1 引言
一方面,随着经济的不断发展,电力电子技术已经在工业、电力和交通等领域广泛应用,大功率电力电子器件如二极管、晶闸管和GTO等组成的电力电子装置在早期被大量使用,其运行过程中产生的大量谐波、无功对电网的电能质量造成了严重的影响;电网中的偶发性故障、大容量负载的冲击和波动以及非对称性负载的运行,也给电网带来了电压波动、暂降以及不对称等问题。另一方面,随着信息化、智能化技术的推广和发展,基于微机控制的电能质量敏感性设备,如芯片测试仪、变频器、制冷电子控制器和数控机床等被大量投入使用,使得用户对电力系统的供电质量提出了更高要求。因此,在数字化、信息化高速发展的今天,如何解决这些电能质量问题已是迫在眉睫[1]。
在诸多电能质量问题中,敏感型负荷用户受电网电压暂降影响而造成的危害最为普遍。针对大型电力用户进行的电压暂降事件统计表明,一年内发生跌落深度超过0.2(pu)的次数约在10~20次左右,发生跌落幅值在0.5(pu)以内的电压跌落次数约占总跌落次数的80%,每次电压跌落都会给用户带来不同程度的经济损失。可见,如何减少电压暂降对用户带来的影响已经成为电能质量优化工作的关键内容。
由于电力系统中室外变电站和传输线路都裸露在大自然中,输电线路易遭受雷击,这一过程所引起的线路对地放电或绝缘子闪络,会触发继电保护装置发生保护动作,从而造成系统中其他设备的供电电压暂降或中断。如我国著名的三大雷区之一雷州半岛地区,其年平均雷暴日数近100天,每年5~9月份是雷暴多发季节,其中7~8月是雷暴高发期,雷暴活动密度高、强度大,极易出现雷击灾害,影响该地区电网的稳定。这一期间内,该地区的供电线路易受雷暴的影响,出现电压暂降的现象,导致负载设备停机,影响企业生产。根据已有的文献资料介绍,在部分地区,约60%的电压暂降与遭受雷击有关,持续时间一般超过100ms,而且电压暂降具有一定的传播特性,且无法避免,在方圆几千平方公里内的任意处雷击都将会影响到该区域内的任一敏感负荷的正常、安全运行。
系统中的短路故障是造成电压暂降的另一因素。目前配电系统中线路主保护以电流保护为主,这种保护方式的最大缺点为无法无延时地切除相当大部分线路区域的故障。即使可以实现无延时保护,但从检测发现故障到断路器的保护动作,最少也需要3~6个工频周期的延时。在这一段时间内,该故障线路和其附近线路上的敏感负荷将会受到影响而退出运行。另外,由于故障未被及时清除,一旦重合闸动作,则电压暂降次数会急剧增加。
某些大型用电企业在生产过程中,需要起停大容量感应电机,由于感应电机全电压起动时电流冲击很大,一般达到额定电流的5倍以上,这一过程会引起电网电压暂降,但跌落深度一般不大,其影响范围相对较小,但对其周边一定范围内的敏感负荷也会带来危害。
随着工业自动化技术的大规模应用,如变频器、可编程逻辑控制器、各种连续性自动化生产线和计算机系统等敏感负荷的大量使用以及未来分布式供能系统的快速发展都对治理电压暂降提出了迫切需求。电压暂降已上升为最重要的电能质量问题,已经成为信息化社会对供电质量提出的新挑战,研究电压暂降治理装置有着重要的社会和经济意义[4,5]。动态电压恢复器(Dynamic Voltage Restorer, DVR)作为一种用户侧串联电压补偿设备,可有效抑制电压闪变等各种问题,确保用户侧电压质量。目前,国内的工业应用多以低压装置为主,但随着大规模具有间歇性和随机性特点的新能源接入电网,电力系统对风电场和光伏电站低电压穿越能力的要求越来越严格,动态电压恢复器的研发和推广已是迫在眉睫,故针对这类装置关键技术的研究具有重要的意义。
2 国内动态电压恢复技术发展
在国内,DVR的研究工作得到了各高校和研究院所的关注。自1998年起,清华大学、华北电力大学等高校就一直致力于DVR的样机研发工作。清华大学研制了基于超导线圈储能的一台150kV·A/0.3MJ低压DVR样机[6]。国网电力科学研究院将蓄电池和超级电容器进行合理配比后应用于低压DVR系统上,使其性价比达到最优。中电普瑞公司开展了10kV动态电压恢复装置的研发工作,并为用户提供了样机。2012年中科院电工研究所无锡分所经过多年联合攻关,成功研制出基于超级电容器的低压动态电压恢复器。可以看出,目前国内的主要研究工作集中在储能方式的研究和低压小功率样机的试验[7],已知的大功率试验样机仅中电普瑞和上海电气输配电集团两家拥有。综上可知,关于动态电压恢复器的关键技术研究工作还有待进一步深入展开。
目前针对于动态电压恢复器的研究内容主要可以分为:电压跌落检测算法和系统控制策略,其中系统控制策略的研究可分为电压补偿策略研究、动态电压跟踪控制方法研究和系统控制策略研究。
关于电压跌落检测算法的国内外研究主要分为:峰值电压法、FFT法、小波变换法、状态空间矩阵法、缺损电压检测方法、瞬时电压DQ变换法、对称分量预估法和Hilbert变换检测法。
关于电压补偿策略的国内外研究主要分为:完全补偿、同相补偿、最小能量补偿以及基于以上方法形成的最小视在功率法等;关于动态电压跟踪控制方法的国内外研究主要分为:PI控制、PR控制、滑模控制、重复控制、预测控制、蚁群算法、H∞控制、无差拍控制和智能控制;系统控制策略的国内外研究主要分为前馈控制、反馈控制以及复合控制等。
3 电压跌落检测算法研究现状
快速而准确地进行电压跌落检测是决定DVR响应时间的重要指标。当电网电压出现电压暂降时,DVR需要及时检测判断出跌落起始和结束时刻,从而快速地投入和切除DVR。同时,电压幅值跌落深度和相位跳变角度也是影响补偿输出的两个关键参数。目前,关于电压跌落检测方法的国内外研究主要有:
(1)峰值电压法。通过对电压信号进行求导,以斜率判断为依据,当斜率值为零时,将该时刻的电压值与参考电压峰值比较,一旦误差超出设定范围,即认为电压跌落发生。利用这一方法可判断出电压跌落深度和跌落起止时刻,算法实现简单。但峰值电压法判断延时较大,求导计算易受干扰,稳定性不高,而且无法识别跌落过程中的相角跳变信息。
(2)FFT法。进行电网电压的FFT分析可以准确获得各频率分量的幅值和相位信息,通过对基波幅值和相位变化的监测可有效检测出电压跌落幅值和相位跳变角。该方法可以有效而准确地计算出基波幅值和相位,但延时较长,至少需要一个工频周期。虽然可以利用正弦半波对称的特点进行半波数据的构造来快速实现FFT计算,以达到减小半个工频周期延时的目的,但在电压跌落时刻的波形却不能保证其仍具有半波对称的特点,因此计算结果将会产生较大的误差。文献[8]用DFT算法进行有效值检测来判断电压跌落。文献[9]介绍了一种三相在线交互式DVR的新型跌落检测算法,这种改进的检测算法采用一个瞬时检测器和RMS变化探测器组合而成。电网电压信号经过DFT和RMS计算,其输出结果由一个瞬时跌落检测器来进行观测。一旦发现跌落,通过RMS变化检测器来进行电压跌落事件的进一步确认,并通过仿真和试验证明了该方法的有效性。
(3)小波变换法。小波变换法是一种时频局部化分析方法,对信号的突变十分敏感,电压跌落起始和结束时刻正是一个信号的奇异变化点,因此利用小波变换法可快速有效检测出电压跌落的起止时刻。文献[10]利用小波变换对信号进行分析,将突变奇异点予以准确定位,从而快速检测出电压跌落的开始和结束时刻。文献[11]通过对连续小波进行二进制离散实现了电网中各种故障信号的快速准确检测。文献[12]通过结合傅里叶变换方法与小波变换方法来实时检测信号的暂态变化。文献[13]介绍了一种基于小波变换分析的故障选相方法。文献[14]为了解决有效值计算方法无法精准判断电压跌落起止时刻的缺点,通过小波变换进行弥补,实现了两种方法的优点互补。文献[15]证明了小波包变换用于电压跌落的信号分析是可行有效的。文献[16] 基于Daubechies小波对信号进行两级分解,获得了准确的起止时刻和跌落深度。但就小波变换法来说,不管是传统电能质量如谐波电压的检测还是动态电压质量如电压跌落的检测,其难点就是选择一个合适的小波基函数,如何选取一个最优或较优的小波基函数是该方法的关键。到目前为止,关于选取方法的理论依据仍在研究当中,经验和已有成果是目前选择小波基函数的重要参考[17,18],所以小波分析方法目前来说实现过于复杂,数据处理量大,同时该方法需要与其他方法结合才能检测出电压跌落的幅值。
