1 引言
超导磁悬浮列车[9]是超导强电应用中的一个重要组成部分[10,11]。超导磁悬浮列车包括低温超导和高温超导磁悬浮列车。1966年美国发明的LTS磁悬浮列车采用工作在液氦温区(4.2K)Nb-Ti线超导磁体与轨道相互作用实现悬浮、导向和驱动[12]。20世纪70年代至今日本一直从事这种低温超导磁悬浮列车的研究与开发。1972年日本研制出长7m,宽2.5m,高2.2m,重3.5t的ML—100低温超导磁悬浮车,悬浮高度6cm。因为实验轨道长只有480m,所以运行速度只有65km/h[13]。1979年12月21日在宫崎7km的轨道上运行速度达到了517km/h[14]。2007年12月日本宣布投资$910亿元建造东京–名古屋–大阪的时速505km的低温超导磁悬浮列车线11[11,15],计划2045年全线通车。
2000年12月31日中国研制成功的世界首辆载人高温超导磁悬浮车“世纪号”,在承载5人的时候净悬浮高度(杜瓦容器下外表面和轨道上表面之间的间隙)大于20mm[8]。
2 高温超导磁悬浮列车
与低温超导体比较,高温超导体具有较高的临界温度、临界电流密度和临界磁场,工作在液氮温区可以大大降低制造和运行成本,节能环保,应用前景十分广阔。HTS磁悬浮列车[18]主要包括用线材和用块材两种形式。和低温超导线材应用原理相似,一代和二代HTS线材可以代替低温超导线材,直接用在磁悬浮列车上。
由于低温超导体块材热不稳定性 致使它不能实际应用。在块材内部产生的局部热会引起大的磁通跳跃,超导体会因此失超。与低温超导体块材相反,HTS体块材具有大的比热,热稳定性好。低温超导MgB2是一个例外,也具有较高的比热。MgB2在很低温度下会发生磁通跳跃,但在高于10K温度时趋于消失[22]。所以,MgB2块材可以捕获大的磁通,能制成超导永久磁体,成为能实现低温超导磁悬浮的一个特例。
高温超导磁悬浮是利用第Ⅱ类超导体磁通钉扎作用,在外磁场中产生一个较大的屏蔽电流实现磁悬浮的同时,部分穿过超导体的磁通实现横向稳定的导向力。所以,HTS磁悬浮的悬浮和导向是唯一不需要任何自动控制的自稳定悬浮系统。HTS块材特别适合磁悬浮应用,因为它在强磁场下具有优良的电流输运能力,其磁能积远远高于现行永久磁体钕铁硼,具有很高的磁通捕获能力。所以,不仅自稳定,而且悬浮力和导向力都很大。
3 高温超导线材磁悬浮车
一代HTS线材(BSCCO)在液氮温区磁通钉扎很弱,不太适合磁悬浮应用。相比之下,二代线材(ReBCO)在液氮温区具有高临界电流密度,低造价,机械性能好以及在高磁场下性能优越,很适合HTS磁悬浮列车应用。应用的方式是将原来低温超导磁悬浮车载超导磁体绕组换成HTS线材。
日本用于磁悬浮列车的HTS磁体研发计划始于1999年。第一个一代HTS线材(Bi2223)超导磁体几何形状与日本低温超导磁悬浮磁体相同。在20K时HTS永久电流开关衰减率0.44%/天,虽然实用意义不大,但证了明用HTS线材绕组在车载磁体中是可行的[37]。
图1
图1
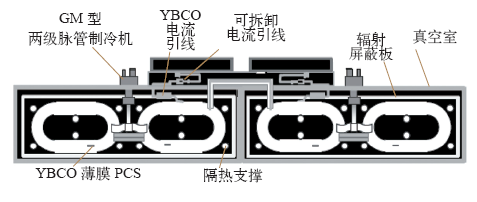
用 Bi2223 线圈的HTS 磁体示意图[45]
Fig.1
Schematic view of HTS magnet using Bi2223 coil
图2
图3
图3
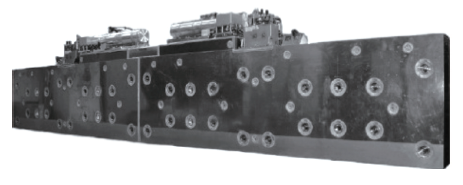
采用二代HTS 线材(ReBCO)的HTS 磁体的优点[49]
Fig.3
Merits of applying HTS 2G wires to a superconducting magnet for the maglev train
