1 引 言
高压输电线路和金具表面的放电可引起能量损失,产生可听噪声和高频无线电干扰,另外放电产生的氧化物及酸性物质还会腐蚀电力设备绝缘材料,加速绝缘介质的劣化和老化速度。近几年来随着电力建设的不断发展,尤其是特高压电网的建设,很多工程途经地区的海拔高度大于3 000m,甚至接近4 000m。在高海拔地区,随着气压的降低,空气间隙的绝缘强度也将降低,输电线路和高压电气设备表面更容易出现放电现象甚至击穿,因而研究气压对放电的影响特性有着重要的学术价值和工程现实意义。
围绕上述问题,国内外的学者进行了大量的实验室研究和现场测试,如文献[4]研究了海拔高度4 000m左右的极不均匀电场在不同类型电压下空气间隙放电特性,提出了基于空气间隙放电弹性系数的计算模型和高海拔修正方法;清华大学研究了气压对棒-板间隙起晕电压的影响以及不同气压下直流和交流电晕流注的脉冲特性[5,6];重庆大学研究了气压对直流正极性下冰柱-冰板间隙电晕放电的影响特性[7,8];华北电力大学研究了气压对导线表面的电晕损失影响特性[9]。国外对极不均匀电场的放电特性也有大量的研究,如文献[10]研究了极不均匀电场中高气压下局部放电特性;文献[11]中研究了气压及电极对极不均匀电场的击穿电压的影响。
上述相关研究大部分是基于脉冲电流法,难以反映放电电离区域的变化特性,对放电强度的变化显示不是很直观。在电晕放电中伴有光信号辐射,但在该放电阶段,其放电往往较微弱,肉眼很难观测到相关的放电现象。近几年一种基于日盲紫外成像的放电检测技术开始在科研和工程中得到应用,相对于脉冲电流法,紫外成像法输出的是二维图像,具有探测灵敏度高和抗干扰能力强的优点,可视化地显示放电电离发光区域大小的变化特性,便于研究放电从起晕到击穿的整个过程中的放电发展过程,为研究极不均匀电场中放电随气压的变化提供了一种新的技术手段。
采用紫外成像法研究放电特性,需提取紫外量化参数,由紫外成像仪的工作原理可知,光斑区域实际上是放电电离发光区域所成的像,为此本文采用数字图像处理技术分割了放电光斑区域并定义了放电光斑面积,算法可参看文献[12,13]。在此基础上,本文以棒-板间隙模型为研究对象,研究了不同棒-板间隙距离下,起晕电压、放电电离发光区域的大小以及击穿电压随气压的变化特性并进行了拟合分析和理论上的初步解释。论文的相关研究对于研究气压对放电的影响具有一定的参考价值。
2 实验平台的构建和实验设计
2.1 试验平台的构建
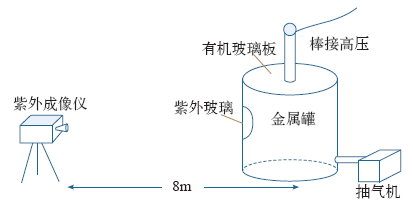
实验在气压可调的封闭金属罐内进行,图1为实验接线示意图。
图1
图1中,密闭金属罐高为150cm ,直径为67.5cm,罐内气压通过抽气机进行控制,气压的控制范围为28.0〜101.5kPa,模拟从平原到高海拔地区(海拔5 000m左右)放电时,气压对放电特性的影响。放电模型为棒-板间隙,棒电极直径为3.2cm,其头部为圆锥形,顶端半径约1.5mm,金属板电极为圆盘形,半径为20cm,为实现棒电极与罐体的绝缘并保证密闭性,罐体的顶部加装了有机玻璃板并采用密封胶进行密封。金属罐体的观测窗体为一块定制的透紫外玻璃,其内外直径分别为20cm、29cm,该玻璃在240〜280nm波段的透光率>98%。实验电压由HY—AC20工频高压发生器提供,紫外成像仪的型号为CoroCAM504,距离棒电极距离为8m,为便于分析放电,紫外成像仪输出的视频信号被存储在外部视频记录设备中。
2.2 实验方法和步骤
为确保实验数据的可比性,保持环境温度为16℃,变动不超过1℃,相对湿度为45%左右,变动不超过1%,紫外成像仪的增益为默认值70%,仪器的其他参数全部采用默认参数设置值。棒-板间隙距离分别定为20cm、15cm和10cm,然后在不同的气压下逐步增加电压,研究从起晕到击穿的整个过程中的放电现象,具体实验步骤如下:
(1)设定棒-板间隙距离为20cm,利用抽气机将罐内气压抽到28.0kPa,然后在该气压下,给间隙施加工频高压,加压步长为3kV。在逐步升压中观测紫外成像仪同时用紫外成像仪录制放电的紫外视频,过程从起晕到击穿。
(2)逐步升高气压,分别在40.0kPa、50.0kPa、60.0kPa、70.0kPa、80.0kPa、90.0kPa和101.5kPa下重复步骤(1)。
(3) 然后改变棒-板间隙分别为15cm、10cm,依次重复步骤(1)、(2)。
考虑到放电的随机性,在后续实验数据分析中,本文对紫外拍摄的紫外视频进行每秒一帧的提取,然后再对每一帧图像的光斑面积进行提取,最后得到平均光斑面积。
3 气压对电晕起始电压的影响
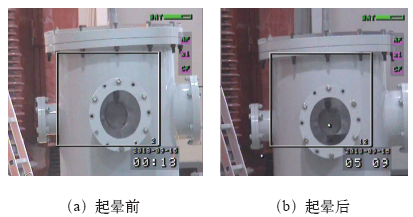