(4)缺损电压检测法。美国学者Tunaboylu提出了缺损电压检测法,用以弥补方均根值检测方法的快速性不足。缺损电压为标准的期望电压减去实际的电网电压所得到的差值。标准的期望电压可通过跌落前的正常电压信息进行人为构造。利用该方法可准确检测出电压跌落的起止时间、相位跳变和补偿电压值等信息。从补偿策略而言,该方法只适用于完全补偿,虽然通过加权处理可以用于准完全补偿[19],但是当电网电压出现不对称和谐波时,此方法由于无法将基波、谐波、正序和负序分量分开,其实际的补偿效果将不尽如人意。
(5)瞬时电压DQ变换法。瞬时电压DQ变换法通过坐标系的同步旋转实现各频次分量的有效提取。基于工频旋转角速度的DQ变换后,基波正序分量为DQ分量中的直流分量,基波负序和谐波分量为DQ分量中的交流分量。若电网电压平衡跌落且无畸变时,DQ变换法可以直接得到电压跌落深度值;若电网电压不平衡跌落或畸变,DQ变换后需要加入低通滤波器才能得到电压跌落深度值,此时,DQ变换法的响应速度受到了影响,延时增大。文献[21]对DQ变换后所得分量进行求导运算,经过DQ微分值和原DQ值的交叉运算可将原DQ分量中的交流成分予以抵消,最后得到直流分量。该方法检测延时短,但一旦输入量中出现谐波,则需要通过带通滤波器实现基波分量的提取,此时检测将会产生较大延时。在实际电网中,发生单相电压跌落的概率远高于三相电压跌落,因此针对单相电压跌落情况,需对DQ变换进行改进。基于文献[20]所提方法,文献[22]提出一种无时延的改进DQ变换,消除了构造三相电压所带来的延时,但在电网电压畸变条件下提取DQ分量中直流分量仍需使用低通滤波器。文献[23]直接将输入电压量和其超前90°的分量构造出αβ坐标系,按照工频角速度旋转后得到DQ分量,将该量经由低通滤波器后得到直流分量。该方法抗干扰能力强,但存在较大延时。总的来看,虽然DQ变换法存在延时,但在各种电压异常情况下都能适用,所以,DQ变换法在电压跌落检测中应用最多[24,25]。
(6)对称分量预估法。文献[26]提出了一种新的对称分量法,此方法基于Widrow-Hoff三角法来进行对称分量的预估,具有易实现、快速收敛且对系统参数变化不敏感等优点。优化后的三角法适用于多输出系统,可将正序、负序和零序分离出来,将电网电压信号按此方法进行分解,便可得到所需的电压补偿量,可以有效解决电压跌落、闪变以及不平衡等问题。
(7)Hilbert 变换检测法。Hilbert变换等效于±π/2的相移,对正频率产生-π/2的相移,对负频率产生π/2相移,或者说,在时域信号中每一频率成分移位1/4波长。因此,希尔伯特变换又称为90°移相器。文献[27,28]利用Hilbert变换将电压跌落信号的幅值包络进行提取,通过向后差分法即可快速判定电压跌落的起止时刻。
(8)LES滤波器检测。为了提高DVR的响应速度,同时实现在电网电压不平衡和谐波条件下能够快速地提取各个特征分量,LES滤波器算法逐渐被应用于DVR的研究工作。LES滤波器又称最小方差滤波器,M.S. Sachdev于1979年提出并应用于数字化阻抗继保中[29]。LES滤波器可以将直流分量、各次谐波分量以及基波分量快速地提取出来,便于后期的数字化分析和处理。文献[29]提出了一种基于LES滤波器提取电网中的基波和谐波分量的方法。文献[30]基于LES滤波器原理构建了自适应感知器以检测电压的扰动、谐波和不平衡分量。文献[31]将卡尔曼滤波器和LES滤波器进行融合,实现干扰噪声的滤除和所需分量的提取,但卡尔曼滤波器数据计算量太大,不易实现。文献[32]利用LES滤波提取电压的幅值和相位,通过计算出电压跌落分量实现补偿控制,但没有进一步将正负序和谐波分量分开,以实现更好补偿。因此,本文在进行锁相环设计和电压跌落检测时,将LES滤波器和对称分量法进行了结合,达到了快速准确的检测效果。
4 控制策略研究现状
控制策略的研究可分为电压补偿策略、动态电压跟踪控制方法和系统控制策略的研究。
4.1 电压补偿策略
(1)完全补偿法。即保持负荷侧电压与电压跌落发生前的幅值和相位一致。该补偿方法适用于相位敏感性负载,其缺点是无法对输出补偿电压的幅值和功率进行控制。
(2)同相补偿法。保持负荷侧电压与跌落后的电网电压同相位,该补偿方法可保证输出补偿电压的幅值最小。其缺点是无法控制输出功率,且不适用于相位敏感型负载。
(3)最小能量补偿法。即以无功功率的支撑为主,尽可能保证DVR最小有功功率输出。在电压跌落情况下,该补偿方法输出的有功功率最小,可最大限度延长储能型DVR的补偿持续时间;在电压突升情况下,该补偿方法所吸收的有功功率最小,可最大限度地抑制能量倒灌。其缺点是所需的输出补偿电压幅值最大,且负荷侧电压存在相位偏移。
(4)最小视在功率法。即从DVR的视在功率出发,提出了一种综合性能较好的控制方式,称为最小视在功率控制。主要针对最小能量补偿存在的问题进行了改进,它能使DVR的视在功率最小,大大减小DVR的容量。在减小DVR的无功功率的同时使其输出的有功功率也保持较小,还能减小DVR的注入电压幅值。此外,计算量小,控制简单、统一,其缺点是补偿后也会有负载侧端电压相位跳变的问题。在用于对电压相位跳变敏感的负载时应在凹陷开始和结束时采用电压相位逐渐变化的策略。
文献[33]完全补偿法的依据是一般最小能量法,总是先求出负序和零序分量值,由DVR将其补偿掉再根据其他条件来满足正序补偿的需要,因此其补偿方式受到一定条件的限制。而完全补偿法则完全根据补偿极限圆的交点来判定,不受其他因素的影响。但这种补偿方法仅是考虑了电压极限,没有考虑受到电流限制情况下对于补偿性能的影响。文献[34]是根据电压与电流相位的关系来确定补偿后电压在哪几个区域为最小能量的补偿点,通过设定一定的条件,画出比较直观的曲线进行分析,得出了如何调整输出电压的相角来逐步实现能量最小补偿。由于考虑了相位敏感负载,所以角度变化的步长选取和负载有很大关系。文献[35]采取最小视在功率控制确实可以减小设备的输出电压幅值,该方法与最小能量法相比主要优势体现在对于无功的补偿差别上。采用最小视在功率控制可以扩大设备的电压补偿域,实现更大范围的能力输出,同时也减小了对输出侧设备的功率要求。文献[36]侧重如何实现有功能量的最小输出,以保证带储能装置的DVR可以实现最大能力的补偿。文献[37]对三种补偿策略进行了分析比对,在各个策略中,分析了不同负载功率下,发生不同电压跌落深度情况下,DVR的功率与输出电压幅值等的关系,可以看出,同相补偿所需的电压幅值最小,能量优化补偿的所需的功率最小、但是电压幅值较大、且会存在相位跳变。因此推荐采用相位渐进的方式实现能量最小的补偿方式,提出了可以通过锁相环参数或设置增益来实现渐变的要求而不至于影响负载。文献[38]先对比了几种补偿策略,指出最小能量补偿的优点是能量利用率高,缺点是会带来电压的尖刺,不适于数字化的负载设备。文献[39,40]提出在实施最小能量补偿或恢复到电压跌落前补偿时,可能会由于注入电压太大,或者直流侧电压的降低而引起调制比过高饱和甚至导致波形畸变的问题。因此该文献提出一种优化的补偿策略,在调制比过高时,开放锁相环来实现从恢复到电压跌落前补偿策略过渡到最小电压补偿模式(同相补偿),这样可以维持调制比而不至于因调制过大而引起波形失真。
4.2 动态电压跟踪控制方法