HTS二代线材绕组车载磁体试验证明[41],在40K和4.5K时分别达到5 T 和6 T。电流密度130A/mm2,这与车载低温超导Ni-Ti磁体类似。单极无辐射屏制冷结构就能满足40K的要求。超导线圈与杜瓦外表面之间仅20mm。这意味着增加了与地轨线圈的链接磁通,达到改善磁悬浮列车系统效率的目的。进一步改善二代线材性能,将可以代替现在运行的低温超导磁悬浮列车车载磁体绕组。
4 高温超导块材磁悬浮车特点
在外磁场低于第Ⅱ类超导体下临界磁场Hc1时表现出类似第Ⅰ类超导体的完全抗磁性。当外磁场在Hc1 <H <Hc3(非互易上临界磁场,低于Hc2)之间的时候,磁力线被逐渐压缩,随着外磁场增加到某个值的时候,部分磁力线通过钉扎中心穿透进块状超导体边沿,形成无损超导屏蔽电流。这个屏蔽电流的方向与外磁场方向相反,由此产生磁悬浮力。显然,这个悬浮力比第Ⅰ类完全抗磁性的悬浮力大得多。这就是众所周知的第Ⅱ类超导体磁通钉扎的结果。除了上述穿透进块状超导体边沿的磁通产生磁悬浮力外,一部分磁通直接从块材中心区域穿透进超导体,这些捕获磁通将提供一个水平的导向力,使系统处于自稳定悬浮状态。磁悬浮力和导向力的大小取决于HTS块材和NdFeB总的磁能积磁本身,也取决于如何充分利用这个总磁能积的优化计算和设计。这些优化包括轨道场结构,HTS块材形状、大小、厚薄、排放位置,低温容器,场冷或零场冷的位置等等。悬浮力和导向力大小分配,可以根据系统实际需要选取。为了得到最佳的悬浮系统要根据不同的实际需要进行专门设计。
单畴HTS块材磁悬浮是唯一的自稳定磁悬浮系统,它具有下列优点:
(1)悬浮和导向是唯一不需要有源控制的自稳定磁悬浮系统,无需车载电源。
(2)在真空管道中超高速运行的HTS磁悬浮车能耗是飞机的约1/20。
(3)无噪声、化学和电磁污染。
(4)悬浮力和导向力与悬浮间隙成指数函数增长,可以保证上下左右长期无故障稳定工作,真正实现安全舒适。
(5)可以实现超高速度运行。
(6)造价和运行成本较低。
5 中/低速高温超导块材磁悬浮车
图4
图4
“交大超导”2000 年12 月31 日在悬浮间隙大于20 mm 时承载5 人的照片
Fig.4
The net levitation gap of the HTS maglev vehicle was more than 20mm when five people stood on the vehicle
表1列出了世界第一辆载人HTS磁悬浮车“世纪号”技术指标,“世纪号”系统主要技术指标具有以下特点:
表1 世界第一辆载人HTS磁悬浮车“世纪号”基本参数
Tab.1
| 参 数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| 乘客座位数 | 4 |
| 轨道长度/ m | 15.5 |
| 车体尺寸/ mm | 2 268×1 038×120 |
| 车外尺寸/ m | 3.5×1.2×0.8 |
| 总悬浮力/ N | 6 350@gap of 20mm |
| 悬浮间隙/ mm | 20 |
| 总导向力/ N | 1 980@gap of 20mm |
| 加速度/ (m/s2) | 1 |
| 驱动形式 | 直线感应电机 |
(1)研制成功底厚3mm的薄底矩形液氮低温容器,实现了轨道与HTS块材之间最小有效作用距离,大大提高了HTS磁悬浮效率,致使HTS磁悬浮车工程应用成为可能。
(2)用略大于一个大气压的密封干燥氮气对高温超导体块材实现了永久保护。
(3)用SCML—01HTS磁悬浮测试系统测量了在永磁轨道上单个车载HTS磁悬浮装置悬浮力,在15mm和8mm悬浮间隙时的悬浮力分别是1 202N 和 1 724N。
