1 引言
直线感应电机的次级一般为铜和铝制成的感应板,该结构简单可靠,易于维护,但是直线感应电机存在效率和功率因数低的缺点。虽然传统的永磁同步直线电机在效率和功率因数方面较直线感应电机有较大优势,但由于永磁体和电枢绕组分别置于初级和次级,因此在长距离驱动场合,无论是将永磁体还是将电枢绕组沿着长定子铺设,势必要增加系统的成本,且不易维护。直线开关磁阻电机次级仅由导磁铁心组成,结构简单、可靠,在长距离驱动系统中具有成本低,便于维护等优点,但是该电机存在功率密度低,推力波动大等缺点。此外,在如电磁弹射等短距离高速驱动场合,直线感应电机是一种可行的方案[1],但是直线感应电机也存在不足之处,如功率因数低、输入电流大等[2,3,4]。传统永磁同步直线电机应用于电磁弹射系统主要有两种结构,一种是高速动子为电枢绕组,永磁体置于次级定子,该结构存在动子带电运行,可靠性低且结构复杂等缺点。另一种结构是永磁体作为高速动子,永磁体置于高速动子,易受振动影响,存在电流冲击和高温退磁风险[5,6,7]。因此,针对以上两种驱动背景,本文将介绍磁通切换型初级永磁电机的结构、原理与控制系统。
2 单边直线磁通切换电机
2.1 结构原理
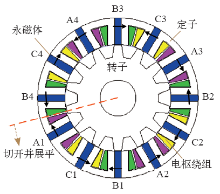
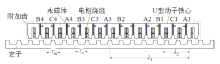
图1所示为一台三相ps/pr极旋转型磁通切换永磁电机(Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet motor,FSPM)结构剖面图(ps = 12为定子极数,pr = 14为转子极数)。由图可见,其定子和转子均为凸极结构,转子上既无绕组也无永磁体,结构非常简单。定子部分由12个U型硅钢片导磁铁心和内置于U型定子铁心的12块永磁体组成。其中,永磁体是沿着切向交替充磁的,其作用是产生聚磁效应。每个U型导磁铁心围成的槽中并排放置了两个集中线圈,12个线圈共分成了三组,每四个串连组成一相,例如图中的A1~A4是A相的四个线圈,以此类推。每个线圈横跨在两个定子齿上,中间嵌有一块永磁体,称为一个定子极。正是这种独特的设计,使得转子齿在与同一个线圈下两个不同的定子齿分别对齐时,线圈中的磁链极性相反。将图1旋转FSPM电机的某一半径切开并展平,可得到一台直线磁通切换永磁电机(Linear FSPM,LFSPM),如图2所示,为了便于讨论,该直线电机称为“4*ABC”结构。同时,为了在一定程度上补偿端部绕组的磁路,在电机的初级两端部各增加了一个附加齿。显然该磁通切换型直线电机的工作原理与旋转磁通切换电机相似。初级向前运动一个定子极距范围,三相电枢绕组中的感应电动势近似为正弦波,因此该电机适用于无刷交流(BLAC)控制。值得说明的是,虽然该电机端部的附加齿可以在一定程度上平衡端部绕组的磁路,但是该电机仍然存在端部相绕组和中间相绕组磁路不对称的问题[8]。
图1
2.2 模块化直线磁通切换电机
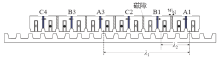
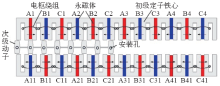
为解决图2电机动子端部相绕组磁路不对称问题,文献[9]基于一台三相12/14极旋转FSPM转电机,提出一种模块化LFSPM(Modular LFSPM,MLFSPM)电机,如图3所示。该电机可由图2所示的4*ABC电机得到,首先将其永磁间隔被替换为磁障,去掉套着磁障的线圈(即线圈A2、A4、B2、B4、C1、C2);其次将剩下的线圈匝数增加一倍,保证每相绕组的总匝数不变。由图3可知,该电机每相由两个E型模块组成,每个E型模块由两个U型齿和夹在中间的永磁体组成,集中线圈置于E型模块的槽中。属于同相的两E型模块之间的距离λ1 = 7τs,相邻两相E型模块之间的距离λ2 = (2 + 1/3)τs。可见,每个E型模块中只有一个线圈,每个线圈均有一个永磁体励磁,相邻两E型模块有磁障间隔,属于一相的两线圈串联组成一相绕组。因此,该电机每个线圈磁路独立,不存在电机“4*ABC”端部相绕组与中间相绕组磁路不对称问题,三相绕组反电动势幅值相同。由于每个线圈磁路独立,因此三相绕组之间的互感很小,容错能力强;模块化设计便于生产,初级动子长度减小。
