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.30.002
URL
[本文引用: 1]

针对单相并网变换器,通过二阶广义积分构造与电网电压、并网电流正交的虚拟电压、电流分量来形成αβ坐标系下的两相系统。将αβ坐标系下的两相系统变换到按电网电压定向的dq旋转坐标系下。推导两相系统在αβ坐标系和dq旋转坐标系下的数学模型,在此基础上简要分析单相并网变换器的矢量控制原理。根据瞬时功率理论和预测方法推导两相系统在dq旋转坐标系下的功率预测模型,根据此模型提出一种预测直接功率控制策略。搭建1kW的样机,对矢量控制和预测直接功率控制进行研究。实验表明预测控制方案的可行性和正确性,与矢量控制相比,预测直接功率控制具有更快的功率响应。