(4)为了完全模拟整车的真实情况,用SCML —01测试系统较准确测试了两条平行永磁轨道上两个车载HTS磁悬浮装置的悬浮力。
(5)用SCML—01测试系统分别较为准确测试了8个车载HTS磁悬浮装置的悬浮力和导向力。在净悬浮间隙20mm的情况下,整车总的悬浮力是6 350N,导向力是1 980N。在净悬浮间隙10mm的情况下,整车总的悬浮力是10 431N。
(6)2000年7月至2001年5月,净悬浮间隙20mm条件下总的磁悬浮力降低了5%,其后变化很小。
(7)长期稳定性测试证明,2001年至2009年约九年后,永磁轨道上单块HTS体块材的悬浮力几乎没有变化[51]。
图5是2001年“世纪号”在国家863计划十五周年成就展览上的照片。2005年“世纪号”参加成都市首届科技节,在春熙路附近三天半连续载人运行,性能如初。
图5
图5
2001 年“世纪号”在中国国家863 计划十五周年成就展览上
Fig.5
The “Century” in review of 15years for national hightech R&D Program (863 Program) of China in Beijing, 2001
在“世纪号”成功三年后,一些国家做了HTS块材磁悬浮车研发工作。
圆环轨道长:80.84m;
NdFeB永久磁体:4.85t;
超导体:YBCO块材;
悬浮力:8.9kN(8〜10mm悬浮间隙时);
车质量:约400kg;
最高速度:20km/h;
悬浮高度:10mm;
推进: 同步短定子直线电机。
图6
图6
德国IFW 小组Supra Trans Ⅱ 高温超导磁悬浮车[66]
Fig.6
Supra Trans Ⅱ large scale HTS Maglev vehicle in IFW, the Germany
图7
图7
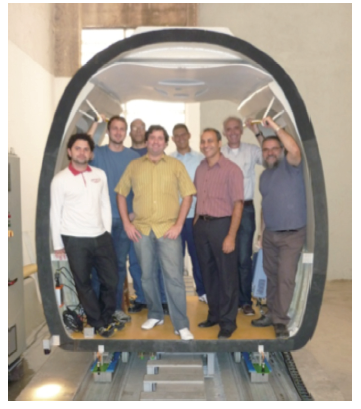
巴西HTS 磁悬浮车(照片由里约热内卢大学Stephan 提供)
Fig.7
HTS maglev vehicle prototype in Brazil
“世纪号”之后的大量的理论和实验研究结果[59]为“交大超导”HTS磁悬浮车继续研究开发奠定了坚实基础。2004年1月西南交大召开了超高速(大于600km/h)真空管道HTS磁悬浮车方案论证会,50多位专家经过一整天的讨论,通过了“交大超导”的论证报告,但暂不进行真空管道和超高速的研究,待时机成熟后再行开展。
表2 交大超导2008年HTS磁悬浮车系统设计参数
Tab.2
| 参 数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| 每米载客数 | 10 |
| 每米载客重/ (kgf/m) | 750 |
| 每米车毛重/ (kgf/m) | 400 |
| 每米悬浮重/ (kgf/m) | 1 150 |
| 车长/ m | 12 |
| 车总重/ t | 13.8 |
| 运行速度/ (km/h) | 100 |
| 加速度/ (m/s2) | 0.8 |
图8
图8
西南交大真空管道HTS 磁悬浮车系统(照片由邓自刚提供)
Fig.8
The ETT HTS maglev vehicle system in SWJTU
6 高速/超高速高温超导块材磁悬浮车
地面交通工具速度大于350km/h时,90%驱动能量消耗在空气动力学阻力上,加之车体表面气动噪声和沿基板方向及其法线方向传播的气动噪声分别与速度成近6次方和8次方的关系,噪音较大,所以,1998年3月国际铁路革新协会(The International Railway Association of Innovation)提出地面交通最高速度350km/h的建议[17]。
