1 直流微电网发展的驱动力
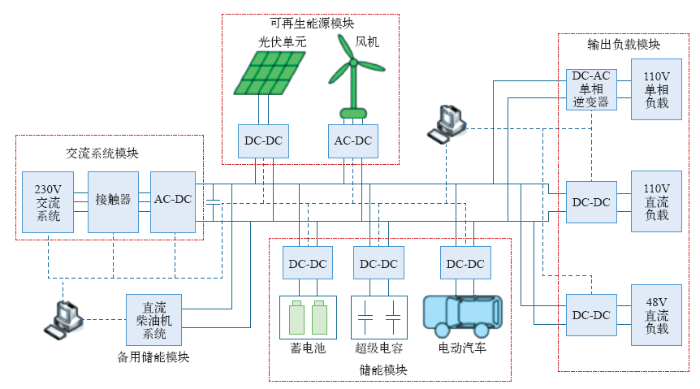
人类早期输配电系统被设计为直流系统,但由于当时直流输配电电压水平低、输送容量小、输送距离短等因素导致直流输配电技术停滞不前。交流变压器等一系列交流设备的发明使交流系统得到大规模发展,奠定了当今世界电力系统的格局。在这场19世纪末开始的“电流形式之战”中,交流输配电取得胜利并最终处于支配地位[1]。然而,随着交流电网的不断发展,交流系统存在的许多固有缺陷也不断暴露出来:严格同步的要求使交流系统易于遭受失步故障的破坏;难于实现长距离大容量电能的廉价、异步输送;对可再生能源发电的消纳缺乏灵活性;对不同负荷特性的电力需求缺乏供用电的可调节性等。以上问题的解决依赖于对电能灵活、准确、高效的控制。近年来随着电力电子技术不断发展以及信息技术、控制技术的进步,对电能灵活有效的控制已成为现实[2]。从发电、输电到配电领域,直流网络化趋势越来越得到重视[3,4,5,6]。随着直流形式的分布式电源迅速发展、直流用电负荷比例的增高、储能装置使用的增多及敏感负荷对供电质量要求的提高,采用直流方式系统化组织电源、储能、负载及监控装置构成的直流微电网将成为未来供用电领域的一种重要模式,图1为一典型直流微电网示例[7]。本文重点针对直流微电网(简称直流微网)的产生、发展、关键技术、控制策略及发展趋势进行探讨。
图1
1.1 直流微网发展的驱动力[8,9,10,11,12]
(1)分布式电源多以直流形式产生电能,因此直流微网更加易于分布式电源的接入。分布式电源主要包括风力发电、光伏发电、燃料电池发电和燃气轮机发电等。其中光伏发电和燃料电池发电以直流形式产生电能,经过DC-DC变换器直接接入直流配网,与接入交流电网相比可以省略DC-AC逆变环节。永磁风力发电和燃气轮机发电接入交流电网需要经过AC-DC和DC-AC两个变换环节,在这种情况下接入直流配网可以省略DC-AC逆变环节。
(2)电力储能多为直流形式,更易于接入直流微网。适用于供用电领域的电力储能装置主要有电池储能、飞轮储能、超导储能等形式。电池储能和超导储能以直流形式储存电能,可以通过DC-DC变换器接入直流微网作为备用电源,从而保证用户供电不中断。飞轮储能经过AC-DC和DC-AC两个变换器接入交流电网,分别用于控制飞轮电机的运行和飞轮储能系统的输出功率,而飞轮储能接入直流微网可以省略DC-AC逆变环节。
(3)许多新型用电设备采用直流供电更方便。如计算机、家用电器、变频器、开关电源、通信设备和电动汽车等,这些用电设备或者采用直流供电,或者具备直流环节,因此更易于接入直流电网。
(4)直流变换技术日趋成熟。随着功率开关器件和DSP控制技术的发展,DC-DC变换技术更加成熟。软开关、同步整流、移相PWM和多电平等技术在DC-DC变换中的应用使直流变换更加高效和可靠。
1.2 直流微网的特点[9,10]
(1)没有无功问题。直流系统中不存在无功电流分量,在提供同样有功功率情况下,直流系统电流幅值及相应损耗较交流系统更小。没有无功问题也使电压分布与线路的电感、电容参数无关,从而更有利于电压控制。