实现DVR输出电压的准确跟踪是DVR的一个重要技术,DVR既要有快速的动态响应又要保证稳定的电压精度,还要能够针对不同类型的负载甚至非线性负载的谐波电压进行补偿。这些都和DVR的控制器设计紧密相关,因此控制器的设计直接关系到DVR的补偿性能,也是研究任务中的难点和重点,目前国内外的主流跟踪控制方法主要有以下几种。
4.2.1 PI控制
PI控制称为比例积分控制,PI控制应用最为广泛,具有可靠性高、研究成熟和稳态误差小等优点。目前PI控制也是DVR技术中研究最多、应用较广的控制方法之一。但PI控制也存在一些局限性,例如在DVR系统中需要对工频跌落和谐波分量进行补偿时,单个PI的参数由于受到本身的固定带宽限制,无法保证既满足基波的准确补偿又实现对谐波分量的准确跟踪[41]。文献[42]为了实现PI控制器在DVR中的应用,需要利用DQ变换将正弦量转化为直流量进行控制,这一方面是为了简化系统的模型,实现有功功率和无功功率的解耦,另一方面解决了PI控制器无法对正弦量实现无静差控制的问题。文献[43]在原有PI控制基础上通过积分重构加入典型的补偿网络控制器和某些状态量预估来取代原来的微分环节,另外再加入一个前馈分量来改善系统的快速响应特性。
4.2.2 PR控制
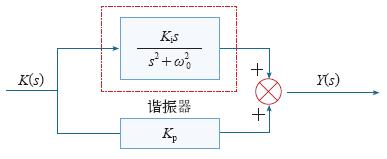
PR控制称为比例谐振控制,如图1所示,在特定某一频率下,该控制器具有无限大的增益,因此可以实现零稳态误差,同时具有很好的稳态裕度和暂态性能。PR控制器可以实现对交流输入的无静差控制。将PR控制器用于DVR的控制系统中,可在两相静止坐标系下对电压进行调节,简化控制过程中的坐标变换,消除电流DQ轴分量之间的耦合关系。此外,应用PR控制器,易于实现低次谐波补偿,这些都有助于简化控制系统的结构。文献[44]采用PR控制可以简化算法,不需要进行DQ坐标变换,也不需要在电流内环加入解耦算法,在静止坐标系下可实现对基波和谐波的跟踪。通过伯德图分析和仿真结果可以看出,PR控制对于基波分量可以实现零误差跟踪,对谐波的跟踪效果较好,对于改善DVR输出电能的质量有着明显的效果。
图1
4.2.3 滑模控制
滑模控制(Sliding Mode Control,SMC)也叫变结构控制,本质上是一类特殊的非线性控制,且非线性表现为控制的不连续性。这种控制策略与其他控制的不同之处在于系统的“结构”并不固定,而是可以在动态过程中,随着DVR系统中不同电压跌落的发生和负载变化所引起的谐波电压的变化,滑模控制可根据当前的状态有目的地不断变化,迫使控制系统按照预定“滑动模态”的状态轨迹运动。由于滑动模态可以进行设计且与对象参数及扰动无关,这就使得滑模控制具有快速响应、对参数变化及扰动不灵敏、无需系统在线辨识、物理实现简单等优点[45,46,47]。但合适的滑模切换面难以确定,而且在实际应用中,为了达到良好的控制效果,数字系统需要有足够高的采样频率。文献[48]介绍了滑模控制的设计思路,滑模面的选择方法,并进行了仿真和实际验证。在电压突升和突降中,滑模控制都具有良好的动态性能和鲁棒性。文献[49]给出了滑模曲面的设计方法,并依据此方法进行了预补偿、同相补偿和最小能量补偿的仿真对比分析,通过矢量三角形方法可以确定DVR的输出补偿角以实现最小能量补偿。
4.2.4 重复控制
重复控制主要基于内模原理,通过周期性的延时进行偏差的重复利用,具有稳态跟踪精度高,输出波形质量好等优点。该方法对于周期性的信号跟踪十分适合,同时使周期性的干扰得到有效抑制,稳定跟踪特性优良,但动态跟踪特性一般。在逆变器中应用重复控制可有效解决因非线性负载引起的畸变问题。在实际应用中,一般将重复控制和其他控制方法复合使用,用于改善输出波形质量,消除重复性的畸变分量[50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57]。文献[58]引入了重复控制,介绍了设计原理和实验结果。文献[59]描述了基于五电平飞跨电容型的DVR,分析了控制系统的状态方程,并引入重复控制。文献[60]将前馈控制、反馈控制和重复控制结合起来进行复合控制, 采用重复控制的方法可以实现DVR装置消除电网系统的谐波对负载的干扰, 实现波形的优化跟踪,前馈控制和反馈控制实现快速响应的应用要求。文献[61]针对原有的重复控制技术易受电网频率波动、自身的直流分量增益过大(含变压器系统)以及非周期性干扰等因素的影响而失稳或影响跟踪效果,提出了改进的重复控制方法,加入了频率变化的适应环节,类似于加入过采样环节,直流分量由低通(高频衰减)加高通滤波器(直流衰减)滤除,最后形成了一种复合控制环,通过对单相DVR的状态方程分析,在原有的重复控制基础之上,增加了局部的纯误差积分环节,使得整体的控制性能得到了提升。文献[62]采用了1/2工频周期数的重复控制,对奇次谐波具有无穷大的增益,以及根据传递函数说明了传递函数的稳定性判据和低通滤波器的设计要求。对于整个优化的重复控制的设计思路和原理予以了充分地阐述,并用仿真证明了其算法的有效性。
4.2.5 预测控制
4.2.6 蚁群算法控制
图2
4.2.7 H∞控制
H∞控制理论,不但可对控制系统进行优化设计,控制精度高,而且还可满足鲁棒性要求;不但有明确的物理意义,而且还有严格的数学基础。H∞控制理论很好地解决了常规频域理论不适于多输入多输出(MIMO)系统设计及 LQG(线性二次高斯)理论不适于模型摄动情况两个难题[79]。该理论已成为目前解决鲁棒分析和鲁棒控制问题比较成功且比较完善的理论体系。鉴于此,文献[80,81]将H∞模型匹配控制技术应用于DVR逆变器输出波形的跟踪控制中,实现了DVR的电压波形动态跟踪补偿优化控制。文献[82]论述了H∞控制器在基频正负序表现出极大的增益,在面对系统参数变化时具有很好的鲁棒性,通过基于权重函数选择方法实现H∞控制器,增强了电流内环调谐和系统抗扰能力等。
4.2.8 无差拍控制
无差拍控制是一种结合反馈信号和系统状态方程进行下一周期控制量计算的方法。通过当前时刻的状态量和下一时刻所需输出的标准参考量即可获得下一周期的实际控制量。该方法可快速修正负载变化带来的波形偏差,具有控制响应速度快、精度高和输出波形品质良好等优点。但由于系统状态方程精确与否决定了无差拍控制的效果,因此,该方法的鲁棒性较差。文献[83]从结构、暂态过程对DVR系统进行了分析,控制中采用了无差拍控制进行了误差优化控制。
4.2.9 智能控制
智能控制主要有模糊控制和神经网络控制两种。模糊控制方法主要以模拟人的模糊信息处理能力为主,属于人的思维外特性;神经网络控制方法主要模拟人处理信息的分布性、并行性、冗余性、非线性、容错性以及自组织、自学习、自适应能力,属于人脑的微观物理结构。
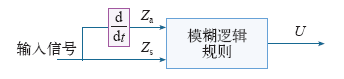
图3所示为模糊控制框图,模糊控制无需精确建立控制对象的数学模型,利用系统特征的模糊描述即可实现控制。该方法对于外界的干扰不敏感,鲁棒性较强,但存在稳态误差,容易在工作点出现小幅振荡。模糊控制相比于其他控制方法而言,动态特性较好,但精准性需要提高。因此文献[84,85]将模糊控制与PI控制复合应用于DVR系统。由于DVR是一种非线性工作的设备,对于此类设备而言,采用非线性控制如神经网络控制则更加适合。文献[86,87]对比分析了神经网络控制和PI控制在DVR中的应用,发现神经网络控制工作范围更广,动态跟踪特性更优。由于神经网络具有自学习自适应的能力,根据输入输出量即可分辨出控制对象的内部非线性关系,因此抗干扰能力强。但是神经网络控制需要大量的样本进行离线训练,如何选择合适的样本和样本数量都决定了控制效果。目前,该控制技术在数字处理器中较难实现,结构复杂、可进行在线学习的神经网络控制技术还未成功应用于实际的DVR装置中。