图2
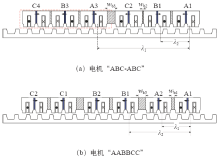
然而,由于该电机每相绕组仅由两个线圈串联组成,两个线圈与定子的相对位置相同。因此该电机不具备旋转FSPM电机和电机“4*ABC”相绕组磁路互补特性。这将导致该电机绕组反电动势谐波含量增大,从而增大电机的推力波动。此外,该电机的定位力也较大。如前所述,为方便比较,将不具有互补特性的该结构电机命名为“ABCABC”。
2.3 磁路互补型、模块化直线 磁通切换电机
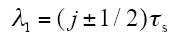

式中,j和k为正整数,图4b中,j = 2,k = 5,λ1 = 2.5τs,λ2 = (5+1/3)τs。
由式(1)可知,属于同相的两线圈在空间上互差180°,因此具有互补特性。由式(2)可知,三相绕组的电磁特性在空间上互差120°,满足三相电机设计要求。为方便比较,该结构电机被命名为“AABBCC”。
图3
图4
2.4 任意极距比模块化磁通切换直线电机设计原则
前面几节先由12/14极旋转磁通切换电机展开来得到一台LFSPM电机,在此基础上讨论几种模块化直线磁通切换型电机的拓扑结构。该研究方法比较直观,也易于得到某一极距比和结构的LFSPM电机。但是该研究方法存在以下不足和局限性:首先,该设计方法受到旋转FSPM电机极距比和结构的限制。该缺点主要体现在三个方面:第一,例如定、转子极数之比为12/12和12/15的FSPM电机不是三相电机,由此FSPM电机直接展开得到的LFSPM电机必然不是一台三相LFSPM电机;第二,即使由某个定、转子极数的三相FSPM电机(如定、转子极数为12/14)展开可以得到一台三相LFSPM电机和MLFSPM电机,也存在端部磁路不对称和相绕组不具有互补的特性的缺点;第三,即使得到的MLFSPM电机具有互补特性,其设计方法也受旋转电机设计方法的限制。其次,所得到的LFSPM电机范围较小,仅从现有的旋转FSPM电机得到,研究范围较窄,不具有通用的指导意义。因此,提出直线FSPM电机结构设计的通用原则和方法具有重要的理论意义和实用价值,该设计方法不仅便于设计LFSPM电机,而且有利于理解“磁通切换”电机的本质原理,拓宽磁通切换电机的研究范围,甚至有利于理解定子永磁型电机的结构联系。文献[11]分析了极距比近似为1的几种MLFSPM电机的结构特性和电磁特性,并指出初级次级极距比近似为13/12的直线电机具有最好的特性。文献[12]对任意极距比直线电机的设计原则及电磁特性进行了深入研究,本文简单介绍通用设计原则。
由于直线电机的结构比较灵活,只要一个E型模块结构满足“磁通切换”原理,就可由此E型模块得到不同结构的MLFSPM电机。如E型模块极距比τm/τs≈n(n为正整数),那么为了得到具有正弦反电动势和较小定位力的MLFSPM电机,最好采用互补结构“ABC-ABC”和“AABBCC”。如E型模块极距比τm/τs = n(n为正整数),那么互补结构“ABC-ABC”和“AABBCC”及非互补结构“ABC”和“ABCABC” 都可采用。
如何设计具有磁通切换原理的E型模块是设计MLFSPM电机的关键。根据前面的分析,可归纳出具有“磁通切换”原理和任意极距比E型模块的通用设计规则
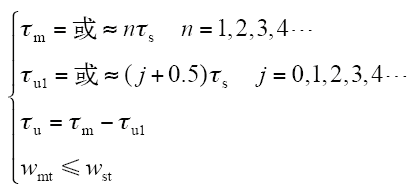
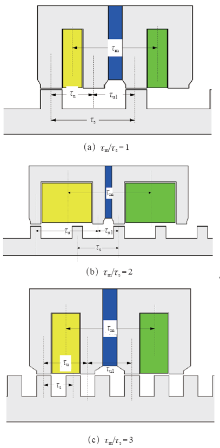