(2)没有相位问题。交流电网中的设备(主要是电源设备)切换与相位、相序、频率等交流电特征量密切相关。连接于直流微网上的设备无需考虑相位问题,设备切换更容易,电压稳定性也得到增强。
(3)直流系统结构简单,省略了许多变换环节,降低了换流损耗,由此也降低了冷却系统的投资与运行费用。
(4)DC-DC换流器多为高频开关过程,因此装置的功率密度远远大于工频变压器,设备体积更小。
(5)供电可靠性高。与交流系统相比,直流系统结构更简单,省略了许多变换环节,因此供电可靠性更高。直流电网易于接入储能装置,更适于敏感负荷供电。
(7)有环保优势。直流电流不会产生交变的电磁场,因此电磁辐射小,更加环保。
当然,直流微网也存在自身的缺点,如直流断路器实现过程复杂、成本较高。除此之外,直流电网通常必须通过DC-AC与交流电网互联,形成交直流微网,这也增加了整体网络控制的复杂性。
2 直流微电网的发展与现状[11,12]
直流微电网这个术语虽然是近年才开始提出的,但直流供电系统早已在工业领域获得应用。数据中心、通信控制中心通常采用直流方式连接主电源、负荷及储能设备。半导体、纺织、造纸和化工等工业用电因为大量使用变频器,车间往往设立直流母线,为多个变频器提供直流电压支撑。在变电站、冶金等大功率用电场合,其控制、操作系统通常采用直流供电,多个设备间通过专设的直流线路连接。这些直流供电系统可以看作直流微网的雏形,但还不能称之为直流微电网。作为直流微电网应该具备下述基本条件:
(1)具有孤网及并网两种运行模式,并可实现两种模式的无缝切换。这就要求微网中具备与储能连接的DC-DC换流器及与交流网连接的DC-AC换流器。
(2)全网优化与协调控制。具备针对全网的监控系统,全网设备信息可用,从而实现面向全网的能量优化及协调控制。
(3)电源及负荷的通用性。以往直流供电系统通常是针对专用负荷的。作为直流微网,供电负荷可能各式各样,且在不断发展。
(4)电源及负荷即插即用。作为通用电网,直流微网必须支持直流微网电源及负荷设备的即插即用功能。设备的接入或退出,不应影响包括全局优化在内的协调控制。
(5)供电负荷比例。一个企业或家庭的个别设备采用直流供电不能称为微电网。微电网的形成需要通过微电网供电的负荷容量达到较高的比例。
依据上述基本原则,目前在世界范围内已构建了大量微电网平台[10,11,12],并在此基础上展开研究。典型项目包括罗马尼亚布加勒斯特大学直流微网系统、日本大阪大学低压双极直流微网、加利福尼亚大学圣地亚哥校区微电网、爱知工业大学AC-DC微电网、丹麦Aalborg大学Intelligent DC Living Lab、台湾国立中正大学实验室demo-house、厦门大学集光伏发电与电动汽车快速充电功能于一体的直流微网等。相关研究工作在直流微电网的设计运行与控制方面取得了一系列重要成果。在世界多个国家,直流微网也得到工业、社区或家庭的示范应用。下表汇总了一些典型微电网的建设示例[13,14,15,16,17]。
表 一些典型微电网的建设示例
Tab.