图3
4.3 系统控制策略
DVR的输出电压控制是实现动态电压补偿的重要方面,当电网出现电压暂降时,如何快速精确的跟踪电压补偿信号,保证负荷侧电压稳定是DVR设计中的关键技术。其控制策略的设计直接关系到DVR系统的工作性能,国内外众多学者进行了大量的研究,主要控制策略有:前馈控制、反馈控制和复合控制等。
4.3.1 前馈控制
前馈控制直接将电压补偿信号输入脉冲生成模块,控制DVR的输出电压,因此具有很高的动态响应速度。但是DVR的输出电压则容易受到电网电压以及负荷特性的影响。前馈控制实际上是一个开环控制,其负载的适应能力不强,如果系统参数设计不当,会造成严重的电压超调。该方法误差大,补偿效果差,而且DVR的输出滤波器所带来的幅值衰减和相位偏差无法消除,因此难以实现精确补偿。
文献[42]利用DQ的坐标变换,通过低通滤波器提取正序分量,再由DQ反变换后与原信号相减得到补偿电压的负序、谐波分量等,利用滞环比较法控制逆变输出。文献[88]指出变压器漏抗和内阻会导致输出补偿电压出现幅值衰减和相位偏移,负载电流一旦增加,这一偏差将会进一步加大。因此,文献[89]引入误差校正方法抑制电网电压和负载电流对输出补偿电压的影响。在此基础上,文献[90]进一步提出同时利用电网电压前馈和负载电流前馈的双前馈开环控制方法, 既保持了开环控制动态响应速度快的优点, 也可基本消除电网电压和负载电流对负载电压的影响。为避免电流前馈微分环节带来的噪声影响,采用了基于负载电压估算负载电流的方法。仿真证明双前馈控制方法优于简单前馈控制,降低了电网电压和负载电流两个干扰量的影响,但其校正效果将会随着负载高频谐波的出现而变差。
4.3.2 反馈控制
反馈控制即将DVR实际输出的电压信号反馈到控制系统与电压检测输出的补偿参考信号进行误差修正,其输出电压幅值和相位接近于参考信号,补偿精度较高,但单电压环闭环控制的动态响应速度相比前馈控制较慢。为了提高控制环响应速度,同时抑制DVR输出滤波器的谐振尖峰,引入电容电流反馈以实现双环控制,其响应速度和负载适应性都得以提高。
文献[32]采用了输出电压和电容电流双闭环反馈控制。文献[91]提出一种共用直流母线,变压器级联并网的一种拓扑结构,并给出在DQ坐标系下的双环控制的正负序解耦框图。通过稳定性和抗扰分析可知,使用该控制策略系统稳定度高,抗干扰能力强。文献[92]对双环控制系统的内外环参数如何设计给出了指导方法,并设计了参数的稳定域。提出了双矢量控制框图,在仿真和试验中予以证明。文献[93]对电压和电流分别进行DQ变换,电压闭环产生正弦波,电流闭环产生三角波,通过比较产生PWM脉冲信号。文献[94]利用全状态变量反馈控制来实现快速的低电压穿越,可实现LC滤波器的有源钳位并改善抗扰动能力以保证负载电压的电能质量。基于同步旋转坐标系实现前馈和反馈控制,所有的交叉耦合项也都进行了细化,其特点是响应快速、可靠性好、精度高和可在同步坐标系下实现LC解耦。该文还在状态变量反馈中加入了抗磁饱和算法。文献[95]先论述了在DVR结构中整流部分位于电网侧和负载侧对电压畸变的影响。整流侧位于负载侧时,电压跌落时充电电流很大且会流过串联变压器引起电压失真,故而谐波含量会增加。为了减小在非线性负载情况下的电压谐波,提出了状态反馈控制策略,经过理论推导和仿真分析,证明了该方法对电压谐波抑制的效果明显。
4.3.3 复合控制
复合控制策略是一种将前馈控制、电压反馈控制和电容电流反馈控制组合而成的综合控制策略,该策略能兼具前馈和反馈控制策略的优点,改善电压补偿效果。
文献[96]提出了该复合控制策略, 并推导了系统传递函数, 进行了伯德图分析, 最后, 通过软件仿真和样机实验验证了复合控制策略的合理性和有效性。实验结果也表明复合控制策略能提高DVR系统的动态性能、跟随性和稳定性。文献[97]提出了另一种复合控制策略,该策略在输出电压和滤波器电容电流双闭环的基础上加入了电网电压前馈环节,在确保快速响应的同时,提高了系统的稳定裕度。但该策略存在系统响应易受直流电压影响,输出侧串联变压器饱和限流控制难以实现,以及在三相电网电压发生不平衡跌落时,系统难以稳定等问题。基于以上缺点,文献[98]在此基础上进行了优化,采用电感电流反馈替代电容电流反馈,并加入负载电流前馈环节。优化后的复合控制策略既弥补了文献[97]所存在的缺点,也保留了优点。
5 结论
本文针对动态电压恢复器的电压跌落检测算法、电压补偿策略、动态电压跟踪控制方法和系统控制策略进行了广泛的研究。结果表明,动态电压恢复器的动态响应速度和稳态控制精度是考核动态电压恢复器性能的重要指标,只有在进行国内外的技术分析的基础上,通过对检测算法和控制技术持续研究和优化,才能积极促进动态电压恢复技术在电能质量领域中的广泛应用。
参考文献
电能质量问题剖析
[J].
Power quality analysis and its development
[J].
动态电压恢复装置的拓扑结构
[J].
A survey on topology of dynamic voltage restorer
[J].
150kVA/0.3MJ电流源型动态电压补偿装置
[J].
A 150 kVA/0.3 MJ current source voltage sag compensation system
[J].
一种基于飞轮储能系统的新型动态电压恢复器
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.exer.2019.107904
URL
PMID:31883460
[本文引用: 1]

This study was conducted to evaluate the impact of varying scleral material properties on the biomechanical response of the cornea under air-puff induced deformation. Twenty pairs of human donor eyes were obtained for this study. One eye from each pair had its sclera stiffened using 4% glutaraldehyde, while the fellow eye served as control for uniaxial strip testing. The whole globes were mounted in a rigid holder and intraocular pressure (IOP) was set using a saline column. Dynamic corneal response parameters were measured before and after scleral stiffening using the CorVis ST, a dynamic Scheimpflug analyzer. IOP was set to 10, 20, 30, and 40 mmHg, with at least 3 examinations performed at each pressure step. Uniaxial tensile testing data were fit to a neo-Hookean model to estimate the Young's modulus of treated and untreated sclera. Scleral Young's modulus was found to be significantly correlated with several