为了更好地理解式(3),图5给出极距比τm/τs = 1、2和3时满足“磁通切换”原理的E型模块结构图。对于图5a所示的E型模块,τm/τs = 1,τu1 = τu = τm/2,即式(3)中的n = 1,j = 0。首先,如果τs和τu1保持不变,将n由1变为2,此时可得到图5b所示的E型模块。该E型模块仍然满足“磁通切换”工作原理,因此基于此模块可以得到不同结构的MLFSPM电机。其次,如果将n由1变为3,j由0变为1,则τm/τs = 3,τu = τu1 = 1.5τs = τm/2,此时图5a所示的E型模块将变为图5c所示的E型模块,该E型模块即为极距比为3的结构。显然,该E型模块满足“磁通切换”工作原理。值得说明的是,当式(3)中τm≈nτs和τu1≈( j+0.5 )τs成立时,需采用“ABC-ABC”和“AABBCC”两互补结构才能得到具有正弦反电动势和较小定位力的CMLFSPM电机。因此,只要E型模块的结构满足式(3),就可以得到不同结构的MLFSPM电机和CMLFSPM电机。
图5
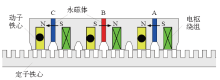
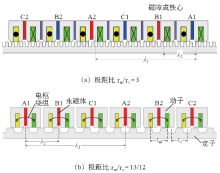
美国学者Huai Lin和John Amdrew Heing于2007年提出一种直线磁通切换型电机,该电机现为美国保德公司一个产品,如图6所示[13]。近年来,该电机及其改进机构也得到相关学者的关注,但该电机的本质结构原理、与由旋转FSPM电机得到的LFSPM电机之间的关系、有何优缺点等内容此前没有被阐明。文献[12]首先分析了该电机的基本原理及演变过程,指出该电机实际上是极距比为3的LFSPM电机。在此基础上,分析了磁障对电机性能的影响,并利用所提出的通用设计原则,提出了多种结构的极距比为3的MLFSPM电机,并找出了最优结构,如图7a所示。进一步比较了该电机与极距比近似为1(即初级极距与次级极距之比为13/12)的最优MLFSPM电机,如图7b所示。研究结果表明,极距比为13/12的磁通切换型初级永磁直线电机具有较大优势:当两种极距比直线电机的初级极距τm、永磁体尺寸、电枢绕组匝数、初级动子速度,次级齿高、轭高等同时(即电机的初级E型模块长度相同、电机外围体积相同),极距比为13/12的电机具有推力大、频率小(约为后者1/3)、漏磁小、电感小、电抗小、功率因数大、次级重量轻及负载能力强等优点,因此极距比近似为1的电机更适合如电磁弹射等高速运行场合。
图6
图7
图7
两种极距比模块化直线磁通切换永磁电机[12]
Fig.7
Linear FSPM motor with two different pole pitch ratios
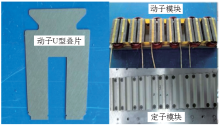
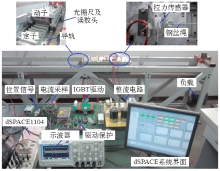
2.5 模块化直线磁通切换电机实验研究
图8
图9
图10
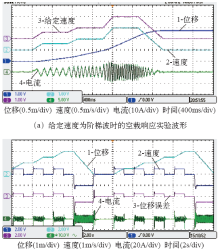
图10
速度和位移闭环实验波形
Fig.10
The measured waveforms of speed and position closed-loop control
3 双边直线磁通切换电机
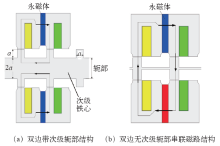
为了进一步提高电机的推力密度,减小摩擦力,双边直线电机得到了广泛研究。从磁路结构来说,双边磁通切换直线电机也分为串联磁路和并联磁路结构,基本模型如图11所示。假定次级齿高、齿宽、轭高,初级齿宽、槽宽相同(等于a),不难发现在一个次级极距τs = 4a范围内,次级轭部占次级总体积的80%。可见,如能减小甚至去除次级轭部,将大大减小次级重量。基于该模型的双边MLFSPM,根据不同的应用场合具有以下优点。
图11
图12
图12
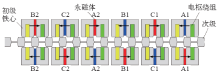
长距离驱动系统用串联磁路双边MLFSPM电机
Fig.12
Double sided MLFSPM motor with series magnetic circuit for long distance drive systems
图13
图13
弹射系统用串联磁路双边MLFSPM电机[17]
Fig.13
Double sided MLFSPM motor with series magnetic circuit for electromagnetic lunch system
参考文献
飞机电磁弹射系统发展综述
[J].