| 项目名称 | 建设地点 |
|---|---|
| 大泻村区域DC-Grid | 日本秋田 |
| Gnesta市数据中心 | 瑞典Gnesta市 |
| 仙台市直流供电示范系统 | 日本仙台 |
| DC House,松下电工、夏普 | 日本福冈 |
| 舰船直流网络,ABB公司 | Myklebusthaug公司舰船 |
| Intel DC Micro Grid | Rio Rancho,美国 |
3 直流微电网的拓扑与构成
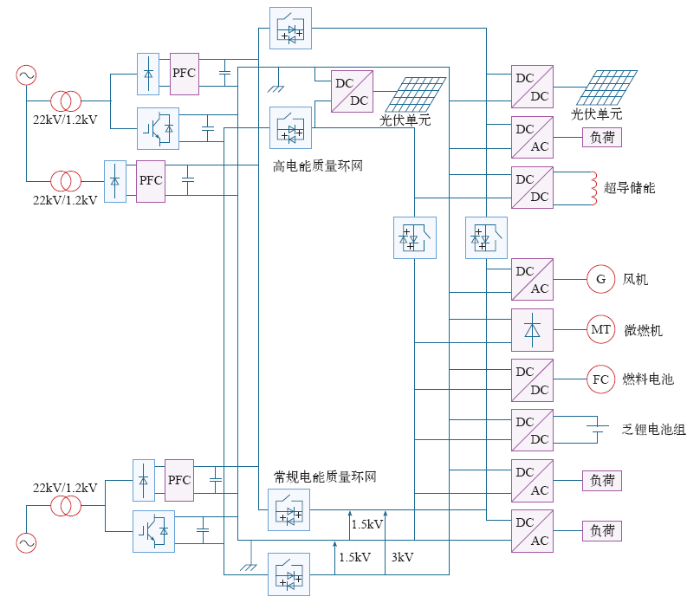
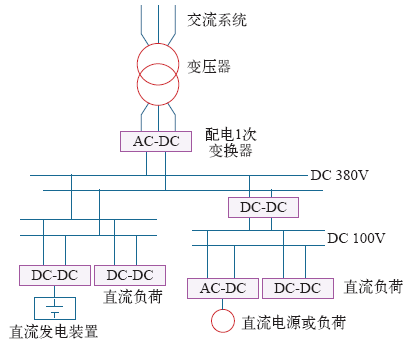
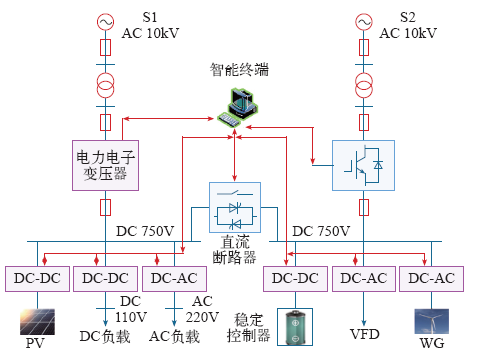
3.1 直流微网的拓扑形式[11,12]
图2
图3
图4
3.2 直流微电网的电压水平
3.3 直流微网的关键设备[11,12]
3.3.1 DC-DC变换器
DC-DC变换器的关键技术包括:①采用合适的控制策略以提高变换器的控制性能。DC-DC变换器控制目标是稳态下,保证直流电压稳态输出误差满足要求;控制系统具有好的控制性能,对电路参数和外界环境的变化鲁棒性较强,具有好的动态负载响应。②采用软开关技术以减少变换器的开关损耗,提高换流效率,抑制电磁干扰。软开关技术是使功率变换器得以高频化的重要技术之一,它应用谐振的原理,使开关器件中的电流(或电压)按正弦或准正弦规律变化。当电流自然过零时,使器件关断(或电压为零时使器件开通),从而减少开关损耗。它不仅可以解决硬开关变换器中的硬开关损耗、容性开通、感性关断及二极管反向恢复问题,而且还能解决由硬开关引起的电磁干扰等问题。
3.3.2 直流断路器
直流断路器是直流系统中一种重要的开关电器设备,它具有通断直流回路的开关功能和可靠切断故障电流的保护功能,已广泛应用于直流输电、地铁牵引和船电系统等领域。
在交流系统中,电流每周波有两次自然过零点,交流断路器就是充分利用此时机熄灭电弧,完成介质恢复,而直流系统不存在自然过零点。因此,开断直流电路就要困难许多。
直流开断的首要任务是熄灭电弧。其次,由于直流系统中电感的存在,系统里储存了大量的能量,需要采取有效手段来耗散这些能量。同时需要抑制过电压,保证间隙完成介质恢复和保护系统设备免受损坏。
3.3.3 DC-AC 换流器
直流微网通常与交流电网联合运行,因此,从设计层面就应考虑直流微网通过DC-AC换流器与交流电网连接。对于较大区域的微网,这种换流器可能不只1台。设计这种换流器应考虑下述因素:①在直流微网并网方式下为微网提供必需的能量及电压支撑;②直流微网并网方式下与DC-DC换流器的协调控制;③直流微网的孤网与并网运行方式的平稳转换;④利用直流微网通过DC-AC换流器为敏感交流负荷供电;⑤满足交流电网的电能质量要求,包括电压波动、不平衡度和谐波等。
3.3.4 直流电缆与直流插座
直流电缆与交流电缆相比有以下特点:①所用系统不同。直流电缆用于直流输电系统,交流电缆常用于工频的电力系统。②与交流电缆相比,直流电缆在传输过程中电能损耗较小。直流电缆的电能损耗主要是导体直流电阻损耗,绝缘损耗部分较小(大小视整流后电流波动大小有关)。而低压交流电缆的交流电阻比直流电阻稍大,高压电缆则更加明显。原因主要是因为邻近效应和趋肤效应的存在,导致绝缘电阻的损耗占较大比例。③输送效率高,线路损失小。④调节电流和改变功率传送方向方便。⑤虽然换流设备价格比变压器要高,但电缆线路使用成本要比交流电缆低得多。直流电缆为正负两极,结构简单,交流电缆为三相四线或五线制,绝缘安全要求高,结构较复杂,电缆成本是直流电缆的三倍多。⑥直流电缆使用安全系数高。⑦直流电缆的安装、维护简单,而且费用较低。
为了区分直流电与交流电,直流插座可以有专门的设计,如插孔的形状不同于交流插座的插孔,以方便用户使用。不同的插孔形状表示不同等级的直流电压。为了提高用电安全性,直流插座的绝缘性能应该予以特别考虑。
3.3.5 直流负荷[19]