response parameters, including Highest Concavity Deformation Amplitude, Peak Distance, Highest Concavity Radius, and Stiffness Parameter-Highest Concavity (SP-HC). The interaction between IOP and scleral Young's modulus was significantly correlated only to HC Deformation Amplitude. There were significant increases in SP-HC after scleral stiffening at multiple levels of IOP, while no significant difference was observed in the corneal Stiffness Parameter - Applanation 1 (SP-A1) at any level of IOP. Scleral mechanical properties significantly influenced the corneal deformation response to an air-puff. The stiffer the sclera, the greater the constraining effect on corneal deformation resulting in lower displaced amplitude. This may have important clinical implications and suggests that both corneal and scleral material properties contribute to the observed corneal response in air-puff induced deformation.
A novel dynamic voltage restorer with flywheel energy storage system
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.exer.2019.107904
URL
PMID:31883460
[本文引用: 1]

This study was conducted to evaluate the impact of varying scleral material properties on the biomechanical response of the cornea under air-puff induced deformation. Twenty pairs of human donor eyes were obtained for this study. One eye from each pair had its sclera stiffened using 4% glutaraldehyde, while the fellow eye served as control for uniaxial strip testing. The whole globes were mounted in a rigid holder and intraocular pressure (IOP) was set using a saline column. Dynamic corneal response parameters were measured before and after scleral stiffening using the CorVis ST, a dynamic Scheimpflug analyzer. IOP was set to 10, 20, 30, and 40 mmHg, with at least 3 examinations performed at each pressure step. Uniaxial tensile testing data were fit to a neo-Hookean model to estimate the Young's modulus of treated and untreated sclera. Scleral Young's modulus was found to be significantly correlated with several response parameters, including Highest Concavity Deformation Amplitude, Peak Distance, Highest Concavity Radius, and Stiffness Parameter-Highest Concavity (SP-HC). The interaction between IOP and scleral Young's modulus was significantly correlated only to HC Deformation Amplitude. There were significant increases in SP-HC after scleral stiffening at multiple levels of IOP, while no significant difference was observed in the corneal Stiffness Parameter - Applanation 1 (SP-A1) at any level of IOP. Scleral mechanical properties significantly influenced the corneal deformation response to an air-puff. The stiffer the sclera, the greater the constraining effect on corneal deformation resulting in lower displaced amplitude. This may have important clinical implications and suggests that both corneal and scleral material properties contribute to the observed corneal response in air-puff induced deformation.
Algorithm for rapid detection of voltage disturbance in dynamic voltage restorer
[C].
Development of line-interactive dynamic voltage restorer with hybrid sag detection
[C].
基于小波变换模极大值的电能质量扰动检测与定位
[J].
Detection and location of power quality disturbances using wavelet transform modulus maxima
[J].
Power quality assessment via wavelet transform analysis
[J].