表3 西南交大真空管道HTS磁悬浮车[73]
Tab.3
| 序号 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 线路长度 | 45m 2014年6月 |
| 2 | 线路特征 | 跑道型 |
| 3 | 悬浮高度 | 10~20mm |
| 4 | 车体承载 | 300kg(载1人)最大 1 000kg |
| 5 | 推进方式 | 长定子直线感应电机 |
| 6 | 直线电机 | 3m(铺设长度) |
| 7 | 最大加速度 | 0.5m/s2 |
| 8 | 运行速度 | 0〜25km/h(载人)0〜50km/h(空载) |
| 9 | 真空度 | 1〜0.1大气压 |
时速480km磁悬浮车为航空能耗的28%,时速3 200km ETT-HTS磁悬浮车为航空能耗的5%,高速/超高速交通运输才能真正实现节能环保。
图9
图9
D. Oster 夫妇在“交大超导”合作期间乘坐“世纪号”( 经Oster 电话同意)
Fig.9
D. Oster and his wife take HTS Maglev vehicle during the period of cooperation
图10
图10
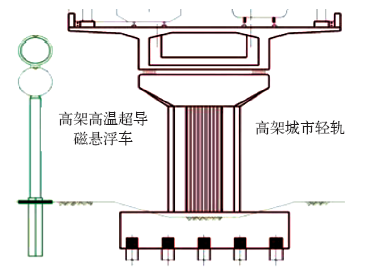
ETT-HTS 磁悬浮车与城市轻轨全系统典型横截面比较示意图[65]
Fig.10
Comparison between of the typical cross section between HTS ETT Maglev train and urban LRV
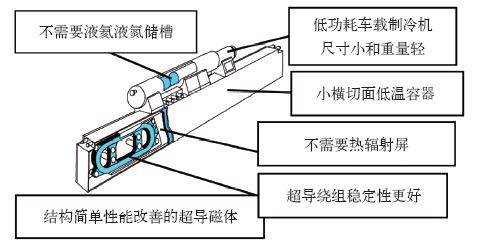
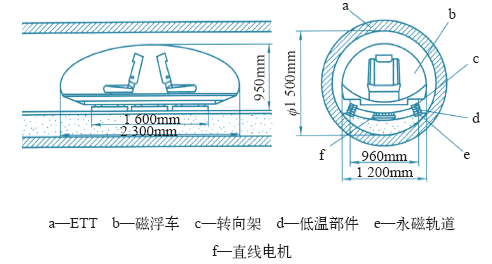
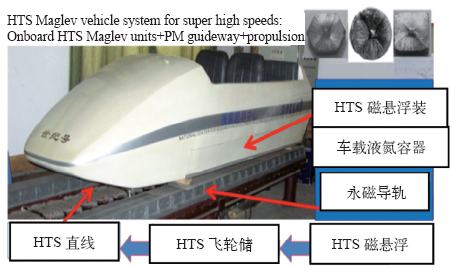
根据HTS磁悬浮车实验研究结果和理论计算,新型永磁导轨上高质量的HTS块材的HTS磁悬浮车系统是可能实现的[74]。图11是设计的在ETT中的超高速HTS磁悬浮车示意图。该系统的设计包括:低温矩形薄底液氮容器必须完全不导磁, 并具有适合于超高速的很高的机械强度,连续工作时间超过12h。两个座位的准椭圆形的磁悬浮车体总重500kg。车体外尺寸是长2.3m,高0.95m和宽1.2m。在净悬浮间隙15mm时,总悬浮力5 000N,导向力1 000N。在1 000m轨道上载人速度是100km/h,不载人最高速度达到600km/h。驱动直线电机不载人最大加速度5g (约49m/s2)。加速和减速运行300m,匀速运行40m。
图11
图11
ETT 中的超高速HTS 磁悬浮车系统示意图[74]
Fig.11
The schematic structure for of the ultra-high speed HTS maglev in the low-pressure tube (LPT) or evacuated tube transport (ETT)
图12
图12
超高速ETT-HTS 磁悬浮车系统设计方案图(未绘出ETT)[17]
Fig.1
2 Design diagram of the super-high speed ETT HTS maglev train
参考文献
The resistance of pure mercury at helium temperatures
[J].