直流负荷是直流微网的主要组成部分,构建直流微网的主要目的就是为各式各样的直流负荷供电。直流微网中的负荷特性对直流微网的控制至关重要。直流网络不存在频率问题,负荷不会出现部分交流负荷那样因频率响应所呈现的动态特性。通常可以依据负荷的构成及特性描述为定电阻、定电流及定功率负荷。直流微网结构设计和控制运行可依据负荷的上述特性进行。
4 直流微电网的控制与运行
4.1 DC-DC换流器控制策略
直流微网中通常设置一台或多台DC-DC换流器,实现对直流微网运行的支撑作用。
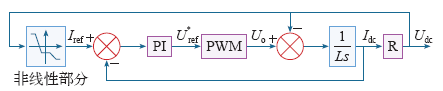
直流微网与交流电网并网状态下,DC-DC 控制目标为实现储能状态管理,参与网络整体能量优化。换流器工作在定电流控制模式;在孤网状态下,储能电池应能起到稳定直流母线电压的作用。换流器需采用双闭环控制策略,如图5所示,其中内环为电流控制环,采用PI控制;外环为电压控制环,采用直流电压下垂控制。
图5
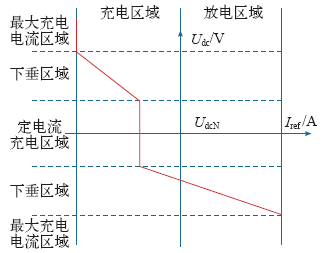
图6所示为一典型电压外环直流母线电压Udc和换流器输出电流参考值Iref的下垂特性。下垂特性设计中通常要考虑调节特性、设备容量、与DC-AC换流器的配合及电流限值。
图6
DC-DC换流器可以通过检测本地电压调节输出电流,从而实现并网及孤网状态下的控制功能。由于换流器之间不需要相互通信,因此控制灵活、可靠,并且降低了系统成本。该控制方法可使直流微网储能单元具备“即插即用”的特性。
4.2 DC-AC换流器控制策略
DC-AC换流器是直流微网连接交流电网的基本方式,其控制性能对直流微网和交流电网的稳定运行和电能质量都有极大的影响。
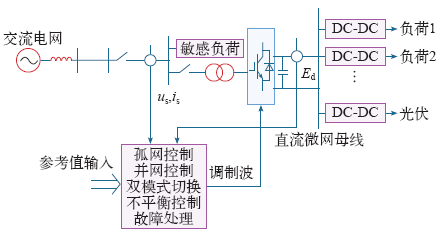
直流微网可运行于孤网和并网两种模式。当直流微网运行于孤网模式时,交流主电网停电,DC-AC换流器的控制目标是为局部交流敏感负荷供电,采用定交流电压、定频率控制。控制策略一般为采用PI控制器的交流电压外环、交流电流内环的双环控制;当交流负荷中含有大量的非线性负荷时,为保证交流电压的电能质量,采用重复控制策略。当直流微网运行于并网模式时,DC-AC换流器的控制目标是维持直流微网电压稳定,为直流微网内的负荷提供稳定可靠的供电,采用定直流电压、定交流电压(定交流侧无功)控制。交流侧三相电压不平衡时,为实现直流微网与交流电网的有功功率交换可控且不含二倍频分量,保证直流微网电压稳定,可采用基于正、负序(d,q)旋转坐标系下电流环控制策略[24];为实现直流微网与交流电网的有功功率和无功功率均可控且不含二倍频分量,可采用基于αβ坐标系下瞬时功率的重复控制策略。DC-AC换流器的主电路图及控制框图如图7所示。
图7
图7
DC-AC换流器的主电路图及控制框图
Fig.7
The main circuit and control block diagram of DC-AC converter
4.3 多代理控制
当系统中有多台储能设备时,各换流器能够根据本地信息调节输出电流,使直流微网在孤网和并网状态下都能稳定运行。但是换流器的效率和输出电流的大小有关,而单一的下垂控制无法合理分配各换流器输出电流。为了实现全局优化,各储能设备需要获得全局的电流信息并进行重新分配,从而提高储能设备的运行效率。
传统的主从控制方案可以实现对系统全局电流的感知,进而合理分配各个换流器的输出电流。但是单一的决策中心增加了系统的风险,并且当某一单元通信发生故障时,其优化过程将无法进行,可靠性和灵活性较差。与此相比,基于自律分散系统的多代理控制策略能够很好地解决这些问题。在多代理(Multi-agent)系统中,各相邻agent能够彼此通信交换信息,并能够根据接收的信息决策自身的行为,从而实现控制目标[27]。直流微电网中每套储能设备都可以视为单个agent,各储能换流器结合自身及相邻agent的电流信息进行迭代计算,最终可获得全局电流信息,实现全局优化。这种方式为微网能量管理与运行提供了可靠的信息平台,灵活性也显著提高。
4.4 直流微电网的能量管理