在研究电晕的起始电压时,需要给出起晕判据,目前对于紫外成像法还未有相关标准。但通过反复试验发现,起晕前紫外图像中仅偶尔出现个别的离散光斑点,光子数多在0〜5之间变化,一旦电压达到某个临界值后,紫外图像中开始出现较为明显的光斑点,光子数可达10个或以上。基于此,本文以10s内的平均光子数达到10及以上作为起晕判据。
图2
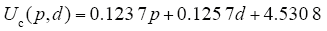
图3
图3
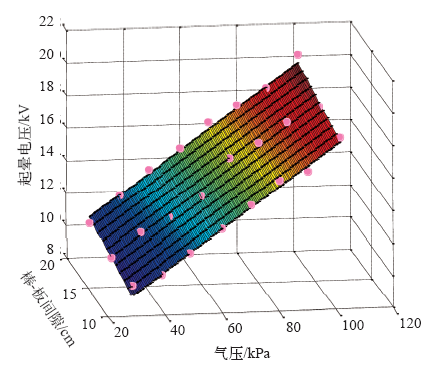
气压、棒-板间隙与起晕电压的关系拟合三维图
Fig.3
Pressure, rod-plate gap and corona onset voltage three-dimensional relationship fitting chart
为检验上述方程的有效性,计算表明拟合结果与测验数据结果的相关系数为0.990 8,F检验值为1 133.020 3,残差绝对值小于0.5,均匀分布于0左右,也即回归模型显著。
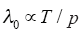
式中,λ0为质点自由行程;T为气体绝对温度;p为气压。
由式(2)得出,当T一定时,气压与质点自由行程成反比,导致在同一外加电压下,气压增大,自由电子所获的动能减少,发生碰撞电离的几率降低,因此碰撞电离系数α减小,使得棒附近积聚的自由电子数达不到自持放电的条件,若要发生电晕,需要升高所加电压,提高电子动能,因此气压越大,起晕电压越高。
4 气压对放电电离区域大小的影响
实验研究发现电压较低时,即起晕阶段由于电子崩出现的随机性,紫外图像中的光斑点很小甚至没有,紫外信号不稳定;而电压较高接近击穿电压时,放电为不稳定的刷状放电,光斑呈现不稳定状态,上述两种情况不便于研究气压对电离发光区域的影响特性,因此本文分别选择了间距10cm、15cm及20cm放电发光面积相对稳定的电压范围以及相对应的气压范围进行相关研究,具体气压和电压范围见表1。
表1 不同间距对应气压与电压区范围
Tab.1
| 间距/cm | 气压区间/kPa | 电压区间/kV |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 70~101.5 | 21~45 |
| 15 | 48.5~101.5 | 21~39 |
| 20 | 48.5~101.5 | 27~36 |
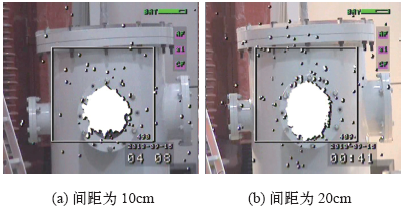
图4
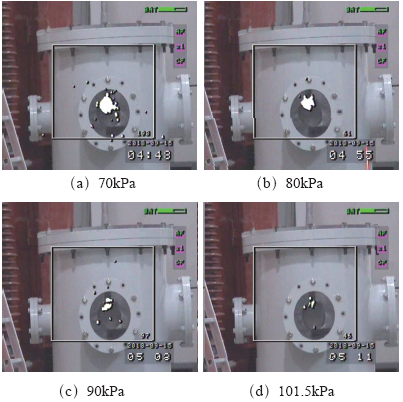
图4
间距10cm电压39kV下不同气压的紫外图片
Fig.4
UV picture of different pressures under 10cm spacing and 39kV voltage
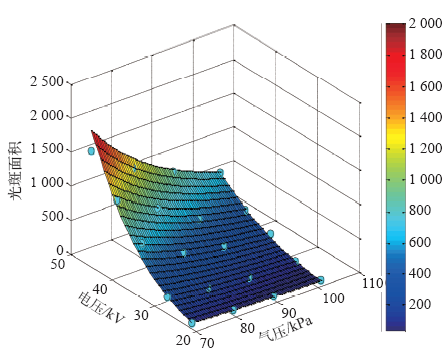
图5
图5
10cm不同电压下气压与放电光斑面积的拟合图
Fig.5
Pressure and discharge spot area of 10cm gap under different voltage fitting graph
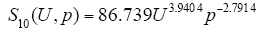
式中,U为所施电压有效值;p为气压。其他的两种间隙下数据的变化趋势与图5类似。 同理15cm、20cm的拟合方程分别为
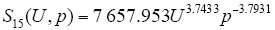
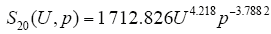
由上述分析可知,电离发光区域大小随气压的增大而降低,满足幂函数关系,原因是气压的增大减小了自由电子的平均自由行程,电子的电离能力下降,并且气压的增大会降低电晕产生的空间电荷的迁移率及扩散率,流注的发展范围受到抑制,因而电离发光区域减小。
5 气压对棒-板间隙的击穿电压的影响
图6
图6
间距10cm及20cm击穿前紫外图片
Fig.6
Before breakdown ultraviolet images of 10cm and 20cm gaps
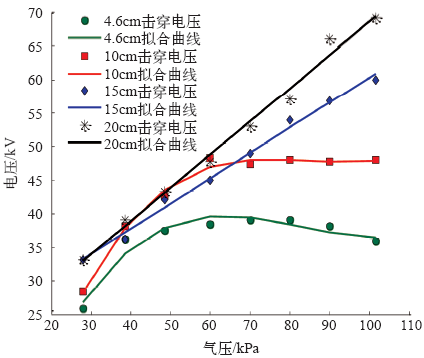
研究发现,对于15cm和20cm的棒-板间隙,随着气压的逐步增加,击穿电压近似线性增加,但对于10cm间隙,当气压大于一定值后,其击穿电压几乎不变,因此本文又增加了对4.6cm的击穿电压与气压的关系研究,结果发现相似的现象,利用一元回归函数polyfit的拟合得到各间隙下气压与击穿电压的曲线,如图7所示。
图7
图7中,间隙距离为15cm及20cm时采用线性函数进行拟合,气压与击穿电压的拟合函数为
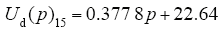