DOI:10.3390/s19030700
URL
PMID:30744059
[本文引用: 1]

Three-dimensional (3D) mapping of power lines is very important for power line inspection. Many remotely-sensed data products like light detection and ranging (LiDAR) have been already studied for power line surveys. More and more data are being obtained via photogrammetric measurements. This increases the need for the implementation of advanced processing techniques. In recent years, there have been several developments in visualisation techniques using UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) platform photography. The most modern of such imaging systems have the ability to generate dense point clouds. However, image-based point cloud accuracy is very often various (unstable) and dependent on the radiometric quality of images and the efficiency of image processing algorithms. The main factor influencing the point cloud quality is noise. Such problems usually arise with data obtained via low-cost UAV platforms. Therefore, generated point clouds representing power lines are usually incomplete and noisy. To obtain a complete and accurate 3D model of power lines and towers, it is necessary to develop improved data processing algorithms. The experiment tested the algorithms on power lines with different voltages. This paper presents the wavelet-based method of processing data acquired with a low-cost UAV camera. The proposed, original method involves the application of algorithms for coarse filtration and precise filtering. In addition, a new way of calculating the recommended flight height was proposed. At the end, the accuracy assessment of this two-stage filtration process was examined. For this, point quality indices were proposed. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm improves the quality of low-cost point clouds. The proposed methods improve the accuracy of determining the parameters of the lines by more than twice. About 10% of noise is reduced by using the wavelet-based approach.
Character-ization of distribution power quality events with Fourier and wavelet transforms
[J].DOI:10.1109/61.847259 URL [本文引用: 1]
基于小波变换的超高压输电线路故障选相新原理
[J].
A new theory for fault phase determination of EHV transmission lines based on wavelet transformation
[J].
用小波变换和有效值算法实现电压凹陷的准确测量
[J].
Measurement method of voltage sag by wavelet transform and RMS method
[J].
基于小波多分辨率分析法的电能质量检测
[J].
Power quality detecting based on wavelet-multiresolution method
[J].
基于小波包变换的电压骤降信号分析
[J].
Voltage sag analysis based on wavelet package transform
[J].
Power disturbance classier using a rule-based method and wavelet packet-based hidden Markov model
[J].DOI:10.1109/61.974212 URL [本文引用: 1]
Wavelet-based signal processing for disturbance classification and measurement
[C].
Voltage sag detection technique for a dynamic voltage restorer
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIA.2003.821801 URL [本文引用: 1]
电压凹陷特征量检测算法的研究
[J].
Research on the detection method of voltage sag characteristics
[J].
动态电压恢复器及其检测方法的探讨
[J].
Study of dynamic voltage restorer and its detecting method
[J].
一种无时延的改进d-q变换在动态电压扰动识别中的应用
[J].
Application of improved d-q transform without time delay in dynamic voltage disturbance identification
[J]
一种新的电压骤降特征量检测方法
[J].
A new method to detect voltage sag characteristics
[J].
A calculation for the compensation voltages in dynamic voltage restorers by use of PQR power theory
[C].
A novel control algorithm for static series compensators by use of PQR instantaneous power theory
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2004.826499 URL [本文引用: 1]
A new approach to control DVR based on symmetrical components estimation
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2007.905537 URL [本文引用: 1]
Three detecting methods of transient power quality disturbances in DVR
[C].
基于Hilbert变换的电压凹陷检测方法
[J].电压凹陷是严重的动态电能质量问题之一,补偿电压凹陷能带来巨大的经济效益.而实现电压凹陷特征量的快速、准确检测是电压凹陷补偿的前提,因此电压凹陷特征量的检测方法及补偿指令的产生成为目前对DVR研究的一个热点.采用Hilbert变换与后差分相结合的检测方法,首先利用Hilbert变换可对凹陷电压信号的幅值进行检测,然后采用后差分得到电压凹陷的起止时刻,不但提高了检测精度,还能实时产生电压补偿指令信号.通过Matlab对其进行仿真,仿真结果表明了该检测方法简单、快速、准确的优点.
Novel detection method of voltage sag based on Hilbert transform
[J].电压凹陷是严重的动态电能质量问题之一,补偿电压凹陷能带来巨大的经济效益.而实现电压凹陷特征量的快速、准确检测是电压凹陷补偿的前提,因此电压凹陷特征量的检测方法及补偿指令的产生成为目前对DVR研究的一个热点.采用Hilbert变换与后差分相结合的检测方法,首先利用Hilbert变换可对凹陷电压信号的幅值进行检测,然后采用后差分得到电压凹陷的起止时刻,不但提高了检测精度,还能实时产生电压补偿指令信号.通过Matlab对其进行仿真,仿真结果表明了该检测方法简单、快速、准确的优点.
A new algorithm for digital impedance relays
[J].
Mitigation of voltage disturbances using adaptive perceptron-based control algorithm
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2004.835036 URL [本文引用: 1]
Combination of Kalman filter and least error square techniques in power system
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2010.2049276 URL [本文引用: 1]
A fast and effective control scheme for the dynamic voltage restorer
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2011.2132808 URL [本文引用: 2]
补偿约束下动态电压恢复器不对称电压暂降补偿方法
[J].A new strategy of unbalance fault voltage compensation for dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) under the equipment’s restriction of compensation voltage is proposed. First draw compensation limit circles of each phase voltage, then rotate phase B and C to gain a mutual area with phase A witch we called effective compensation area. And we get the ideal compensation arc though compute the angle between the intersection points of the effective compensation area and the reference voltage. Then, rotate load voltage along the arc to get the minimum energy injection voltage of DVR for each phase. This method is simple and clear that able to compensate all kinds of sags. It maximizes the compensation bound of DVR for it needn’t eliminate zero and negative sequence voltage first. The computation speed is also fast because the whole process does not conclude repetitive search.
A method to compensate asymmetrical voltage sag of dynamic voltage restorer under constraint of compensation voltage injection
[J].A new strategy of unbalance fault voltage compensation for dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) under the equipment’s restriction of compensation voltage is proposed. First draw compensation limit circles of each phase voltage, then rotate phase B and C to gain a mutual area with phase A witch we called effective compensation area. And we get the ideal compensation arc though compute the angle between the intersection points of the effective compensation area and the reference voltage. Then, rotate load voltage along the arc to get the minimum energy injection voltage of DVR for each phase. This method is simple and clear that able to compensate all kinds of sags. It maximizes the compensation bound of DVR for it needn’t eliminate zero and negative sequence voltage first. The computation speed is also fast because the whole process does not conclude repetitive search.
动态电压恢复器的改进最小能量控制
[J].
Advanced minimum-energy control of dynamic voltage restorer
[J].
动态电压恢复器的最小视在功率控制
[J].
Minimum apparent power control of dynamic voltage restorer
[J].
动态电压恢复器的能量稳定控制
[J].An energy steady control strategy for dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) is proposed, in which the advantages of existing three load voltage control strategies, i.e., the pre-fault compensation, the inphase voltage compensation and the energy optimal compensation, are integrated and the demerits of them are avoided. The energy exchange process between a DVR and the power system is optimized while the compensation target is implemented, therefore the equipment’s capacity required by DVR can be reduced and the effective compensating time is increased, thus the economy and reliability are improved. Using the proposed control strategy, without rectifying and charging unit the energy in DC energy storage unit of DVR can be restored within a shorter time period after the voltage sag or swell occurred, meanwhile the danger to security from the overvoltage at DC side caused by the absorbed energy of DVR during the rising of system voltage can be avoided. The practicability and effectiveness are verified by simulation results.