直流微网的能量管理系统用于实现分布式电源、储能设备、负载及交流主电源间的能量优化与协调。其中,依据不同运行方式和电池荷电状态(SOC)对电池进行充放电管理成为能量管理的重要内容[28]。直流微网的能量管理系统通常可采用两种方式:集中方式和分散方式。集中方式采用中心控制单位,收集所有节点信息,统一分析和决策。这类系统具有设备安装设置方面、控制能力强的优点,但存在一个节点失效,整个系统崩溃、系统扩展困难等问题。分散方式则每个单元具有自律性,通过与相邻节点的信息交流得到全局信息,自主做出分析和决策。这类系统具有不易出现系统性瓦解,易于扩展等优点。
能量管理系统应使在电能质量得到保障的前提下,风电、光伏实现最大出力。管理系统应使电池处于合理的荷电状态,不同电池组、不同储能方式间应实现协调控制。换流器并联出力的分配与系统的效率密切相关。能量管理也包括对并联运行的功率分配的控制,多代理方式已被用来实现这一控制。
5 直流微电网的故障行为与保护方式
直流微网的故障检测与保护及人身与设备安全与接地方式密切相关。直流微电网接地电阻包括不接地、高阻接地和低阻接地。接地方式有双极方式和中性点接地。这种方式接地电流大,易于检测与保护,故障极停运不影响正常极;单极接地(通常正极通过高阻接地,减少电蚀作用),接地电流小,电压波动小,对负载的影响小。但故障不易检测,发生停运故障时,所有负荷停运。
对于低压直流系统,人们已开发出多种装置切除故障电流,包括熔断器、机械断路器和电力电子断路器等。由于直流电流无自然过零点,装置必需具备足够的灭弧能力。基于晶闸管、IGBT的电力电子开关具有开断迅速、灭弧容易的特点,但存在正常运行过程中损耗大的问题。结合机械式与电力电子式各自特点的混合方式低压直流断路器已开发成功[29]。
6 直流微电网的应用展望
在强调绿色环保的当今社会,电力生产的格局正在发生巨大变化,分布式、可再生能源发电逐渐成为重要发电方式。电力负荷的形态也在发生显著的变化,包括变频驱动、LED照明、办公与家庭IT电源等的大多数负荷正在经历电力电子化的变革,特别是电动汽车的发展无论在用电量方面还是供电方式方面都对电网提出新的要求[30]。直流微电网的提出和推广应用为上述问题的解决提供了可行方案。值得强调的是近年来得到快速发展的电力电子技术、信息与控制技术为直流微电网的实施提供了有效的解决方案。本文在探讨直流微电网发展驱动力的基础上,描述了直流微电网的主要特征,给出了直流微电网的主要拓扑形式和电压水平,论述了直流微电网中的关键设备及相应的关键技术。文章也从设备和系统层面探讨了直流微电网相关的控制策略。直流微网要得到很好的发展和应用,还有很多问题亟待探讨和解决。从换流器效率的提升、暂态特性的改善到多换流器协调控制、系统可靠性的提高等都需要进一步研究与发展。另外,作为新型供用电模式,标准化及运行管理模式也是重要的工作内容。一项技术的生命力在很大程度上取决于其经济性,直流微网也必须具备一定的经济优势才能真正得到广泛应用。
参考文献
Advanced LVDC electrical power architectures and microgrids: a step toward a new generation of power distribution networks
[J].DOI:10.1109/MELE.2013.2297033 URL [本文引用: 2]
Edison's revenge: the rise of DC power
[J].
Future energy systems: Integrating renewable energy sources into the smart power grid through industrial electronics
[J].
Toward a smart grid: power delivery for the 21st century
[J].
HVDC grid feasibility study
[R].
DC, come home: DC microgrids and the birth of the "Enernet"
[J].DOI:10.1109/MPE.2012.2212610 URL [本文引用: 1]
Future electronic power distribution systems a contemplative view
[C].
Microgrids
[C].