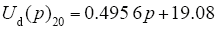
拟合函数的决定系数均在0.99以上(决定系数越接近于1,拟合得到的关系函数越准确),也即间隙距离为15cm及20cm时,击穿电压与气压几乎呈线性正比关系,而间距为10cm及4.6cm时的气压与击穿电压成非线性关系,气压较低时,随着气压增加,击穿电压增加,但当气压达到一定程度后,随着气压的增加其击穿电压几乎不变。
对于上述击穿电压与气压的关系,本文认为可从空间电荷对电场的畸变作用和气压对自由电子平均自由行程的影响两个角度进行定性分析。随着气压的增大,一方面电子平均自由行程在减小,碰撞电离能量下降,有利于提高击穿电压,但另一方面气压增大后,气体的密度较大,带电质点不易向空间扩散,因而对电场的畸变作用必然加强,该过程有助于流注的发展,降低击穿电压,因而上述两个因素具有相反的作用效果,击穿电压是上述两者共同作用和影响的结果。
对于间距为15cm及20cm的气隙,由于间隙距离大,棒-板间距间的空间电荷比相对于短气隙(10cm和4.7cm)时更容易迁移和扩散,因此在同一气压下,长气隙的空间电场畸变的程度小于短气隙,电子的平均自由行程的减小影响程度在整个过程中一直大于电场畸变作用,因而击穿电压随气压的增大呈正比线性关系。而对于间距为10cm及4.6cm的棒-板间隙,其击穿电压随气压的变化分为三个阶段,以10cm为例,在气压<40kPa时,击穿电压与气压近似呈线性增大,其原因可能在于此时气压低,气体密度低,带电质点易于扩散,电子自由行程减小作用大于空间离子畸变电场作用,因而气压增加,击穿电压也相应增加;60kPa>气压>40kPa时,击穿电压增加的陡度逐渐减小,其原因可能在于此时空间电荷对电场的加强作用逐渐增大,并呈现与电子平均自由行程减小作用相等的趋势;在气压>60kPa时,空间电荷对电场的畸变进一步增强,导致气压对气隙的击穿电压影响减小,此时击穿电压随气压的增加则几乎不增加或增加很少。对于上述现象本文下一步还将尝试采用数值仿真的方法进行更深入的理论分析。
6 现场紫外检测
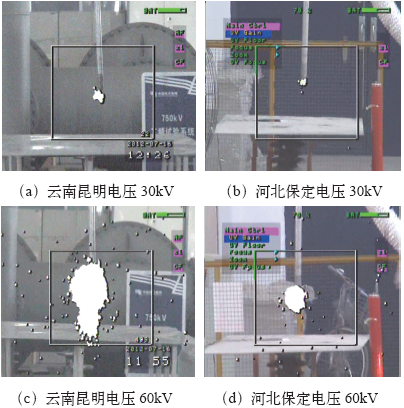
为进一步验证实验结果的有效性,本文在河北保定(平原地区)和云南昆明(高海波地区)分别进行了棒-板模型的放电紫外成像检测。为尽可能降低除气压以外其他实验条件和环境因素的影响,两地实验时的棒电极与试验室研究中的棒电极相同,采用了同一台紫外成像仪。保定试验基地的气象条件为:海拔约为10m,气压为101.6kPa,温度为28℃,相对湿度为75%;云南昆明试验基地的气象条件为:海拔约为2 000m,气压为79.8kPa,温度为22℃,相对湿度为74%;试验以20cm的棒-板间隙为研究对象,对间隙逐步施加电压直到击穿,利用紫外成像仪采集了从起晕到击穿的放电视频信号。
图8
图8
昆明和保定地区电压为30kV和60kV时的紫外图片
Fig.8
UV imges with the voltage of 30kV and 60kV in Kunmming and Baoding
图9
图9
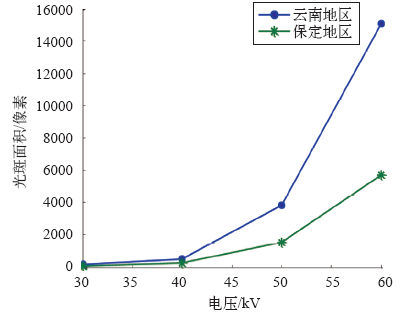
昆明与保定地区放电光斑面积与电压关系曲线
Fig.9
Relationship curves of discharge facular area to voltage in Kunming and Baoding
表2为该间隙的起晕电压、击穿电压以及光斑面积变化的预测值和现场值。
表2 现场检测结果与预测结果
Tab.2
| 地区 | 起晕电压/kV | 击穿电压/kV | 光斑面积/像素 (30kV) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 现场值 | 预测值 | 现场值 | 预测值 | 现场值 | 预测值 | |
| 保定 | 20 | 19.57 | 69.5 | 69.43 | 72 | 73 |
| 云南 | 16 | 16.87 | 60.5 | 58.74 | 171 | 181 |
表2中所谓预测值,是指根据实验室得到的相关规律曲线计算得到的起晕电压值、击穿电压值和光斑面积值。由上述实验数据和分析结果可知,对于20cm的棒-板间隙,其起晕电压、击穿电压以及光斑面积的变化特性,现场测试结果与实验结果一致。
7 结论
本文以棒-板间隙为研究对象,对电晕放电、电离发光区域及击穿电压随气压的变化特性进行了实验研究,得到如下结论:
(1)棒-板间隙起晕电压随气压的增加而增大,随间距的增大而增大。二者与起晕电压均具有线性关系。
(2)气压越高,电离发光区域减小,经拟合分析表明,两者近似满足幂函数关系。