Overview on a significant technology of modern aircraftcarrier-electromagnetic aircraft launch system
[J].
Design and comparison of linear synchronous motor and linear induction motor for electromagnetic aircraft launch system
[C].
Design and simulation of an electromagnetic aircraft launch system
[C].
用于电磁飞机弹射系统的直线电机设计综述
[J].
Survey of design of linear machine for electromagnetic lunch system
[J].
Analysis and design of moving-magnet-type linear synchronous motor for electromagnetic launch system
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPS.2010.2053722 URL [本文引用: 1]
Design and simulation of a permanent-magnet electromagnetic aircraft launcher
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIA.2005.844404 URL [本文引用: 1]
Finite difference study of unconventional structures of permanent-magnet linear machines for electromagnetic aircraft launch system
[J].DOI:10.1109/TMAG.2004.838990 URL [本文引用: 1]
Influence of leading design parameters on the force performance of a complementary and modular linear flux-switching permanent magnet motor
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TIE.2013.2271603
URL
[本文引用: 1]

This paper investigates the influence of some leading design parameters on the force performance of a new complementary and modular linear flux-switching permanent-magnet (LFSPM) motor. The originality of the proposed structure is that each phase consists of two "E"-shaped modules, whose positions are mutually 180 degrees electrical degrees apart. Also, there is a flux barrier between the two modules. First, the structure and influence of some leading design parameters on the force performance of the complementary and modular LFSPM motor are analyzed. Then, a conventional LFSPM motor obtained directly from a rotary FSPM motor is optimized and compared with the complementary and modular LFSPM motor based on finite-element method. The results reveal that the proposed motor has sinusoidal and symmetrical three-phase back electromotive force waveforms and smaller cogging force and force ripple than the existing motors. Moreover, a prototype of the proposed motor is built to validate the study.
A modular permanent magnet flux-switching linear machine with fault tolerant capability
[J].
DOI:10.1155/2014/483080
URL
PMID:24982959
[本文引用: 1]

This paper proposes a new linear fault-tolerant permanent-magnet (PM) vernier (LFTPMV) machine, which can offer high thrust by using the magnetic gear effect. Both PMs and windings of the proposed machine are on short mover, while the long stator is only manufactured from iron. Hence, the proposed machine is very suitable for long stroke system applications. The key of this machine is that the magnetizer splits the two movers with modular and complementary structures. Hence, the proposed machine offers improved symmetrical and sinusoidal back electromotive force waveform and reduced detent force. Furthermore, owing to the complementary structure, the proposed machine possesses favorable fault-tolerant capability, namely, independent phases. In particular, differing from the existing fault-tolerant machines, the proposed machine offers fault tolerance without sacrificing thrust density. This is because neither fault-tolerant teeth nor the flux-barriers are adopted. The electromagnetic characteristics of the proposed machine are analyzed using the time-stepping finite-element method, which verifies the effectiveness of the theoretical analysis.