Energy steady control for dynamic voltage restorer
[J].An energy steady control strategy for dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) is proposed, in which the advantages of existing three load voltage control strategies, i.e., the pre-fault compensation, the inphase voltage compensation and the energy optimal compensation, are integrated and the demerits of them are avoided. The energy exchange process between a DVR and the power system is optimized while the compensation target is implemented, therefore the equipment’s capacity required by DVR can be reduced and the effective compensating time is increased, thus the economy and reliability are improved. Using the proposed control strategy, without rectifying and charging unit the energy in DC energy storage unit of DVR can be restored within a shorter time period after the voltage sag or swell occurred, meanwhile the danger to security from the overvoltage at DC side caused by the absorbed energy of DVR during the rising of system voltage can be avoided. The practicability and effectiveness are verified by simulation results.
Analysis of sag compensation with dynamic voltage restorer
[C].
Control strategies and comparison of the dynamic voltage restorer
[C].
Experimental verification of an optimized control strategy for a medium-voltage DVR
[C].
Optimized control strategy for a medium-voltage DVR
[C].
Different control strategies for power quality improvement using dynamic voltage restorer
[C].
"SRF Theory revisited" to control self supported dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) for unbalanced and nonlinear loads
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIA.2013.2261273 URL [本文引用: 2]
Generalized proportional-integral control for voltage-sag compensation in dynamic voltage restorers
[C].
Proportional-resonant based high-performance control strategy for voltage-quality in dynamic voltage restorer system
[C].
Phase-locked loop topology based on a synchronous reference frame and sliding mode approach for DVR applications
[C].
Controlling dynamic voltage restorers using Alfa/Beta vectors and sliding mode
[C].
Variable structure systems with sliding mode
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.isatra.2019.08.061
URL
PMID:31495590
[本文引用: 1]

The high-performance Direct Torque Control (DTC) requires accurate knowledge of flux and speed information. Furthermore, the elimination of sensors leads to reduced overall cost and size of the electric drive system and subsequently improving its reliability. This paper proposes an effective sensorless direct torque control scheme for induction motor drive. The proposed scheme consists of enhancing the decoupling structure and variable estimation as well. Therefore, an enhanced direct flux and torque control based on feedback linearization is implemented in one hand. This allows obtaining a linear decoupled control together with minimized flux and torque ripples. In another hand, a combined sliding mode observer and model reference adaptive system is associated with the control scheme as sensorless algorithms for rotor speed and flux estimation. This conjunction is intended to enhance the sliding mode observer performances especially at low speed operations and reduce its sensitivity to noise and system uncertainties as well. The effectiveness of the proposed control algorithm has been verified through simulation and experimental work using MATLAB/Simulink software and dSpace 1104 implementation board respectively.
Experimental investigation of DVR with sliding mode control
[C].
Sliding mode control of DVR with minimized energy injection
[C].
Application of a repetitive controller for a three-phase active power filter
[J],DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2006.886609 URL [本文引用: 1]
The internal model principle of control theory
[J].
DOI:10.3389/fncel.2019.00439
URL
PMID:31649509
[本文引用: 1]

Optimal control mechanisms require prediction capabilities. If one cannot predict the consequences of a motor act or behavior, one will continually collide with walls or become a social pariah. "Looking into the future" is thus one of the most important prerequisites for smooth movements and social interactions. To achieve this goal, the brain must constantly predict future events. This principle applies to all domains of information processing, including motor and cognitive control, as well as the development of decision-making skills, theory of mind, and virtually all cognitive processes. Sequencing is suggested to support the predictive capacity of the brain. To recognize that events are related, the brain must discover links among them in the spatiotemporal domain. To achieve this, the brain must often hold one event in working memory and compare it to a second one, and the characteristics of the two must be compared and correctly placed in space and time. Among the different brain structures involved in sequencing, the cerebellum has been proposed to have a central function. We have suggested that the operational mode of the cerebellum is based on "sequence detection" and that this process is crucial for prediction. Patterns of temporally or spatially structured events are conveyed to the cerebellum via the pontine nuclei and compared with actual ones conveyed through the climbing fibers olivary inputs. Through this interaction, data on previously encountered sequences can be obtained and used to generate internal models from which predictions can be made. This mechanism would allow the cerebellum not only to recognize sequences but also to detect sequence violations. Cerebellar pattern detection and prediction would thus be a means to allow feedforward control based on anticipation. We will argue that cerebellar sequencing allows implementation of prediction by setting the correct excitatory levels in defined brain areas to implement the adaptive response for a given pattern of stimuli that embeds sufficient information to be recognized as a previously encountered template. Here, we will discuss results from human and animal studies and correlate them with the present understanding of cerebellar function in cognition and behavior.
Digital repetitive learning controller for three-phase CVCF PWM inverter
[J],DOI:10.1109/41.937415 URL [本文引用: 1]
Unified robust zero-error tracking control of CVCF PWM converters
[J].
Design of noise and periodtime robust high-order repetitive control, with application to optical storage
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.automatica.2007.04.011
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Abstract
Repetitive control is useful if periodic disturbances or setpoints act on a control system. Perfect (asymptotic) disturbance rejection is achieved if the period time is exactly known. The improved disturbance rejection at the periodic frequency and its harmonics is achieved at the expense of a degraded system sensitivity at intermediate frequencies. A convex optimization problem is defined for the design of high-order repetitive controllers, where a trade-off can be made between robustness for changes in the period time and for reduction of the error spectrum in-between the harmonic frequencies. The high-order repetitive control algorithms are successfully applied in experiments with the tracking control of a CD-player system.
Adaptive repetitive control to track variable periodic signals with fixed sampling rate
[J].DOI:10.1109/TMECH.2002.802730 URL [本文引用: 1]
Active control of radial rotor vibrations
[D].
DOI:10.3390/s17040763
URL
PMID:28375189
[本文引用: 1]

Harmonic force and torque, which are caused by rotor imbalance and sensor runout, are the dominant disturbances in active magnetic bearing (AMB) systems. To eliminate the harmonic force and torque, a novel control method based on repetitive control and notch filters is proposed. Firstly, the dynamics of a four radial degrees of freedom AMB system is described, and the AMB model can be described in terms of the translational and rotational motions, respectively. Next, a closed-loop generalized notch filter is utilized to identify the synchronous displacement resulting from the rotor imbalance, and a feed-forward compensation of the synchronous force and torque related to the AMB displacement stiffness is formulated by using the identified synchronous displacement. Then, a plug-in repetitive controller is designed to track the synchronous feed-forward compensation adaptively and to suppress the harmonic vibrations due to the sensor runout. Finally, the proposed control method is verified by simulations and experiments. The control algorithm is insensitive to the parameter variations of the power amplifiers and can precisely suppress the harmonic force and torque. Its practicality stems from its low computational load.
Physiological motion rejection in flexible endoscopy using visual servoing and repetitive control: improvements on non-periodic reference tracking and nonperiodic disturbance rejection
[C].
Repetitive control for a dynamic voltage restorer for power-quality improvement
[C].
Dynamic voltage restorer based on flying capacitor multilevel converters operated by repetitive control
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2008.2005885 URL [本文引用: 1]
A versatile control scheme for a dynamic voltage restorer for power-quality improvement
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2008.2002967 URL [本文引用: 1]
Adaptive repetitive controller for a three-phase dynamic voltage restorer
[C].