(3)15cm及20cm的棒-板间隙的击穿电压随气压的增大而增大,二者也具有一定的线性关系,但10cm以及4.6cm的击穿电压开始时呈增高趋势,却在气压达到一定程度时呈现非线性特性。由于极不均匀电场的击穿电压具有一定的分散性,因此需要进一步进行实验研究分析。
(4)高海拔现场极不均匀电场放电的紫外测试结果与实验研究结论一致。
参考文献
特高压电晕笼直流分裂导线正极性电晕起始特性分析
[J].In order to study the corona onset characteristic of the positive conductor in the UHV corona cage, the charge simulation method is applied to calculate the space electric field and corona onset voltage of the stranded conductor in the corona cage. Each strand is simulated by 8 space charges, based on the corona sustainable criterion in extreme uneven electric filed and the secondary emission process of the photoelectrons. The corona loss test of the single aluminum cable steel reinforced (LGJ)900-75, 6*LGJ900-75, 8*LGJ400-35 conductors in dry and rain conditions is done in the UHV corona cage, and the chosen rain rate are 2.4mm/h, 20mm/h and 30mm/h. The tangent line method is used to determine the test corona onset voltage, and the comparative study proves that the calculation model can be used to calculate the positive corona onset voltage of the bundle conductors in the UHV corona cage. A further analysis shows that: the positive corona onset voltage increases with the bundle number, and decreases with the bundle space and also increases with the diameter of the sub -conductor; the surface irregularity coefficient decreases with the rain rate, while at the same time, it tends to be saturated.
Analysis of the positive corona onset characteristic of the bundle conductors in the UHV corona cafe
[J].In order to study the corona onset characteristic of the positive conductor in the UHV corona cage, the charge simulation method is applied to calculate the space electric field and corona onset voltage of the stranded conductor in the corona cage. Each strand is simulated by 8 space charges, based on the corona sustainable criterion in extreme uneven electric filed and the secondary emission process of the photoelectrons. The corona loss test of the single aluminum cable steel reinforced (LGJ)900-75, 6*LGJ900-75, 8*LGJ400-35 conductors in dry and rain