直流配电网研究现状与展望
[J].In contrast to the AC distribution network, the DC distribution network has higher power supply capability, lower line losses, better power quality, freedom from reactive compensation, and is suitable for all kinds of power supply(including renewable energy power) and load access, etc. This paper deals with the DC distribution(relative to the AC distribution) characteristics, its advantages and overall concept in detail; puts forward its network topology structure; and summarizes the network planning design, dispatching control, relay protection, key equipment, and other aspects of the research. Finally, it is pointed out that the DC distribution network optimization dispatching, fault diagnosis and location, DC breaker, etc, are problems for further study.
Research status developing prospect of DC distribution network
[J].In contrast to the AC distribution network, the DC distribution network has higher power supply capability, lower line losses, better power quality, freedom from reactive compensation, and is suitable for all kinds of power supply(including renewable energy power) and load access, etc. This paper deals with the DC distribution(relative to the AC distribution) characteristics, its advantages and overall concept in detail; puts forward its network topology structure; and summarizes the network planning design, dispatching control, relay protection, key equipment, and other aspects of the research. Finally, it is pointed out that the DC distribution network optimization dispatching, fault diagnosis and location, DC breaker, etc, are problems for further study.
国外数据通信设备高压直流供电新系统 (上)
[J].分析了数据通信供电的特点,交直流供电系统的可靠性、安全性和工程应用,并对近十年来<国际电信能源会议>(INTELEC)中有关电信和数据通信局的高效节能、高压直流供电系统论文和实施试点进行跟踪,最后介绍了瑞典、日本、法国和美国等有关通信公司近几年来实施的不同系统结构的高压直流供电系统.