磁路互补型模块化磁通切换永磁直线电机
[J].新型模块化初级永磁直线电机的永磁体和电枢绕组都置于初级短动子,而次级长定子结构简单,仅由导磁铁心组成,若应用在轨道交通等长定子等场合,可大大降低系统成本。在深入分析现有电机结构特点的基础上,提出一种基于磁通切换原理磁路互补的新结构。结构的互补性使每相绕组的反电势更正弦、电机总的定位力更小。介绍了模块化初级永磁直线电机的结构特点和运行原理,并基于有限元法,研究了其静态特性,具体包括对空载和单相绕组通电时的磁场及气隙磁通密度、绕组永磁磁链、空载反电动势、定位力、绕组电感以及静态推力等,并分析了永磁磁场和电枢磁场之间的相互耦合作用对电感特性的影响。理论分析和样机实验结果验证了设计方案的正确性和有效性。
Novel modularized flux-switching permanent magnet linear machine with complementary magnetic circuits
[J].新型模块化初级永磁直线电机的永磁体和电枢绕组都置于初级短动子,而次级长定子结构简单,仅由导磁铁心组成,若应用在轨道交通等长定子等场合,可大大降低系统成本。在深入分析现有电机结构特点的基础上,提出一种基于磁通切换原理磁路互补的新结构。结构的互补性使每相绕组的反电势更正弦、电机总的定位力更小。介绍了模块化初级永磁直线电机的结构特点和运行原理,并基于有限元法,研究了其静态特性,具体包括对空载和单相绕组通电时的磁场及气隙磁通密度、绕组永磁磁链、空载反电动势、定位力、绕组电感以及静态推力等,并分析了永磁磁场和电枢磁场之间的相互耦合作用对电感特性的影响。理论分析和样机实验结果验证了设计方案的正确性和有效性。
Comparison of complementary and modular linear flux-switching motors with different mover and stator pole pitch
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TMAG.2012.2233208
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Linear flux-switching permanent magnet (LFSPM) motors with both permanent magnets and armature windings on the short primary mover have attracted considerable attention due to their simple and cheap stator which only consists of iron. Hence, this kind of liner motor is very suitable for long stator applications such as in urban rail transportations. However, the conventional LFSPM motors directly split from rotary FSPM motor suffer from drawbacks such as unbalanced magnetic circuit of end coil, heavy mover, and bigger cogging force and force ripple. Modular LFSPM (MLFSPM) motors can mitigate the problem of unbalanced magnetic circuit of end coil. But some MLFSPM motors with different stator/mover pole pitch tau(s)/tau(m) = 12/14, 12/10 don't have complementary phase armature windings, which will lead to asymmetrical and non-sinusoidal back-electromotive force, bigger cogging force and thrust force ripple. The key of this paper is to propose, investigate, and compare four complementary and modular structures for the LFSPM motors with different tau(s)/tau(m). The electromagnetic performance and dimensions of the proposed complementary MLFSPM motors with different tau(s)/tau(m) are investigated, compared and confirmed by the means of finite element analysis and experimental results. Based on the analysis results, two complementary MLFSPM motors with tau(s)/tau(m) = 12/13 are chosen to be the two best motors, which can offer the biggest thrust force, relatively smaller cogging force and thrust force ripple, and shorter mover length.
Investigation and general design principle of a new series of complementary and modular linear FSPM motors
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TIE.2012.2230605
URL
[本文引用: 3]

The conventional linear flux-switching permanent-magnet (FSPM) motors directly split from a rotary FSPM motor suffer from drawbacks such as unbalanced magnetic circuit of end coil, bigger cogging force, and force ripple. In this paper, to reduce cogging force and thrust force ripple, some complementary and modular linear FSPM (LFSPM) (MLFSPM) motors with mover/stator pole pitch ratio tau(m)/tau(s) of about one, namely, tau(m)/tau(s) = 10/12, 11/12, 12/12, 13/12, 14/12, 15/12, will be investigated using finite-element method (FEM) and experimental method at first. Then, another new LFSPM motor with tau(m)/tau(s) = 3 is analyzed. Based on tau(m)/tau(s) = 3, some new MLFSPM motors are designed, investigated, and compared using FEM. To fully investigate these motors, the optimal MLFSPM motor with tau(m)/tau(s) = 3 is quantitatively compared with the two optimal motors with tau(m)/tau(s) approximate to 1. Finally, the general design principle for this series of MLFSPM motors with different tau(m)/tau(s) values is concluded.
Andrew Heilig John. Linear hybrid brushless servo motor: US 7230355 B2
[P].
Modeling of a complementary and modular linear flux-switching permanent magnet motor
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TEC.2012.2190985
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In this paper, a complementary and modular linear flux-switching permanent magnet (MLFSPM) motor is investigated, in which both the magnets and armature windings are placed in the short mover, while the long stator consists of iron core only. The proposed MLFSPM motor incorporates the high power density of a linear permanent magnet synchronous motor and the simple structure of a linear induction motor. It is especially suitable for long stator applications such as urban rail transit. The objective of this paper is to build the mathematical model for the purpose of control of this motor. The simulation results by means of finite-element analysis (FEA) verified the theoretical analysis and the effectiveness of this model. Both the analytical model and the FEA results are validated by experiments based on a prototype motor.
Speed control of complementary and modular linear flux-switching permanent magnet motor
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2015.2390194 URL [本文引用: 1]
A new modular and complementary double-sided linear flux-switching permanent magnet motor with yokeless secondary
[C].