conditions is done in the UHV corona cage, and the chosen rain rate are 2.4mm/h, 20mm/h and 30mm/h. The tangent line method is used to determine the test corona onset voltage, and the comparative study proves that the calculation model can be used to calculate the positive corona onset voltage of the bundle conductors in the UHV corona cage. A further analysis shows that: the positive corona onset voltage increases with the bundle number, and decreases with the bundle space and also increases with the diameter of the sub -conductor; the surface irregularity coefficient decreases with the rain rate, while at the same time, it tends to be saturated.
Influence of pressure and humidity on the amplitude-phase distribution of AC corona pulse
[C].
Negative corona inception voltages in rod-plane gaps at various air pressures and humidities
[J].The variation of negative dc corona inception voltages with air pressure and humidity, using a point/plane electrode system, was studied using a perspex chamber in which the pressure and humidity could be varied. A method of calculation was developed to determine the corona inception voltages over a range of air pressures and humidities. The effective ionization coefficient was calculated as a linear interpolation of the effective ionization coefficients for dry air and water vapor. The validity of these calculations was confirmed by a series of experimental determinations of the corona inception voltages for the same range of pressures and humidities. A comparison of the negative and positive corona inception mechanisms was also made. Both the negative and positive corona inception voltages decreased with a decrease in the air pressure and an increase in the humidity. The greater values of the effective ionization intensity found in the critical zone for the negative corona accounted for their lower inception voltages. The mechanisms of the affect of the photo-absorption coefficient and Townsend's second coefficient on the negative and positive corona were also considered.