Faster than a speeding bullet train: China is throttling up a 430km/h magnetically levitated train to link Shanghai and its airpor
[C].
Experience in operation and maintenance of Shanghai maglev demonstration line and further application of maglev in China
[C].
High speed transport by magnetically suspended trains
[C].
A 300 mph magnetically suspended trains
[J].
The first man-loading high temperature maglev test vehicle in the world
[J].
超导磁浮列车的研究与发展
[J].
Research and development of superconducting maglev train
[J].
Recent main events in applied superconductivity in China
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2009.2019244 URL [本文引用: 1]
Superconductivity and the environment: a roadmap
[J].
Magnetic levitation technology of tracked vehicles present status and prospects
[J].DOI:10.1109/TMAG.1976.1059125 URL [本文引用: 1]
Superconducting maglev developed by RTRI and JR central. Railway technology today 12
[J].
DOI:10.1093/icvts/ivz304
URL
PMID:31899511
[本文引用: 1]

This study aimed to evaluate the safety and reliability of percutaneous computed tomography (CT)-guided lipiodol marking for undetectable pulmonary lesions before video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS).
Outlook of the Superconducting Maglev
[J].DOI:10.1109/JPROC.2009.2030246 URL [本文引用: 1]
Past, Present and Future R & D of HTS maglev in China
[C].
高温超导磁浮车
[J].
High temperature superconducting maglev
[J].
A floating magnet
[J].DOI:10.1038/160330b0 URL PMID:20261770 [本文引用: 1]
Potential methods for the fabrication of high-Tc superconductors for wires and cables
[J].DOI:10.1109/5.34113 URL
Magnetic field trapping in MgB2 bulks and inserts
[J].
DOI:10.1109/TASC.2010.2086043
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In order to realize superconductive permanent magnets to be used in power applications like the magnetic levitation or electrical motors, we have studied the magnetic field trapping capability of MgB2 discs of different shapes, at temperatures >10 K. In particular we have compared MgB2 bulk discs with MgB2 Superconductive Inserts in Metallic Substrates (SIMS) of diameters of 70 mm. Both superconductive devices have been produced by the Reactive Mg Liquid Infiltration (Mg-RLI) process. The magnetization was performed by the application and removal of an external magnetic field up to 2 T, produced by a superconducting magnet, or by Field Cooling of the superconductive devices nearby NdFeB permanent magnets. The SIMS devices showed a higher stability of the trapped fields with respect to the bulk discs. Typical trapped fields, measured at 1 mm from the surface of the device, are of the order of 1 T. The density distribution of the supercurrents has been estimated by measuring the trapped field at various temperatures up to T-c and performing magnetic levitation forces measurements.
Levitation of a magnet over a flat Type 2 superconductor
[J].DOI:10.1063/1.340262 URL [本文引用: 1]
Observation of enhanced properties in samples of silver oxide doped YBa2Cu3Ox
[J].DOI:10.1063/1.99775 URL [本文引用: 1]
Levitation in physics
[J].