Low-voltage bipolar-type DC microgrid for super high quality distribution
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2010.2077682 URL [本文引用: 1]
Edison redux: 380Vdc brings reliability and efficiency to sustainable data centers
[J].
Configuration and control of a DC microgrid for residential houses
[C].
Design and development of dc-distributed system with grid connection for residential applications
[C].
Modeling, control and protection of low-voltage DC microgrids
[D].
Micro-grid autonomous operation during and subsequent to islanding process
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2004.835051 URL [本文引用: 1]
Hierarchical control of droop-controlled AC and DC microgrids—a general approach toward standardization
[J].DOI:10.1109/TIE.2010.2066534 URL [本文引用: 1]
Supervisory control of an adaptive-droop regulated DC microgrid with battery management capability
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2013.2257857
URL
[本文引用: 1]

DC power systems are gaining an increasing interest in renewable energy applications because of the good matching with dc output type sources such as photovoltaic (PV) systems and secondary batteries. In this paper, several distributed generators (DGs) have been merged together with a pair of batteries and loads to form an autonomous dc microgrid (MG). To overcome the control challenge associated with coordination of multiple batteries within one stand-alone MG, a double-layer hierarchical control strategy was proposed. 1) The unit-level primary control layer was established by an adaptive voltage-droop method aimed to regulate the common bus voltage and to sustain the states of charge (SOCs) of batteries close to each other during moderate replenishment. The control of every unit was expanded with unit-specific algorithm, i.e., finish-of-charging for batteries and maximum power-point tracking (MPPT) for renewable energy sources, with which a smooth online overlap was designed and 2) the supervisory control layer was designed to use the low-bandwidth communication interface between the central controller and sources in order to collect data needed for adaptive calculation of virtual resistances (VRs) as well as transit criteria for changing unit-level operating modes. A small-signal stability for the whole range of VRs. The performance of developed control was assessed through experimental results.
直流微网研究中的关键技术
[J].DC micro-grids, as a self-management grid form of integrating distributed energy systems with utility power systems, will realize the value and benefit of the distributed energy resources efficiently and have a more flexible capability of reconfiguration. However, the barriers of its effective promotion are both the struggling quench of the DC current arc and the lack of common standards and guidelines, leading to a long conversion process mixed with conventional AC technologies and novel DC approaches. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of the current key technologies for DC micro-grid, including control, protection, netting modes, communication, power electronic converters, presenting with a goal of identifying DC micro-grid better. In the end, combined with China's actual power system conditions, it is proposed a tailor-made scheme brought into the residential sub-districts in cities.
Key technology for DC microgrids
[J].DC micro-grids, as a self-management grid form of integrating distributed energy systems with utility power systems, will realize the value and benefit of the distributed energy resources efficiently and have a more flexible capability of reconfiguration. However, the barriers of its effective promotion are both the struggling quench of the DC current arc and the lack of common standards and guidelines, leading to a long conversion process mixed with conventional AC technologies and novel DC approaches. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of the current key technologies for DC micro-grid, including control, protection, netting modes, communication, power electronic converters, presenting with a goal of identifying DC micro-grid better. In the end, combined with China's actual power system conditions, it is proposed a tailor-made scheme brought into the residential sub-districts in cities.
不对称电网电压条件下三相并网型逆变器的控制
[J].This paper proposes a novel control scheme of three-phase grid-connected inverters (GCIs), in which a proportional plus resonant (PR) regulator is adopted. The PR regulator, which is tuned at the synchronous angular frequency, can be applied in the stationary αβ reference frame directly. Furthermore, the PR regulator does not require any decomposition of positive- and negative-sequence currents. It will improve the performance of the grid-connected inverters during the transient process of the unbalanced grid voltage fault condition, and its fault ride through capability will be enhanced as well. Compared with the conventional PI control scheme and dual-PI control scheme, the correctness of the theoretical analysis and the feasibility of the unbalanced control scheme with the PR current regulator are validated by detailed experimental tests.