气压对直流正极性下冰柱-冰板间隙电晕放电的影响
[J].为进一步了解低气压下覆冰对绝缘子的危害,该文选择冰柱-冰板间隙模型,借助数据采集卡、紫外线成像仪和自行设计的电流传感器等设备,在人工气候室内研究低气压下冰柱-冰板模型的电晕放电特性。文章分析了气压对冰柱-冰板间隙的起晕电压、平均放电量和冰柱尖端处的放电区域等方面的影响。结果表明:起晕电压随着气压的降低而降低,平均放电量和冰柱尖端处的放电区域均随着气压的降低而减小,同时,在较低气压下,起始放电更容易形成辉光放电,放电测量也更困难。
Influence of atmospheric pressure on DC positive corona discharge in icicle to iced plate electrode system
[J].为进一步了解低气压下覆冰对绝缘子的危害,该文选择冰柱-冰板间隙模型,借助数据采集卡、紫外线成像仪和自行设计的电流传感器等设备,在人工气候室内研究低气压下冰柱-冰板模型的电晕放电特性。文章分析了气压对冰柱-冰板间隙的起晕电压、平均放电量和冰柱尖端处的放电区域等方面的影响。结果表明:起晕电压随着气压的降低而降低,平均放电量和冰柱尖端处的放电区域均随着气压的降低而减小,同时,在较低气压下,起始放电更容易形成辉光放电,放电测量也更困难。
Partial discharge mechanism in a non-uniform electric field at higher pressure
[J].
DOI:10.3791/58233
URL
PMID:30417884
[本文引用: 1]

During energy conversion, material production, and metallurgy processes, reactions often have the features of unsteadiness, multistep, and multi-intermediates. Thermogravimetry-mass spectrum (TG-MS) is seen as a powerful tool to study reaction features. However, reaction details and reaction mechanics have not been effectively obtained directly from the ion current of TG-MS. Here, we provide a method of an equivalent characteristic spectrum analysis (ECSA) for analyzing the mass spectrum and giving the mass flow rate of reaction gases as precise as possible. The ECSA can effectively separate overlapping ion peaks and then eliminate the mass discrimination and temperature-dependent effect. Two example experiments are presented: (1) the decomposition of CaCO3 with evolved gas of CO2 and the decomposition of hydromagnesite with evolved gas of CO2 and H2O, to evaluate the ECSA on single-component system measurement and (2) the thermal pyrolysis of Zhundong coal with evolved gases of inorganic gases CO, H2, and CO2, and organic gases C2H4, C2H6, C3H8, C6H14, etc., to evaluate the ECSA on multi-component system measurement. Based on the successful calibration of the characteristic spectrum and relative sensitivity of specific gas and the ECSA on mass spectrum, we demonstrate that the ECSA accurately gives the mass flow rates of each evolved gas, including organic or inorganic gases, for not only single but multi-component reactions, which cannot be implemented by the traditional measurements.
Investigations on breakdown voltage of solid barrier under non-uniform electric field simulation and experiment
[C].
基于放电紫外成像参量的绝缘子污秽状态评估的研究
[J].污秽绝缘子在一定的湿度条件下会形成放电并辐射出紫外光信号, 本文提出了一种基于日盲紫外成像的污秽状态评估方法。首先在人工气候室中研究了几种不同污秽度的绝缘子在不同湿度下的放电现象, 通过对放电视频信号的分析并结合图像处理算法提取了平稳紫外光斑面积、间歇性紫外光斑面积以及间歇性紫外光斑重复次数三个特征参数。由于污秽放电具有一定的随机性, 而基于视频和图像分析法提取的特征参数具有模糊性, 论文采用了模糊逻辑推理的方法建立了绝缘子的污秽状态评估模型, 测试表明该推理模型具有较高的准确性和稳定性。
Contamination condition evaluation of insulators based on discharge ultraviolet imaging parameters
[J].污秽绝缘子在一定的湿度条件下会形成放电并辐射出紫外光信号, 本文提出了一种基于日盲紫外成像的污秽状态评估方法。首先在人工气候室中研究了几种不同污秽度的绝缘子在不同湿度下的放电现象, 通过对放电视频信号的分析并结合图像处理算法提取了平稳紫外光斑面积、间歇性紫外光斑面积以及间歇性紫外光斑重复次数三个特征参数。由于污秽放电具有一定的随机性, 而基于视频和图像分析法提取的特征参数具有模糊性, 论文采用了模糊逻辑推理的方法建立了绝缘子的污秽状态评估模型, 测试表明该推理模型具有较高的准确性和稳定性。
放电日盲紫外成像检测图像参数提取方法研究
[J].
Study on parameters extraction method of discharge based on solar-blind ultraviolet maging detection
[J].