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.100.052112
URL
PMID:31869978
[本文引用: 1]

Video images are being used with increased frequency in science, supplanting current methods such as light scattering by statistical evaluation of the images. In this study we use light turbidity data due to density-induced refractive index fluctuations to obtain critical amplitudes from image analysis. In order to bring hydrogen (H_{2}) very close to its critical point, we place the sample cell under weightlessness using a magnetic levitation device. Images of an H_{2}-filled cell are taken near its critical temperature of 33 K by illuminating the cell with three different filters. We fit the turbidity data to a theoretical expression that allows us to estimate the critical amplitudes of isothermal compressibility and fluctuation correlation length. The values of isothermal compressibility and correlation length obtained from turbidity fitting are compared against literature values. Our data analysis shows a large sensitivity of the fitting parameters to the refractive index value and to even minute density deviations from criticality.
Measurement and analysis of a HTSC maglev
[C].
Superconductively levitated transport system—the supratrans project
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2005.849636 URL [本文引用: 2]
Magnetically levitated high-speed carriages on the basis of bulk HTS elements
[C].
A superconducting levitation vehicle prototype
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.physc.2004.03.169 URL [本文引用: 1]
Experiments in a real scale maglev vehicle prototype
[C].
Running performance of a pinning-type superconducting magnetic levitation guide
[J].DOI:10.1088/1742-6596/43/1/244 URL [本文引用: 1]
Running performance of a pinning-type superconducting magnetic levitation guide
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.physc.2008.05.154 URL [本文引用: 1]
Superconductor bearings, flywheels and transportation
[J].DOI:10.1088/0953-2048/25/1/014007 URL [本文引用: 1]
Proceedings of International Workshop on HTS Maglev
[C].
The R&D project of HTS magnets for the superconducting maglev
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.avsg.2019.02.032
URL
PMID:31075453
[本文引用: 1]

To compare hospital outcomes of aortic aneurysm surgery, casemix correction for preoperative variables is essential. Most of these variables can be deduced from mortality risk prediction models. Our aim was to identify the optimal set of preoperative variables associated with mortality to establish a relevant and efficient casemix model.
The project overview of the HTS magnet for superconducting maglev
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2007.899691 URL [本文引用: 1]
The running tests of the superconducting maglev using the HTS magnet
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2007.899003 URL [本文引用: 2]
Basic study of HTS magnet using 2G wires for maglev train
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.physc.2010.05.206 URL [本文引用: 1]
Fabrication of 5 T magnet using 2G wires directed at maglev application
[J].
Drift of levitated/suspended body in high-Tc superconducting levitation systems under vibration—part I: a criterion based on magnetic force-gap relation for gap varying with time
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2007.902104 URL [本文引用: 1]
Y. 3-D modeling of high-Tc superconductor for magnetic levitation/suspension application—part I: introduction to the method
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2010.2044795 URL [本文引用: 1]
高温超导磁悬浮测试系统
[J].
High Tc superconducting magnetic levitation measurement system
[J].
A high-temperature superconducting maglev dynamic measurement system
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2008.920568 URL [本文引用: 3]
Levitation force of the YBaCuO bulk high temperature superconductor over the NdFeB guideway
[J].DOI:10.1109/77.920136 URL [本文引用: 1]
The present status of HTS Maglev vehicle in China
[J].DOI:10.1088/0953-2048/18/2/044 URL [本文引用: 1]
高温超导电磁悬浮
[J].
High temperature superconducting electromagnetic levitation
[J].
High temperature superconducting maglev equipment on vehicle
[J].DOI:10.1016/S0921-4534(02)02158-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
车载YBCO高温超导块材长期运行悬浮稳定性研究
[J].
Research on the long-term operation stability of the bulk YBCO on vehicle
[J].
High-temperature supercon-ductor bulk magnets that can trap magnetic fields of over 17 tesla at 29K
[J].