Fast repetitive controller based low-voltage dynamic voltage restorer for voltage-quality issues in distribution system
[C].
Model predictive control of an asymmetric flying capacitor converter
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2008.2007545 URL [本文引用: 1]
Predictive torque control for inverter-fed induction machines
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2007.892628 URL [本文引用: 1]
Optimal predictive control of three-phase NPC multilevel converter for power quality applications
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2008.928156 URL [本文引用: 1]
Predictive current control of voltage source inverter
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.isatra.2015.10.007
URL
PMID:26549566
[本文引用: 1]

Due to its fault tolerance, a multiphase brushless direct current (BLDC) motor can meet high reliability demand for application in electric vehicles. The voltage-source inverter (VSI) supplying the motor is subjected to open circuit faults. Therefore, it is necessary to design a fault-tolerant (FT) control algorithm with an embedded fault diagnosis (FD) block. In this paper, finite control set-model predictive control (FCS-MPC) is developed to implement the fault-tolerant control algorithm of a five-phase BLDC motor. The developed control method is fast, simple, and flexible. A FD method based on available information from the control block is proposed; this method is simple, robust to common transients in motor and able to localize multiple open circuit faults. The proposed FD and FT control algorithm are embedded in a five-phase BLDC motor drive. In order to validate the theory presented, simulation and experimental results are conducted on a five-phase two-level VSI supplying a five-phase BLDC motor.
Optimal predictive control of three-phase NPC multilevel inverter: Comparison to robust sliding mode controller
[C].
Predictive control of a three-phase neutral-point-clamped inverter
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.isatra.2017.07.027
URL
PMID:28823416
[本文引用: 1]

This paper presents a new control strategy based on finite-control-set model-predictive control (FCS-MPC) for Neutral-point-clamped (NPC) three-level converters. Containing some advantages like fast dynamic response, easy inclusion of constraints and simple control loop, makes the FCS-MPC method attractive to use as a switching strategy for converters. However, the large amount of required calculations is a problem in the widespread of this method. In this way, to resolve this problem this paper presents a modified method that effectively reduces the computation load compare with conventional FCS-MPC method and at the same time does not affect on control performance. The proposed method can be used for exchanging power between electrical grid and DC resources by providing active and reactive power compensations. Experiments on three-level converter for three Power Factor Correction (PFC), inductive and capacitive compensation modes verify the good and comparable performance. The results have been simulated using MATLAB/SIMULINK software.
Optimal predictive phase quadrature synchronization controller: Portuguese, PT-104141[P]
Conversão electrónica multinível.optimização para aplicações em qualidade de energia eléctrica
[D].
A dual-functional medium voltage level DVR to limit downstream fault currents
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2007.900589 URL [本文引用: 1]
Predictive control in power electronics and drives
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.isatra.2019.08.052
URL
PMID:31506164
[本文引用: 1]

Finite control set model-based predictive control techniques are distinguished by being an interesting alternative to traditional field oriented control techniques for multiphase drives due to their fast dynamic response and flexibility in the introduction of constraints. However, those predictive control techniques have some drawbacks regulating the (x-y) current components which can cause machine losses as well as a high computational burden. This paper presents a comparative study of an enhanced predictive current control technique with a conventional predictive control technique and two hybrid predictive control techniques applied to an asymmetrical six-phase induction motor drive in terms of current tracking, total harmonic distortion of stator currents and computational burden. Experimental results are reported to demonstrate the benefits of the different current control techniques by using the mean squared error and total harmonic distortion of stator currents as quality figures of merit and the number of floating point operations to measure the computational burden of each predictive control, thus concluding the advantages and limitations of each technique at transient and steady regimes.
Model predictive control—A simple and powerful method to control power converters
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2008.2008349 URL [本文引用: 1]
Multilevel optimal predictive dynamic voltage restorer
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2009.2034172 URL [本文引用: 1]
Defining a standard for particle swarm optimization
[C].
An analysis of particle swarm optimizer
[D].
DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0217634
URL
PMID:31150467
[本文引用: 1]

Solar energy is a major type of renewable energy, and its estimation is important for decision-makers. This study introduces a new prediction model for solar radiation based on support vector regression (SVR) and the improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) algorithm. The new version of algorithm attempts to enhance the global search ability for the PSO. In practice, the SVR method has a few parameters that should be determined through a trial-and-error procedure while developing the prediction model. This procedure usually leads to non-optimal choices for these parameters and, hence, poor prediction accuracy. Therefore, there is a need to integrate the SVR model with an optimization algorithm to achieve optimal choices for these parameters. Thus, the IPSO algorithm, as an optimizer is integrated with SVR to obtain optimal values for the SVR parameters. To examine the proposed model, two solar radiation stations, Adana, Antakya and Konya, in Turkey, are considered for this study. In addition, different models have been tested for this prediction, namely, the M5 tree model (M5T), genetic programming (GP), SVR integrated with four different optimization algorithms SVR-PSO, SVR-IPSO, Genetic Algorithm (SVR-GA), FireFly Algorithm (SVR-FFA) and the multivariate adaptive regression (MARS) model. The sensitivity analysis is performed to achieve the highest accuracy level of the prediction by choosing different input parameters. Several performance measuring indices have been considered to examine the efficiency of all the prediction methods. The results show that SVR-IPSO outperformed M5T and MARS.
A modified particle swarm optimizer for the coordination of directional overcurrent relays
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2007.899259 URL [本文引用: 1]
Unbalanced voltage sag correction with dynamic voltage restorer using particle swarm optimization
[C].
电能质量控制中心与统一电能质量调节器的研究
[J].
Studies on quality control center and unified power quality conditioner
[J].
H∞ control for a single phase active power filter: a systematic approach
[C].
A robust control scheme for medium-voltage-level DVR implementation
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2007.894771 URL [本文引用: 1]
Structures and control of a dynamic voltage regulator (DVR)
[C].
Fuzzy logic control of a dynamic voltage restorer
[C].
A fuzzy-controlled versatile system for harmonics, unbalance and voltage sag compensation
[C].
Compensation of voltage sag and harmonics by dynamic voltage restorer without zero sequence blocking
[C].
Dynamic voltage restorer based on fuzzy logic control for voltage sag restoration
[C].
串联电压控制器的控制策略
[J].
Control strategy on series voltage controller
[J].
动态电压恢复器的控制策略
[J].
Control strategy of dynamic voltage restorer
[J].
动态电压恢复器的双前馈控制策略研究
[J].
Double feed-forward control strategy for dynamic voltage restorer
[J].
Operation and control of a dynamic voltage restorer realized using cascaded H-bridge converters
[C].
Transient performance improvement of static series compensator by double vector control
[C].
Power quality improvement using DVR with two fast vector control
[C].
Design and implementation of a fast dynamic control scheme for capacitor-supported dynamic voltage restorers
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2007.911780 URL [本文引用: 1]
Design of a state-feedback controller for series voltage-sag compensators
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIA.2008.2009606 URL [本文引用: 1]
An experimental investigation of dynamic voltage restorer (DVR)
[C].