Investigation on control of three-phase grid connected inverters under unbalanced grid voltage conditions
[J].This paper proposes a novel control scheme of three-phase grid-connected inverters (GCIs), in which a proportional plus resonant (PR) regulator is adopted. The PR regulator, which is tuned at the synchronous angular frequency, can be applied in the stationary αβ reference frame directly. Furthermore, the PR regulator does not require any decomposition of positive- and negative-sequence currents. It will improve the performance of the grid-connected inverters during the transient process of the unbalanced grid voltage fault condition, and its fault ride through capability will be enhanced as well. Compared with the conventional PI control scheme and dual-PI control scheme, the correctness of the theoretical analysis and the feasibility of the unbalanced control scheme with the PR current regulator are validated by detailed experimental tests.
Self-synchronized synchronverters: inverters without a dedicated synchronization unit
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TPEL.2013.2258684
URL
[本文引用: 1]

A synchronverter is an inverter that mimics synchronous generators, which offers a mechanism for power systems to control grid-connected renewable energy and facilitates smart grid integration. Similar to other grid-connected inverters, it needs a dedicated synchronization unit, e. g., a phase-locked loop (PLL), to provide the phase, frequency, and amplitude of the grid voltage as references. In this paper, a radical step is taken to improve the synchronverter as a self-synchronized synchronverter by removing the dedicated synchronization unit. It can automatically synchronize itself with the grid before connection and track the grid frequency after connection. This considerably improves the performance, reduces the complexity, and computational burden of the controller. All the functions of the original synchronverter, such as frequency and voltage regulation, real power, and reactive power control, are maintained. Both simulation and experimental results are presented to validate the control strategy. Experimental results have shown that the proposed control strategy can improve the performance of frequency tracking by more than 65%, the performance of real power control by 83%, and the performance of reactive power control by about 70%.
基于自适应全局滑模控制的微电网稳定控制策略
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.31.010
URL
[本文引用: 1]

设计了一种基于自适应全局滑模控制的微电网稳定控制策略,并基于储能设备开发了相应的微电网稳定控制器。根据微电网的不同运行方式,首先分析稳定控制器的运行特性,建立稳定控制器的数学模型。考虑到系统的不确定性和非线性,该文为微电网稳定控制器提出自适应鲁棒全局滑模控制系统,保证系统在参数不确定、存在外界干扰等情况下的稳态及动态特性。仿真和实验结果证明,微电网稳定控制器能够保证微电网在不同运行模式下的稳定性。在微电网并网运行时有效地抑制微电网与主电网交换功率波动,达到微电网与主电网交换功率可控;在微电网孤岛运行时,提供电压、频率支持;实现微电网在2种运行模式之间无缝切换。
Stability control strategy for microgrid based on adaptive total sliding-mode control
[J].
DOI:10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.31.010
URL
[本文引用: 1]

设计了一种基于自适应全局滑模控制的微电网稳定控制策略,并基于储能设备开发了相应的微电网稳定控制器。根据微电网的不同运行方式,首先分析稳定控制器的运行特性,建立稳定控制器的数学模型。考虑到系统的不确定性和非线性,该文为微电网稳定控制器提出自适应鲁棒全局滑模控制系统,保证系统在参数不确定、存在外界干扰等情况下的稳态及动态特性。仿真和实验结果证明,微电网稳定控制器能够保证微电网在不同运行模式下的稳定性。在微电网并网运行时有效地抑制微电网与主电网交换功率波动,达到微电网与主电网交换功率可控;在微电网孤岛运行时,提供电压、频率支持;实现微电网在2种运行模式之间无缝切换。
Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems
[J].DOI:10.1109/JPROC.2006.887293 URL [本文引用: 1]
独立光伏系统中超级电容器蓄电池有源式混合储能方案的研究
[J].
Study on an control battery/ultracapacitor hybrid in stand-alone PV system
[J].
A DC hybrid circuit breaker with ultra-fast contact opening and integrated gate-commutated thyristors (IGCTs)
[J].DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2006.870981 URL [本文引用: 1]
A new DC micro-grid system using renewable energy and electric vehicles for smart energy delivery
[C].