DOI:10.1038/nature01350
URL
PMID:12556888
[本文引用: 1]

Large-grain high-temperature superconductors of the form RE-Ba-Cu-O (where RE is a rare-earth element) can trap magnetic fields of several tesla at low temperatures, and so can be used for permanent magnet applications. The magnitude of the trapped field is proportional to the critical current density and the volume of the superconductor. Various potential engineering applications for such magnets have emerged, and some have already been commercialized. However, the range of applications is limited by poor mechanical stability and low thermal conductivity of the bulk superconductors; RE-Ba-Cu-O magnets have been found to fracture during high-field activation, owing to magnetic pressure. Here we present a post-fabrication treatment that improves the mechanical properties as well as thermal conductivity of a bulk Y-Ba-Cu-O magnet, thereby increasing its field-trapping capacity. First, resin impregnation and wrapping the materials in carbon fibre improves the mechanical properties. Second, a small hole drilled into the centre of the magnet allows impregnation of Bi-Pb-Sn-Cd alloy into the superconductor and inclusion of an aluminium wire support, which results in a significant enhancement of thermal stability and internal mechanical strength. As a result, 17.24 T could be trapped, without fracturing, in a bulk Y-Ba-Cu-O sample of 2.65 cm diameter at 29 K.
A trapped field of 17. 6T in melt-processed, bulk Gd-Ba-Cu-O reinforced with shrink-fit steel
[J].
Production run of 2cm diameter YBCO trapped field magnets with surface field of 2 T at 77 K
[J].DOI:10.1088/0953-2048/26/10/105014 URL [本文引用: 1]
Supra trans II-research facility for large scale HTS applications
[C].
Feasibility study of an HTS-Maglev line at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro
[C].
The first full scale functional prototype of the superconducting magnetically levitate vehicle maglev-cobra
[C].
Recent Up-Scaling in HTS Magnetic Device Technology
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2010.2086036 URL [本文引用: 1]
Design consideration of a high temperature superconductor maglev vehicle system
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2005.849629 URL [本文引用: 3]
Past, present and future R&D of HTS maglev in China
[C].
Feasibility of a goods transportation system with a superconducting magnetic levitation guide-load characteristics of a magnetic levitation guide using a bulk high-Tc superconductor
[J].DOI:10.1016/S0921-4534(02)02111-1 URL [本文引用: 2]
高温超导磁悬浮轴承的研究进展
[J].As one of the most representative applications of self-stable high temperature superconducting magnetic levitation technology, high temperature superconducting magnetic bearing (SMB) can realize passive high-speed rotation without any friction, which provides a new way to markedly improve and upgrade the performance of present machinery and equipment with common bearings. In order to summarize the research and development status of SMB, the typical prototypes are described respectively from America, Germany, Japan and Korea, as well as other domestic and foreign groups. The key technical issues and present hotspot are pointed out and discussed to explain the future development and potential prospect.
Research and development status of high temperature superconducting magnetic bearings
[J].As one of the most representative applications of self-stable high temperature superconducting magnetic levitation technology, high temperature superconducting magnetic bearing (SMB) can realize passive high-speed rotation without any friction, which provides a new way to markedly improve and upgrade the performance of present machinery and equipment with common bearings. In order to summarize the research and development status of SMB, the typical prototypes are described respectively from America, Germany, Japan and Korea, as well as other domestic and foreign groups. The key technical issues and present hotspot are pointed out and discussed to explain the future development and potential prospect.
高温超导飞轮储能技术发展现状
[J].
Status of high temperature superconducting flywheel energy storage system
[J].
A single-sided linear synchronous motor with a high temperature superconducting coil as the excitation system
[J].DOI:10.1088/0953-2048/23/10/105015 URL [本文引用: 1]
Laboratory-scale high temperature superconducting maglev launch system
[J].DOI:10.1109/TASC.2007.898367 URL [本文引用: 1]